|
UCL Faculty Of Mathematical And Physical Sciences
The UCL Faculty of Mathematical and Physical Sciences is one of the 11 constituent faculties of University College London (UCL). The Faculty, the UCL Faculty of Engineering Sciences and the UCL Faculty of the Built Envirornment (The Bartlett) together form the UCL School of the Built Environment, Engineering and Mathematical and Physical Sciences. Departments The Faculty currently comprises the following departments: *UCL Department of Chemistry *UCL Department of Earth Sciences *UCL Department of Mathematics **''Chalkdust'' is an online mathematics interest magazine published by Department of Mathematics students starting in 2015 *UCL Department of Natural Sciences *UCL Department of Physics & Astronomy * UCL Department of Science and Technology Studies * UCL Department of Space & Climate Physics (Mullard Space Science Laboratory) *UCL Department of Statistical Science *London Centre for Nanotechnology - a joint venture between UCL and Imperial College London established in 20 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ivan Parkin
Ivan () is a Slavic male given name, connected with the variant of the Greek name (English: John) from Hebrew meaning 'God is gracious'. It is associated worldwide with Slavic countries. The earliest person known to bear the name was Bulgarian tsar Ivan Vladislav. It is very popular in Russia, Ukraine, Croatia, Serbia, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Slovenia, Bulgaria, Belarus, North Macedonia, and Montenegro and has also become more popular in Romance-speaking countries since the 20th century. Etymology Ivan is the common Slavic Latin spelling, while Cyrillic spelling is two-fold: in Bulgarian, Russian, Macedonian, Serbian and Montenegrin it is Иван, while in Belarusian and Ukrainian it is Іван. The Old Church Slavonic (or Old Cyrillic) spelling is . It is the Slavic relative of the Latin name , corresponding to English ''John''. This Slavic version of the name originates from New Testament Greek (''Iōánnēs'') rather than from the Latin . The Greek name is in turn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Engineer
Engineers, as practitioners of engineering, are professionals who invent, design, analyze, build and test machines, complex systems, structures, gadgets and materials to fulfill functional objectives and requirements while considering the limitations imposed by practicality, regulation, safety and cost. "Science is knowledge based on our observed facts and tested truths arranged in an orderly system that can be validated and communicated to other people. Engineering is the creative application of scientific principles used to plan, build, direct, guide, manage, or work on systems to maintain and improve our daily lives." The word ''engineer'' (Latin ) is derived from the Latin words ("to contrive, devise") and ("cleverness"). The foundational qualifications of an engineer typically include a four-year bachelor's degree in an engineering discipline, or in some jurisdictions, a master's degree in an engineering discipline plus four to six years of peer-reviewed professiona ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paul Davies
Paul Charles William Davies (born 22 April 1946) is an English physicist, writer and broadcaster, a professor in Arizona State University and Director of BEYOND: Center for Fundamental Concepts in Science. He is affiliated with the Institute for Quantum Studies in Chapman University in California. He previously held academic appointments in the University of Cambridge, University College London, University of Newcastle upon Tyne, University of Adelaide and Macquarie University. His research interests are in the fields of cosmology, quantum field theory, and astrobiology. In 2005, he took up the chair of the SETI: Post-Detection Science and Technology Taskgroup of the International Academy of Astronautics. Davies serves on the Advisory Council of METI (Messaging Extraterrestrial Intelligence). Education Born on 22 April 1946, Davies was brought up in Finchley, London. He attended Woodhouse Grammar School and studied physics at University College London, gaining a Bachelor o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Andrew Fisher (physicist)
Andrew James Fisher is Professor of Physics in the Department of Physics and Astronomy at University College London. His team is part of the Condensed Matter and Materials Physics group, and based in the London Centre for Nanotechnology (a joint venture between UCL and Imperial College, London).London-nano.com profile at London Centre for Nanotechnology. Research His research area is in understanding the behaviour of electrons in . Predicting the behaviour of electrons using quantum mechanics theory, to compare with experimental data. Current funded project topics include:See list of publications at UCL: ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sigurd Zienau
Sigurd Zienau (1921–1976) was a physicist notable for the theory of the polaron. Education His undergraduate studies were in mathematics at Birkbeck College. His further studies in physics were very much in the 'old school' European style at the time and he variously studied under Walter Heitler, Wolfgang Pauli, and Herbert Fröhlich. Career In 1954, he became an ICI Fellow and lecturer at the University of Liverpool. Then in 1965, he became a Reader in Physics at University College London until his early death at the age of 55. As well as his work on polarons he is remembered for his insightful revisions of Walter Heitler's book ''Quantum Theory of Radiation'' and Nevill Francis Mott & Harrie Massey's book ''The Theory of Atomic Collisions.'' See also * Polaron * Edwin Power * Walter Heitler Walter Heinrich Heitler (; 2 January 1904 – 15 November 1981) was a German physicist who made contributions to quantum electrodynamics and quantum field theory. He brought che ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Steven T
Stephen or Steven is a common English first name. It is particularly significant to Christians, as it belonged to Saint Stephen ( grc-gre, Στέφανος ), an early disciple and deacon who, according to the Book of Acts, was stoned to death; he is widely regarded as the first martyr (or "protomartyr") of the Christian Church. In English, Stephen is most commonly pronounced as ' (). The name, in both the forms Stephen and Steven, is often shortened to Steve or Stevie. The spelling as Stephen can also be pronounced which is from the Greek original version, Stephanos. In English, the female version of the name is Stephanie. Many surnames are derived from the first name, including Stephens, Stevens, Stephenson, and Stevenson, all of which mean "Stephen's (son)". In modern times the name has sometimes been given with intentionally non-standard spelling, such as Stevan or Stevon. A common variant of the name used in English is Stephan ; related names that have found some curr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William Ramsay
