|
Unique-event Polymorphism
In genetic genealogy, a unique-event polymorphism (UEP) is a genetic marker that corresponds to a mutation that is likely to occur so infrequently that it is believed overwhelmingly probable that all the individuals who share the marker, worldwide, will have inherited it from the same common ancestor, and the same single mutation event. Generally, UEP is an allele for which all copies derive from a single mutational event. In genetic genealogy, the mutations considered to be UEPs can be any germline mutation. They are usually single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNP) – the replacement of one letter by another in the DNA sequence, and the terms UEP and SNP are often loosely used interchangeably. But UEPs may also be large-scale additions, such as the YAP insertion that defines Y-DNA haplogroup DE, inversions or deletions. The discovery and widespread testing of new UEPs has been the key to the increasingly detailed analysis of the patrilineal and matrilineal ancestry of ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genetic Genealogy
Genetic genealogy is the use of genealogical DNA tests, i.e., DNA profiling and DNA testing, in combination with traditional genealogical methods, to infer genetic relationships between individuals. This application of genetics came to be used by family historians in the 21st century, as DNA tests became affordable. The tests have been promoted by amateur groups, such as surname study groups or regional genealogical groups, as well as research projects such as the Genographic Project. As of 2019, about 30 million people had been tested. As the field developed, the aims of practitioners broadened, with many seeking knowledge of their ancestry beyond the recent centuries, for which traditional pedigrees can be constructed. History The investigation of surnames in genetics can be said to go back to George Darwin, a son of Charles Darwin and Charles' first cousin Emma Darwin. In 1875, George Darwin used surnames to estimate the frequency of first-cousin marriages and calcula ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MtDNA
Mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA or mDNA) is the DNA located in mitochondrion, mitochondria, cellular organelles within eukaryotic cells that convert chemical energy from food into a form that cells can use, such as adenosine triphosphate (ATP). Mitochondrial DNA is only a small portion of the DNA in a eukaryotic cell; most of the DNA can be found in the cell nucleus and, in plants and algae, also in plastids such as chloroplasts. Human mitochondrial DNA was the first significant part of the human genome to be sequenced. This sequencing revealed that the human mtDNA includes 16,569 base pairs and encodes 13 proteins. Since animal mtDNA evolves faster than nuclear genetic markers, it represents a mainstay of phylogenetics and evolutionary biology. It also permits an examination of the relatedness of populations, and so has become important in anthropology and biogeography. Origin Nuclear and mitochondrial DNA are thought to be of separate evolutionary origin, with the mtDNA being ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
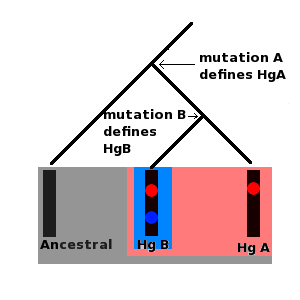
Haplogroup
A haplotype is a group of alleles in an organism that are inherited together from a single parent, and a haplogroup ( haploid from the el, ἁπλοῦς, ''haploûs'', "onefold, simple" and en, group) is a group of similar haplotypes that share a common ancestor with a single-nucleotide polymorphism mutation. More specifically, a haplogroup is a combination of alleles at different chromosomal regions that are closely linked and that tend to be inherited together. As a haplogroup consists of similar haplotypes, it is usually possible to predict a haplogroup from haplotypes. Haplogroups pertain to a single line of descent. As such, membership of a haplogroup, by any individual, relies on a relatively small proportion of the genetic material possessed by that individual. Each haplogroup originates from, and remains part of, a preceding single haplogroup (or paragroup). As such, any related group of haplogroups may be precisely modelled as a nested hierarchy, in which each set ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Haplogroup J (Y-DNA)
Haplogroup J-M304, also known as J, ISOGGbr> ''Y-DNA Haplogroup J and its Subclades - 2016'' (2 February 2016). is a human Y-chromosome DNA haplogroup. It is believed to have evolved in Western Asia. The clade spread from there during the Neolithic, primarily into North Africa, the Horn of Africa, the Socotra Archipelago, the Caucasus, Europe, Western Asia, Central Asia, South Asia, and Southeast Asia. Haplogroup J-M304 is divided into two main subclades (branches), J-M267 and J-M172. Origins Haplogroup J-M304 is believed to have split from the haplogroup I-M170 roughly 43,000 years ago in Western Asia, as both lineages are haplogroup IJ subclades. Haplogroup IJ and haplogroup K derive from haplogroup IJK, and only at this level of classification does haplogroup IJK join with Haplogroup G-M201 and Haplogroup H as immediate descendants of Haplogroup F-M89. J-M304 is defined by the M304 genetic marker, or the equivalent 12f2.1 marker. The main current subgroups J-M267 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Y-STR
A Y-STR is a short tandem repeat (STR) on the Y-chromosome. Y-STRs are often used in forensics, paternity, and genealogical DNA testing. Y-STRs are taken specifically from the male Y chromosome. These Y-STRs provide a weaker analysis than autosomal STRs because the Y chromosome is only found in males, which are only passed down by the father, making the Y chromosome in any paternal line practically identical. This causes a significantly smaller amount of distinction between Y-STR samples. Autosomal STRs provide a much stronger analytical power because of the random matching that occurs between pairs of chromosomes during the zygote making process. Nomenclature Y-STRs are assigned names by the HUGO gene nomenclature committee (HGNC). Some testing companies have different formats for the way STR markers are written. For example, the marker DYS455 may be written as DYS455, DYS 455, DYS#455, or DYS# 455. The scientific standard accepted by HUGO and NIST is DYS455. DYS DYS is a variat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Haplotype
A haplotype ( haploid genotype) is a group of alleles in an organism that are inherited together from a single parent. Many organisms contain genetic material ( DNA) which is inherited from two parents. Normally these organisms have their DNA organized in two sets of pairwise similar chromosomes. The offspring gets one chromosome in each pair from each parent. A set of pairs of chromosomes is called diploid and a set of only one half of each pair is called haploid. The haploid genotype (haplotype) is a genotype that considers the singular chromosomes rather than the pairs of chromosomes. It can be all the chromosomes from one of the parents or a minor part of a chromosome, for example a sequence of 9000 base pairs. However, there are other uses of this term. First, it is used to mean a collection of specific alleles (that is, specific DNA sequences) in a cluster of tightly linked genes on a chromosome that are likely to be inherited together—that is, they are likely to be co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genealogical DNA Test
A genealogical DNA test is a DNA-based test used in genetic genealogy that looks at specific locations of a person's genome in order to find or verify ancestral genealogical relationships, or (with lower reliability) to estimate the ethnic mixture of an individual. Since different testing companies use different ethnic reference groups and different matching algorithms, ethnicity estimates for an individual vary between tests, sometimes dramatically. Three principal types of genealogical DNA tests are available, with each looking at a different part of the genome and being useful for different types of genealogical research: autosomal (atDNA), mitochondrial (mtDNA), and Y-DNA. Autosomal tests may result in a large number of DNA matches to both males and females who have also tested with the same company. Each match will typically show an estimated degree of relatedness, i.e., a close family match, 1st-2nd cousins, 3rd-4th cousins, etc. The furthest degree of relationship ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Short Tandem Repeat
A microsatellite is a tract of repetitive DNA in which certain DNA motifs (ranging in length from one to six or more base pairs) are repeated, typically 5–50 times. Microsatellites occur at thousands of locations within an organism's genome. They have a higher mutation rate than other areas of DNA leading to high genetic diversity. Microsatellites are often referred to as short tandem repeats (STRs) by forensic geneticists and in genetic genealogy, or as simple sequence repeats (SSRs) by plant geneticists. Microsatellites and their longer cousins, the minisatellites, together are classified as VNTR (variable number of tandem repeats) DNA. The name "satellite" DNA refers to the early observation that centrifugation of genomic DNA in a test tube separates a prominent layer of bulk DNA from accompanying "satellite" layers of repetitive DNA. They are widely used for DNA profiling in cancer diagnosis, in kinship analysis (especially paternity testing) and in forensic identificat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Autosome
An autosome is any chromosome that is not a sex chromosome. The members of an autosome pair in a diploid cell have the same morphology, unlike those in allosomal (sex chromosome) pairs, which may have different structures. The DNA in autosomes is collectively known as atDNA or auDNA. For example, humans have a diploid genome that usually contains 22 pairs of autosomes and one allosome pair (46 chromosomes total). The autosome pairs are labeled with numbers (1–22 in humans) roughly in order of their sizes in base pairs, while allosomes are labelled with their letters. By contrast, the allosome pair consists of two X chromosomes in females or one X and one Y chromosome in males. Unusual combinations of XYY, XXY, XXX, XXXX, XXXXX or XXYY, among other Salome combinations, are known to occur and usually cause developmental abnormalities. Autosomes still contain sexual determination genes even though they are not sex chromosomes. For example, the SRY gene on the Y chr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
X Chromosome
The X chromosome is one of the two sex-determining chromosomes ( allosomes) in many organisms, including mammals (the other is the Y chromosome), and is found in both males and females. It is a part of the XY sex-determination system and XO sex-determination system. The X chromosome was named for its unique properties by early researchers, which resulted in the naming of its counterpart Y chromosome, for the next letter in the alphabet, following its subsequent discovery. Discovery It was first noted that the X chromosome was special in 1890 by Hermann Henking in Leipzig. Henking was studying the testicles of ''Pyrrhocoris'' and noticed that one chromosome did not take part in meiosis. Chromosomes are so named because of their ability to take up staining (''chroma'' in Greek means ''color''). Although the X chromosome could be stained just as well as the others, Henking was unsure whether it was a different class of object and consequently named it ''X element'', which later ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Haplogroup
A haplotype is a group of alleles in an organism that are inherited together from a single parent, and a haplogroup ( haploid from the el, ἁπλοῦς, ''haploûs'', "onefold, simple" and en, group) is a group of similar haplotypes that share a common ancestor with a single-nucleotide polymorphism mutation. More specifically, a haplogroup is a combination of alleles at different chromosomal regions that are closely linked and that tend to be inherited together. As a haplogroup consists of similar haplotypes, it is usually possible to predict a haplogroup from haplotypes. Haplogroups pertain to a single line of descent. As such, membership of a haplogroup, by any individual, relies on a relatively small proportion of the genetic material possessed by that individual. Each haplogroup originates from, and remains part of, a preceding single haplogroup (or paragroup). As such, any related group of haplogroups may be precisely modelled as a nested hierarchy, in which each set ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Y-DNA
The Y chromosome is one of two sex chromosomes ( allosomes) in therian mammals, including humans, and many other animals. The other is the X chromosome. Y is normally the sex-determining chromosome in many species, since it is the presence or absence of Y that determines the male or female sex of offspring produced in sexual reproduction. In mammals, the Y chromosome contains the gene SRY, which triggers male development. The DNA in the human Y chromosome is composed of about 59 million base pairs, making it similar in size to chromosome 19. The Y chromosome is passed only from father to son. With a 30% difference between humans and chimpanzees, the Y chromosome is one of the fastest-evolving parts of the human genome. The human Y chromosome carries an estimated 100–200 genes, with between 45 and 73 of these being protein-coding. All single-copy Y-linked genes are hemizygous (present on only one chromosome) except in cases of aneuploidy such as XYY syndrome or XXYY s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |