|
Upogebia Capensis
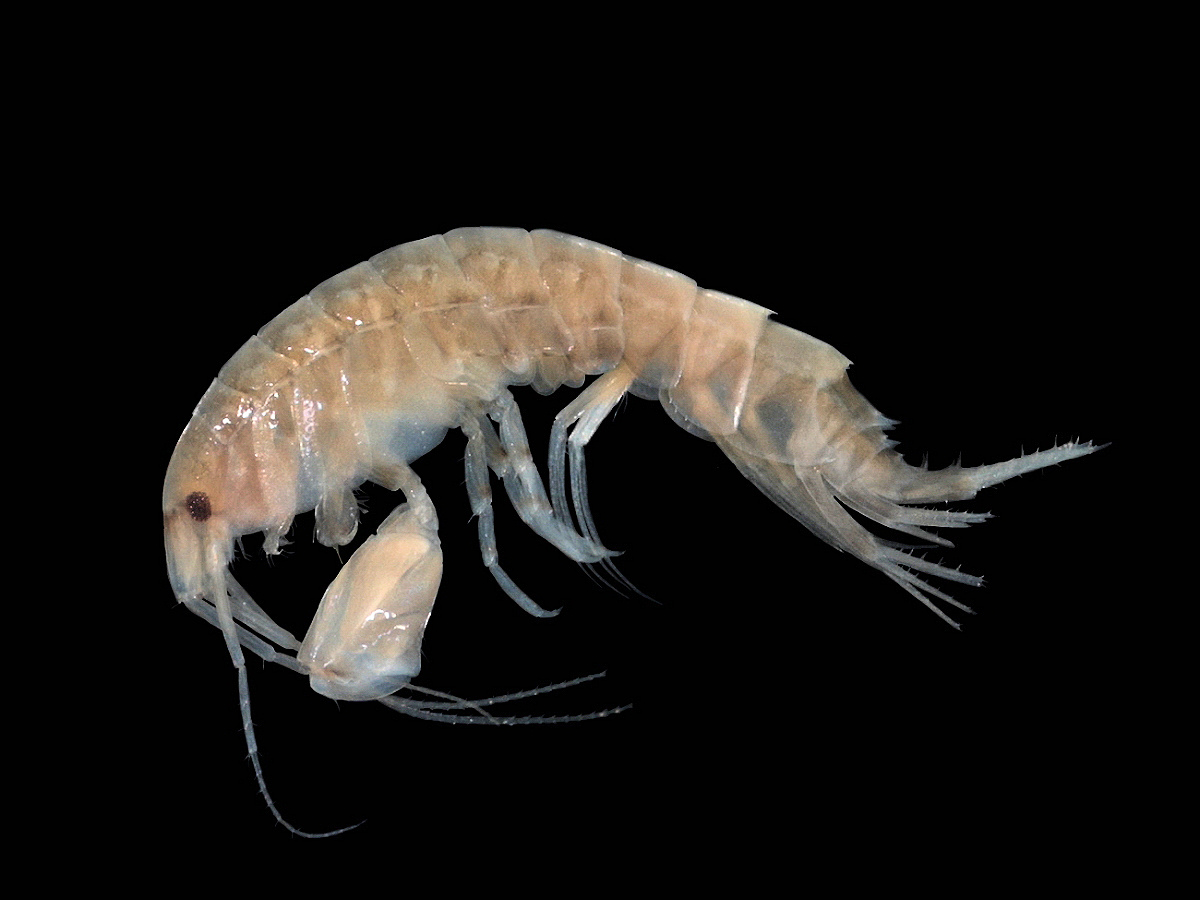
''Upogebia capensis'', or Cape mud shrimp, is a mud shrimp of the family Upogebiidae. It is endemic to the Atlantic and Indian Ocean coasts of southern Africa and occurs from Namibia ( Luderitz) to Mozambique. ''Upogebia capensis'' lives in a permanent burrow under stones on the open coast, but never in estuaries. It is similar to ''Upogebia africana ''Upogebia africana'' is a mud shrimp of the family Upogebiidae. It is endemic to the Atlantic and Indian Ocean coasts of southern Africa and occurs between Langebaan in South Africa and Inhambane Inhambane, also known as Terra de Boa Gente ...'', but the walking legs of ''capensis'' do not have spines at their bases. References Thalassinidea Crustaceans of the Atlantic Ocean Crustaceans of the Indian Ocean Crustaceans of South Africa Crustaceans described in 1843 Taxa named by Christian Ferdinand Friedrich Krauss {{decapod-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Christian Ferdinand Friedrich Krauss
Christian Ferdinand Friedrich Krauss (Stuttgart, 9 July 1812 – 15 September 1890), was a German scientist, traveler and collector. Early life He was an apothecary's apprentice and worked as a pharmacist for a while, but then took up the study of mineralogy, zoology and chemistry at Tübingen and Heidelberg, where he excelled academically and was awarded a PhD ''summa cum laude'' in 1836. South Africa Cape Province 7 May 1838 - 2 June 1839 The following year Baron von Ludwig, famous for his garden in Cape Town, visited Germany and persuaded Krauss to visit South Africa. They sailed from Portsmouth aboard the 676-ton barque ''La Belle Alliance'' (the same vessel that had carried 1820 Settlers from England to the Eastern Cape) and arrived in Cape Town 81 days later on 7 May 1838. Krauss started collecting and studying the fauna, flora and geology of Cape Town and environs in earnest after a short trip to Tulbagh. He collected molluscs and crustaceans, marine algae and fish. Plannin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thalassinidea
Thalassinidea is a former infraorder of decapod crustaceans that live in burrows in muddy bottoms of the world's oceans. In Australian English, the littoral thalassinidean ''Trypaea australiensis'' is referred to as the ''yabby'' (a term which also refers to freshwater crayfish of the genus ''Cherax''), frequently used as bait for estuarine fishing; elsewhere, however, they are poorly known, and as such have few vernacular names, "mud lobster" and "ghost shrimp" counting among them. The burrows made by thalassinideans are frequently preserved, and the fossil record of thalassinideans reaches back to the late Jurassic. The group was abandoned when it became clear that it represented two separate lineages, now both recognised as infraorders: Gebiidea and Axiidea. Recent molecular analyses have shown that thalassinideans are most closely related to Brachyura (crabs) and Anomura (hermit crabs and their allies). There are believed to be 556 extant species of thalassinideans in 96 gene ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Family (biology)
Family ( la, familia, plural ') is one of the eight major hierarchical taxonomic ranks in Linnaean taxonomy. It is classified between order and genus. A family may be divided into subfamilies, which are intermediate ranks between the ranks of family and genus. The official family names are Latin in origin; however, popular names are often used: for example, walnut trees and hickory trees belong to the family Juglandaceae, but that family is commonly referred to as the "walnut family". What belongs to a family—or if a described family should be recognized at all—are proposed and determined by practicing taxonomists. There are no hard rules for describing or recognizing a family, but in plants, they can be characterized on the basis of both vegetative and reproductive features of plant species. Taxonomists often take different positions about descriptions, and there may be no broad consensus across the scientific community for some time. The publishing of new data and opini ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Upogebiidae
Upogebiidae is a family of mud shrimp crustaceans belonging to the infraorder Gebiidea Gebiidea is an infraorder of decapod crustaceans. Gebiidea and Axiidea are divergent infraoders of the former infraorder Thalassinidea. These infraorders have converged ecologically and morphologically as burrowing forms.Dworschak, Peter C. ( ..., within the order Decapoda Genera *'' Acutigebia'' Sakai, 1982 *'' Aethogebia'' A. B. Williams, 1993 *'' Arabigebicula'' Sakai, 2006 *'' Austinogebia'' Ngoc-Ho, 2001 *'' Gebiacantha'' Ngoc-Ho, 1989 *'' Gebicula'' Alcock, 1901 *'' Mantisgebia'' Sakai, 2006 *'' Neogebicula'' Sakai, 1982 *'' Paragebicula'' Sakai, 2006 *'' Pomatogebia'' Williams & Ngoc-Ho, 1990 *'' Tuerkayogebia'' Sakai, 1982 *'' Upogebia'' Leach, 1814 *'' Wolffogebia'' Sakai, 1982 References * Thalassinidea Decapod families {{decapod-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Endemic
Endemism is the state of a species being found in a single defined geographic location, such as an island, state, nation, country or other defined zone; organisms that are indigenous to a place are not endemic to it if they are also found elsewhere. For example, the Cape sugarbird is found exclusively in southwestern South Africa and is therefore said to be ''endemic'' to that particular part of the world. An endemic species can be also be referred to as an ''endemism'' or in scientific literature as an ''endemite''. For example '' Cytisus aeolicus'' is an endemite of the Italian flora. '' Adzharia renschi'' was once believed to be an endemite of the Caucasus, but it was later discovered to be a non-indigenous species from South America belonging to a different genus. The extreme opposite of an endemic species is one with a cosmopolitan distribution, having a global or widespread range. A rare alternative term for a species that is endemic is "precinctive", which applies to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Upogebia Africana
''Upogebia africana'' is a mud shrimp of the family Upogebiidae. It is endemic to the Atlantic and Indian Ocean coasts of southern Africa and occurs between Langebaan in South Africa and Inhambane Inhambane, also known as Terra de Boa Gente (''Land of Good People''), is a city located in southern Mozambique, lying on Inhambane Bay, 470 km northeast of Maputo. It is the capital of the Inhambane Province and according to the 2017 census ... in Mozambique. References Thalassinidea Crustaceans described in 1894 Crustaceans of the Atlantic Ocean Crustaceans of the Indian Ocean Crustaceans of South Africa Taxa named by Arnold Edward Ortmann {{decapod-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crustaceans Of The Atlantic Ocean
Crustaceans (Crustacea, ) form a large, diverse arthropod taxon which includes such animals as decapods, seed shrimp, branchiopods, fish lice, krill, remipedes, isopods, barnacles, copepods, amphipods and mantis shrimp. The crustacean group can be treated as a subphylum under the clade Mandibulata. It is now well accepted that the hexapods emerged deep in the Crustacean group, with the completed group referred to as Pancrustacea. Some crustaceans (Remipedia, Cephalocarida, Branchiopoda) are more closely related to insects and the other hexapods than they are to certain other crustaceans. The 67,000 described species range in size from '' Stygotantulus stocki'' at , to the Japanese spider crab with a leg span of up to and a mass of . Like other arthropods, crustaceans have an exoskeleton, which they moult to grow. They are distinguished from other groups of arthropods, such as insects, myriapods and chelicerates, by the possession of biramous (two-parted) limbs, and by their ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crustaceans Of The Indian Ocean
Crustaceans (Crustacea, ) form a large, diverse arthropod taxon which includes such animals as decapods, seed shrimp, branchiopods, fish lice, krill, remipedes, isopods, barnacles, copepods, amphipods and mantis shrimp. The crustacean group can be treated as a subphylum under the clade Mandibulata. It is now well accepted that the hexapods emerged deep in the Crustacean group, with the completed group referred to as Pancrustacea. Some crustaceans (Remipedia, Cephalocarida, Branchiopoda) are more closely related to insects and the other hexapods than they are to certain other crustaceans. The 67,000 described species range in size from '' Stygotantulus stocki'' at , to the Japanese spider crab with a leg span of up to and a mass of . Like other arthropods, crustaceans have an exoskeleton, which they moult to grow. They are distinguished from other groups of arthropods, such as insects, myriapods and chelicerates, by the possession of biramous (two-parted) limbs, and by their ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crustaceans Of South Africa
Crustaceans (Crustacea, ) form a large, diverse arthropod taxon which includes such animals as decapods, seed shrimp, branchiopods, fish lice, krill, remipedes, isopods, barnacles, copepods, amphipods and mantis shrimp. The crustacean group can be treated as a subphylum under the clade Mandibulata. It is now well accepted that the hexapods emerged deep in the Crustacean group, with the completed group referred to as Pancrustacea. Some crustaceans ( Remipedia, Cephalocarida, Branchiopoda) are more closely related to insects and the other hexapods than they are to certain other crustaceans. The 67,000 described species range in size from '' Stygotantulus stocki'' at , to the Japanese spider crab with a leg span of up to and a mass of . Like other arthropods, crustaceans have an exoskeleton, which they moult to grow. They are distinguished from other groups of arthropods, such as insects, myriapods and chelicerates, by the possession of biramous (two-parted) limbs, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crustaceans Described In 1843
Crustaceans (Crustacea, ) form a large, diverse arthropod taxon which includes such animals as decapods, seed shrimp, branchiopods, fish lice, krill, remipedes, isopods, barnacles, copepods, amphipods and mantis shrimp. The crustacean group can be treated as a subphylum under the clade Mandibulata. It is now well accepted that the hexapods emerged deep in the Crustacean group, with the completed group referred to as Pancrustacea. Some crustaceans (Remipedia, Cephalocarida, Branchiopoda) are more closely related to insects and the other hexapods than they are to certain other crustaceans. The 67,000 described species range in size from '' Stygotantulus stocki'' at , to the Japanese spider crab with a leg span of up to and a mass of . Like other arthropods, crustaceans have an exoskeleton, which they moult to grow. They are distinguished from other groups of arthropods, such as insects, myriapods and chelicerates, by the possession of biramous (two-parted) limbs, and by their ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)