Sir William Ramsay (; 2 October 1852 – 23 July 1916) was a Scottish chemist who discovered the noble gases and received the Nobel Prize in Chemistry in 1904 "in recognition of his services in the discovery of the inert gaseous elements in air" along with his collaborator, John William Strutt, 3rd Baron Rayleigh, who received the Nobel Prize in Physics that same year for their discovery of argon. After the two men identified argon, Ramsay investigated other atmospheric gases. His work in isolating argon, helium, neon, krypton, and xenon led to the development of a new section of the periodic table. Early years Ramsay was born at 2 Clifton StreetGlasgow Post Office Directory 1852 in Glasgow on 2 October 1852, the son of civil engineer and surveyor, William C. Ramsay, and his wife, Catherine Robertson. The family lived at 2 Clifton Street in the city centre, a three-storey and basement Georgian townhouse. The family moved to 1 Oakvale Place in the Hillhead district in his ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Michael Abraham (chemist)
Michael H Abraham was a prominent chemist and also an artist. He worked in the fields of physical and organic chemistry at University College London, where he held the seat of professor. Specifically, his research interests included hydrogen bonding, linear free energy relationships (LFER), quantitative structure-activity relationships (QSAR) and solvent effects, solute-solvent interactions. His work has led to him being on Thomson Reuters' list of most cited scientists. As well as his research science, he was a hobby artist. Examples of his work can be found on his research page in external links. Michael Abraham died January 19th 2021, aged 89. Key works done by Michael Abraham and UCL co-workers include the measuring and calculation of molecular properties of thousands of molecules. These properties include H-bond acidity and basicity, dipolarity and polarisability. References External links List of PublicationsUCL Profile Page Year of birth missing (living people ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
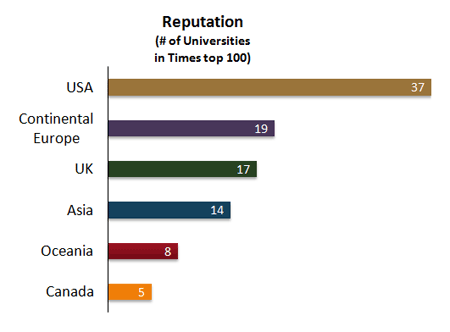
Times Higher Education World University Rankings
The ''Times Higher Education World University Rankings'' (often referred to as the THE Rankings) is an annual publication of university rankings by the ''Times Higher Education'' (THE) magazine. The publisher had collaborated with Quacquarelli Symonds (QS) to publish the joint ''THE-QS World University Rankings'' from 2004 to 2009 before it turned to Thomson Reuters for a new ranking system from 2010 to 2013. In 2014, the magazine then signed a deal with Elsevier to provide it with the data used to compile the rankings. The publication now comprises global, subject, and reputation rankings, alongside three regional league tables for Asia, Latin America, and BRICS & emerging economies, which are generated using different weightings. The THE Rankings is often considered one of the most widely observed university rankings together with the ''Academic Ranking of World Universities'', the ''QS World University Rankings'', and others. It is praised for having a new, improved ranking ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
QS World University Rankings
''QS World University Rankings'' is an annual publication of university rankings by Quacquarelli Symonds (QS). The QS system comprises three parts: the global overall ranking, the subject rankings (which name the world's top universities for the study of 51 different subjects and five composite faculty areas), and five independent regional tables—namely Asia, Latin America, Emerging Europe and Central Asia, the Arab Region, and BRICS. The QS ranking receives approval from the International Ranking Expert Group (IREG), and is viewed as one of the most-widely read university rankings in the world, along with '' Academic Ranking of World Universities'' and ''Times Higher Education World University Rankings''. According to Alexa Internet, it is the most widely viewed university ranking worldwide. However, it has been criticized for its overreliance on subjective indicators and reputation surveys, which tend to fluctuate over time. Concern also exists regarding the global consistenc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Academic Ranking Of World Universities
The ''Academic Ranking of World Universities'' (''ARWU''), also known as the Shanghai Ranking, is one of the annual publications of world university rankings. The league table was originally compiled and issued by Shanghai Jiao Tong University in 2003, making it the first global university ranking with multifarious indicators. Since 2009, ARWU has been published and copyrighted annually by Shanghai Ranking Consultancy, an organization focusing on higher education that is not legally subordinated to any universities or government agencies. In 2011, a board of international advisory consisting of scholars and policy researchers was established to provide suggestions. The publication currently includes global league tables for institutions as a whole and for a selection of individual subjects, alongside independent regional ''Greater China Ranking'' and ''Macedonian HEIs Ranking''. ARWU is regarded as one of the three most influential and widely observed university rankings, alon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thomas Young Centre
The Thomas Young Centre (TYC) is an alliance of London research groups working on the theory and simulation of materials (TSM). It is named after the celebrated scientist and polymath Thomas Young (1773–1829), who lived and worked in London and is known in the world of science for a number of important discoveries concerning the wave nature of light, the theory of vision, the elastic properties of solids, and the theory of surface tension. The participating research groups are based mainly at Imperial College London, King's College London, Queen Mary University of London (QMUL) and University College London (UCL), but there are also members at the National Physical Laboratory in Teddington. The aims of the TYC are to foster collaboration between TSM research groups in London, to provide a world-class source of graduate education in the field, and to address problems of major importance to industry and society. The current (2009) membership of TYC numbers about 80 research gr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |