|
United States V. John (1978)
''United States v. John'', 437 U.S. 634 (1978), was a case in which the Supreme Court of the United States held that lands designated as a reservation in Mississippi are "Indian country" as defined by statute, although the reservation was established nearly a century after Indian removal and related treaties. The court ruled that, under the Major Crimes Act, the State has no jurisdiction to try a Native American for crimes covered by that act that occurred on reservation land. Background History The Choctaw lived in Mississippi and other areas of the Southeast since well before the Revolutionary War, and were recognized by their treaty with the United States in 1786. When Mississippi became a state in 1817, the Choctaw still held three-quarters of the land in the state. There was pressure from European Americans on the federal government and state to open these lands for white settlement. Federal policy at that time was to encourage the removal of the Choctaw and othe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
5th Cir
Fifth is the ordinal form of the number five. Fifth or The Fifth may refer to: * Fifth Amendment to the United States Constitution, as in the expression "pleading the Fifth" * Fifth column, a political term * Fifth disease, a contagious rash that spreads in school-aged children * Fifth force, a proposed force of nature in addition to the four known fundamental forces * Fifth (Stargate), a robotic character in the television series ''Stargate SG-1'' * Fifth (unit), a unit of volume used for distilled beverages in the U.S. * Fifth-generation programming language * The fifth in a series, or four after the first: see ordinal numbers * 1st Battalion, 5th Marines * The Fraction 1/5 * The royal fifth (Spanish and Portuguese), an old royal tax of 20% Music * A musical interval (music); specifically, a ** perfect fifth ** diminished fifth ** augmented fifth * Quintal harmony, in which chords concatenate fifth intervals (rather than the third intervals of tertian harmony) * Fifth (chord) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indian Reservation
An Indian reservation is an area of land held and governed by a federally recognized Native American tribal nation whose government is accountable to the United States Bureau of Indian Affairs and not to the state government in which it is located. Some of the country's 574 federally recognized tribes govern more than one of the 326 Indian reservations in the United States, while some share reservations, and others have no reservation at all. Historical piecemeal land allocations under the Dawes Act facilitated sales to non–Native Americans, resulting in some reservations becoming severely fragmented, with pieces of tribal and privately held land being treated as separate enclaves. This jumble of private and public real estate creates significant administrative, political and legal difficulties. The total area of all reservations is , approximately 2.3% of the total area of the United States and about the size of the state of Idaho. While most reservations are small c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Concurrent Jurisdiction
Concurrent jurisdiction exists where two or more courts from different systems simultaneously have jurisdiction over a specific case. This situation leads to forum shopping, as parties will try to have their civil or criminal case heard in the court that they perceive will be most favorable to them. United States In the United States, concurrent jurisdiction exists to the extent that the United States Constitution permits federal courts to hear actions that can also be heard by state courts. For example, when a party from Alabama sues a party from Florida for a breach of contract, the Alabama party can sue in either federal court (under its diversity jurisdiction) or in the state court located in Florida (under its personal jurisdiction over the defendant). Concurrent jurisdiction may also be created where the United States Congress, in creating a cause of action, permits the courts of the states to hear cases alleging that cause of action. For example, a state court may hear ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Exclusive Jurisdiction
Exclusive jurisdiction exists in civil procedure if one court has the power to adjudicate a case to the exclusion of all other courts. The opposite situation is concurrent jurisdiction (or non-exclusive jurisdiction) in which more than one court may take jurisdiction over the case. Exclusive jurisdiction is typically defined in terms of subject matter. For example, gives the United States district courts exclusive jurisdiction over all matters arising in bankruptcy with a few exceptions. On the federal level, exclusive jurisdiction allows the US Supreme Court to review the decisions in lower courts. See also *Original jurisdiction--the power of a court to hear a case for the first time *Appellate jurisdiction--the power of a court to hear a case on appeal In law, an appeal is the process in which cases are reviewed by a higher authority, where parties request a formal change to an official decision. Appeals function both as a process for error correction as well as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Major Crimes Act
The Major Crimes Act (U.S. Statutes at Large, 23:385)U.S. Statutes at Large Vol. 23, Chap. 341 (). is a law passed by the in 1885 as the final section of the Indian Appropriations Act of that year. The law places certain crimes under federal jurisdiction if they are committed by a [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States Congress
The United States Congress is the legislature of the federal government of the United States. It is bicameral, composed of a lower body, the House of Representatives, and an upper body, the Senate. It meets in the U.S. Capitol in Washington, D.C. Senators and representatives are chosen through direct election, though vacancies in the Senate may be filled by a governor's appointment. Congress has 535 voting members: 100 senators and 435 representatives. The U.S. vice president has a vote in the Senate only when senators are evenly divided. The House of Representatives has six non-voting members. The sitting of a Congress is for a two-year term, at present, beginning every other January. Elections are held every even-numbered year on Election Day. The members of the House of Representatives are elected for the two-year term of a Congress. The Reapportionment Act of 1929 establishes that there be 435 representatives and the Uniform Congressional Redistricting Act requires ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ex Parte Crow Dog
''Ex parte Crow Dog'', 109 U.S. 556 (1883), is a landmark decision of the Supreme Court of the United States that followed the death of one member of a Native American tribe at the hands of another on reservation land. Crow Dog was a member of the Brulé band of the Lakota Sioux. On August 5, 1881 he shot and killed Spotted Tail, a Lakota chief; there are different accounts of the background to the killing. The tribal council dealt with the incident according to Sioux tradition, and Crow Dog paid restitution to the dead man's family. However, the U.S. authorities then prosecuted Crow Dog for murder in a federal court. He was found guilty and sentenced to hang. The defendant then petitioned the Supreme Court for a writ of habeas corpus, arguing that the federal court had no jurisdiction to try cases where the offense had already been tried by the tribal council. The court found unanimously for the plaintiff and Crow Dog was therefore released. This case was the first time in h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Habeas Corpus
''Habeas corpus'' (; from Medieval Latin, ) is a recourse in law through which a person can report an unlawful detention or imprisonment to a court and request that the court order the custodian of the person, usually a prison official, to bring the prisoner to court, to determine whether the detention is lawful. The writ of ''habeas corpus'' was described in the eighteenth century by William Blackstone as a "great and efficacious writ in all manner of illegal confinement". It is a summons with the force of a court order; it is addressed to the custodian (a prison official, for example) and demands that a prisoner be brought before the court, and that the custodian present proof of authority, allowing the court to determine whether the custodian has lawful authority to detain the prisoner. If the custodian is acting beyond their authority, then the prisoner must be released. Any prisoner, or another person acting on their behalf, may petition the court, or a judge, for a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
South Dakota
South Dakota (; Sioux language, Sioux: , ) is a U.S. state in the West North Central states, North Central region of the United States. It is also part of the Great Plains. South Dakota is named after the Lakota people, Lakota and Dakota people, Dakota Sioux Native Americans in the United States, Native American tribes, who comprise a large portion of the population with nine Indian reservation, reservations currently in the state and have historically dominated the territory. South Dakota is the List of U.S. states and territories by area, seventeenth largest by area, but the List of U.S. states and territories by population, 5th least populous, and the List of U.S. states and territories by population density, 5th least densely populated of the List of U.S. states, 50 United States. As the southern part of the former Dakota Territory, South Dakota became a state on November 2, 1889, simultaneously with North Dakota. They are the 39th and 40th states admitted to the union; Pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
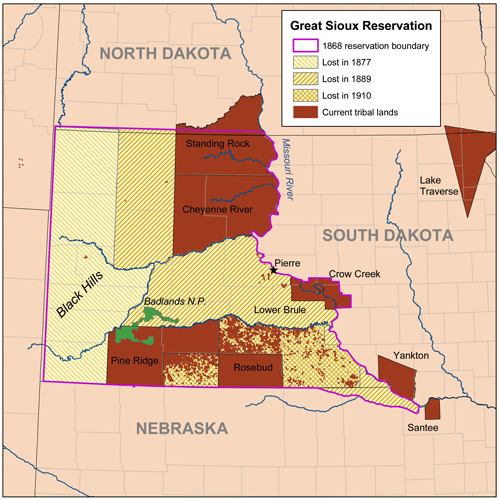
Great Sioux Reservation
The Great Sioux Reservation initially set aside land west of the Missouri River in South Dakota and Nebraska for the use of the Lakota Sioux, who had dominated this territory. The reservation was established in the Fort Laramie Treaty of 1868. It included all of present-day western South Dakota (commonly known as "West River" South Dakota) and modern Boyd County, Nebraska. This area was established by the United States as a reservation for the Teton Sioux, also known as the Lakota: the seven western bands of the "Seven Council Fires" (the Great Sioux Nation). Today, the Sioux primarily live on reservations in Minnesota, Nebraska, North Dakota, South Dakota, and Montana. From the 1860s through the 1870s the American frontier was a mess with battle between the United States and the Sioux. United States settlements expanded into the west and interfered with the Sioux's homes and lives. Reservation In addition to the reservation dedicated to the Lakota, the treaty gave the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spotted Tail
Spotted Tail (Siŋté Glešká pronounced ''gleh-shka''; birth name T'at'aŋka Napsíca "Jumping Buffalo"Ingham (2013) uses 'c' to represent 'č'. ); born c. 1823 – died August 5, 1881) was a Brulé Lakota tribal chief. Although a great warrior in his youth, and having taken part in the Grattan massacre, he declined to participate in Red Cloud's War. He had become convinced of the futility of opposing the white incursions into his homeland; he became a statesman, speaking for peace and defending the rights of his tribe. He made several trips to Washington, D.C. in the 1870s to represent his people, and was noted for his interest in bringing education to the Sioux. He was shot and killed by Crow Dog, a Brulé Lakota subchief, in 1881 for reasons which have been disputed. Early years Spotted Tail was born about 1823 in the White River country west of the Missouri River in present-day South Dakota. His father, Cunka or Tangle Hair, was from the Saône band, and his moth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crow Dog
Crow Dog (also Kȟaŋǧí Šúŋka, Jerome Crow Dog; 1833 – August 1912) was a Brulé Lakota subchief, born at Horse Stealing Creek, Montana Territory. Family He was the nephew of former principal chief Conquering Bear, who was killed in 1854 in an incident which would be known as the Grattan massacre. He was the great-grandfather of Leonard Crow Dog (1942–2021), a practitioner of traditional herbal medicine, a leader of Sun Dance ceremonies, and preserver of Lakota traditions. Life Crow Dog was a traditionalist and one of the leaders who helped popularize the Ghost Dance. After receiving a vision, Jerome warned several dancers to stay away from a large gathering of tribes in 1890 thus saving them from being victims of the Wounded Knee Massacre. Murder trial On August 5, 1881, after a long-simmering feud, Crow Dog shot and killed principal chief Spotted Tail (who was also at the Grattan massacre), on the Rosebud Indian Reservation. A grand jury was convened and he was trie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |