|
University Of California, Santa Cruz, Arboretum
The Arboretum & Botanic Garden at the University of California, Santa Cruz, is located on the campus of the University of California, Santa Cruz, in the United States. Description The Arboretum site has remarkable climatic and topographic diversity and a wide variety of soils, since the underlying rocks include granite, schist, limestone, and several sandstones. The Arboretum officially started in 1964, when the UCSC campus was established, with about 90 species of eucalyptus. Its gradual expansion has focused mainly on mediterranean-climate plants of the Southern Hemisphere, and now includes a comprehensive collection of conifers, exotic South African proteas, Australian and New Zealand plants, and a fine collection of native Californian shrubs and trees. Major collections * Australian Garden – over 2,000 species, forms, and cultivars (out of some 20,000 species native to the subcontinent), and believed to be the largest collection of Australian plants outside Australia. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Botanical Garden
A botanical garden or botanic gardenThe terms ''botanic'' and ''botanical'' and ''garden'' or ''gardens'' are used more-or-less interchangeably, although the word ''botanic'' is generally reserved for the earlier, more traditional gardens, and is the more usual term in the United Kingdom. is a garden with a documented collection of living plants for the purpose of scientific research, conservation, display, and education. Typically plants are labelled with their botanical names. It may contain specialist plant collections such as cactus, cacti and other succulent plants, herb gardens, plants from particular parts of the world, and so on; there may be greenhouses, shadehouses, again with special collections such as tropical plants, alpine plants, or other exotic plants. Most are at least partly open to the public, and may offer guided tours, educational displays, art exhibitions, book rooms, open-air theatrical and musical performances, and other entertainment. Botanical gard ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Melaleuca
''Melaleuca'' () is a genus of nearly 300 species of plants in the myrtle family, Myrtaceae, commonly known as paperbarks, honey-myrtles or tea-trees (although the last name is also applied to species of '' Leptospermum''). They range in size from small shrubs that rarely grow to more than high, to trees up to . Their flowers generally occur in groups, forming a "head" or "spike" resembling a brush used for cleaning bottles, containing up to 80 individual flowers. Melaleucas are an important food source for nectarivorous insects, birds, and mammals. Many are popular garden plants, either for their attractive flowers or as dense screens and a few have economic value for producing fencing and oils such as "tea tree" oil. Most melaleucas are endemic to Australia, with a few also occurring in Malesia. Seven are endemic to New Caledonia, and one is found only on (Australia's) Lord Howe Island. Melaleucas are found in a wide variety of habitats. Many are adapted for life in swamp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Populus Sect
''Populus'' is a genus of 25–30 species of deciduous flowering plants in the family Salicaceae, native to most of the Northern Hemisphere. English names variously applied to different species include poplar (), aspen, and cottonwood. The western balsam poplar ('' P. trichocarpa'') was the first tree to have its full DNA code determined by DNA sequencing, in 2006. Description The genus has a large genetic diversity, and can grow from tall, with trunks up to in diameter. The bark on young trees is smooth, white to greenish or dark gray, and often has conspicuous lenticels; on old trees, it remains smooth in some species, but becomes rough and deeply fissured in others. The shoots are stout, with (unlike in the related willows) the terminal bud present. The leaves are spirally arranged, and vary in shape from triangular to circular or (rarely) lobed, and with a long petiole; in species in the sections ''Populus'' and ''Aigeiros'', the petioles are laterally flattened ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Willow
Willows, also called sallows and osiers, from the genus ''Salix'', comprise around 400 speciesMabberley, D.J. 1997. The Plant Book, Cambridge University Press #2: Cambridge. of typically deciduous trees and shrubs, found primarily on moist soils in cold and temperate regions. Most species are known as willow, but some narrow-leaved shrub species are called osier, and some broader-leaved species are referred to as sallow (from Old English ''sealh'', related to the Latin word ''salix'', willow). Some willows (particularly arctic and alpine species) are low-growing or creeping shrubs; for example, the dwarf willow (''Salix herbacea'') rarely exceeds in height, though it spreads widely across the ground. Description Willows all have abundant watery bark sap, which is heavily charged with salicylic acid, soft, usually pliant, tough wood, slender branches, and large, fibrous, often stoloniferous roots. The roots are remarkable for their toughness, size, and tenacity to live ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Umbellularia
''Umbellularia californica'' is a large hardwood tree native to coastal forests and the Sierra foothills of California, and to coastal forests extending into Oregon. It is endemic to the California Floristic Province. It is the sole species in the genus ''Umbellularia''. The tree was formerly known as ''Oreodaphne californica''. In Yuki, it is called pōl’-cum ōl. In Oregon, this tree is known as Oregon myrtle, while in California it is called California bay laurel, which may be shortened to California bay or California laurel. It has also been called pepperwood, spicebush, cinnamon bush, peppernut tree, headache tree, mountain laurel, and balm of heaven. The tree's pungent leaves have a similar flavor to bay leaves, though stronger, and it may be mistaken for bay laurel. The dry wood has a color range from blonde (like maple) to brown (like walnut). It is considered an excellent tonewood and is sought after by luthiers and woodworkers. The tree is a host of the pathogen tha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coast Live Oak
''Quercus agrifolia'', the California live oak, or coast live oak, is a highly variable, often evergreen oak tree, a type of live oak, native to the California Floristic Province. It may be shrubby, depending on age and growing location, but is generally a medium-sized tree. It grows west of the Sierra Nevada mountain range from Mendocino County, California, south to northern Baja California in Mexico. It is classified in the red oak section of oaks (''Quercus'' sect. ''Lobatae''). This species is commonly sympatric with canyon live oak (''Q. chrysolepis''), and the two may be hard to distinguish because their spinose leaves are superficially similar. Description Coast live oak typically has a much-branched trunk and reaches a mature height of . Some specimens may attain an age exceeding 1,000 years. Examples of this include the Grand Oak of Cherry Valley, California, the Encino Oak Tree, which died in the 1990s (part of the stump has been preserved) and the Pechanga Gre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Douglas Fir
The Douglas fir (''Pseudotsuga menziesii'') is an evergreen conifer species in the pine family, Pinaceae. It is native to western North America and is also known as Douglas-fir, Douglas spruce, Oregon pine, and Columbian pine. There are three varieties: coast Douglas-fir (''P. menziesii'' var. ''menziesii''), Rocky Mountain Douglas-fir (''P. menziesii'' var. ''glauca'') and Mexican Douglas-fir (''P. menziesii'' var. ''lindleyana''). Despite its common names, it is not a true fir (genus ''Abies''), spruce (genus '' Picea''), or pine (genus ''Pinus''). It is also not a hemlock; the genus name ''Pseudotsuga'' means "false hemlock". Description Douglas-firs are medium-size to extremely large evergreen trees, tall (although only ''Pseudotsuga menziesii var. menziesii'', common name coast Douglas-firs, reach heights near 100 m) and commonly reach in diameter, although trees with diameters of almost exist. The largest coast Douglas-firs regularly live over 500 years, with the old ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
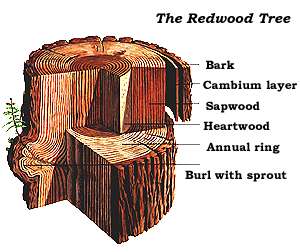
Coast Redwood
''Sequoia sempervirens'' ()''Sunset Western Garden Book,'' 1995:606–607 is the sole living species of the genus '' Sequoia'' in the cypress family Cupressaceae (formerly treated in Taxodiaceae). Common names include coast redwood, coastal redwood, and California redwood. It is an evergreen, long-lived, monoecious tree living 1,200–2,200 years or more. This species includes the tallest living trees on Earth, reaching up to in height (without the roots) and up to in diameter at breast height. These trees are also among the oldest living things on Earth. Before commercial logging and clearing began by the 1850s, this massive tree occurred naturally in an estimated along much of coastal California (excluding southern California where rainfall is not sufficient) and the southwestern corner of coastal Oregon within the United States. The name sequoia sometimes refers to the subfamily Sequoioideae, which includes ''S. sempervirens'' along with ''Sequoiadendron'' (gi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ponderosa Pine
''Pinus ponderosa'', commonly known as the ponderosa pine, bull pine, blackjack pine, western yellow-pine, or filipinus pine is a very large pine tree species of variable habitat native to mountainous regions of western North America. It is the most widely distributed pine species in North America.Safford, H.D. 2013. Natural Range of Variation (NRV) for yellow pine and mixed conifer forests in the bioregional assessment area, including the Sierra Nevada, southern Cascades, and Modoc and Inyo National Forests. Unpublished report. USDA Forest Service, Pacific Southwest Region, Vallejo, CA/ref> ''Pinus ponderosa'' grows in various erect forms from British Columbia southward and eastward through 16 western U.S. states and has been successfully introduced in temperate regions of Europe, and in New Zealand. It was first documented in modern science in 1826 in eastern Washington near present-day Spokane (of which it is the official city tree). On that occasion, David Douglas misidenti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Waratah
Waratah (''Telopea'') is an Australian-endemic genus of five species of large shrubs or small trees, native to the southeastern parts of Australia (New South Wales, Victoria, and Tasmania). The best-known species in this genus is ''Telopea speciosissima'', which has bright red flowers and is the New South Wales (NSW) state emblem. The waratah is a member of the family Proteaceae, flowering plants distributed in the Southern Hemisphere. The key diagnostic feature of Proteaceae is the inflorescence, which is often very large, brightly coloured and showy, consisting of many small flowers densely packed into a compact head or spike. Species of waratah boast such inflorescences ranging from 6–15 cm in diameter with a basal ring of coloured bracts. The leaves are spirally arranged, 10–20 cm long and 2–3 cm broad with entire or serrated margins. The name ''waratah'' comes from the Eora Aboriginal people, the pre-European inhabitants of the Sydney area. Taxonomy The genus ''Telopea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Waratah
Waratah (''Telopea'') is an Australian-endemic genus of five species of large shrubs or small trees, native to the southeastern parts of Australia (New South Wales, Victoria, and Tasmania). The best-known species in this genus is ''Telopea speciosissima'', which has bright red flowers and is the New South Wales (NSW) state emblem. The waratah is a member of the family Proteaceae, flowering plants distributed in the Southern Hemisphere. The key diagnostic feature of Proteaceae is the inflorescence, which is often very large, brightly coloured and showy, consisting of many small flowers densely packed into a compact head or spike. Species of waratah boast such inflorescences ranging from 6–15 cm in diameter with a basal ring of coloured bracts. The leaves are spirally arranged, 10–20 cm long and 2–3 cm broad with entire or serrated margins. The name ''waratah'' comes from the Eora Aboriginal people, the pre-European inhabitants of the Sydney area. Taxonomy The genus ''Telopea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Banksia
''Banksia'' is a genus of around 170 species in the plant family Proteaceae. These Australian wildflowers and popular garden plants are easily recognised by their characteristic flower spikes, and fruiting "cones" and heads. ''Banksias'' range in size from prostrate woody shrubs to trees up to 30 metres (100 ft) tall. They are found in a wide variety of landscapes: sclerophyll forest, (occasionally) rainforest, shrubland, and some more arid landscapes, though not in Australia's deserts. Heavy producers of nectar, ''banksias'' are a vital part of the food chain in the Australian bush. They are an important food source for nectarivorous animals, including birds, bats, rats, possums, stingless bees and a host of invertebrates. Further, they are of economic importance to Australia's nursery and cut flower industries. However, these plants are threatened by a number of processes including land clearing, frequent burning and disease, and a number of species are rare and endangered. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |