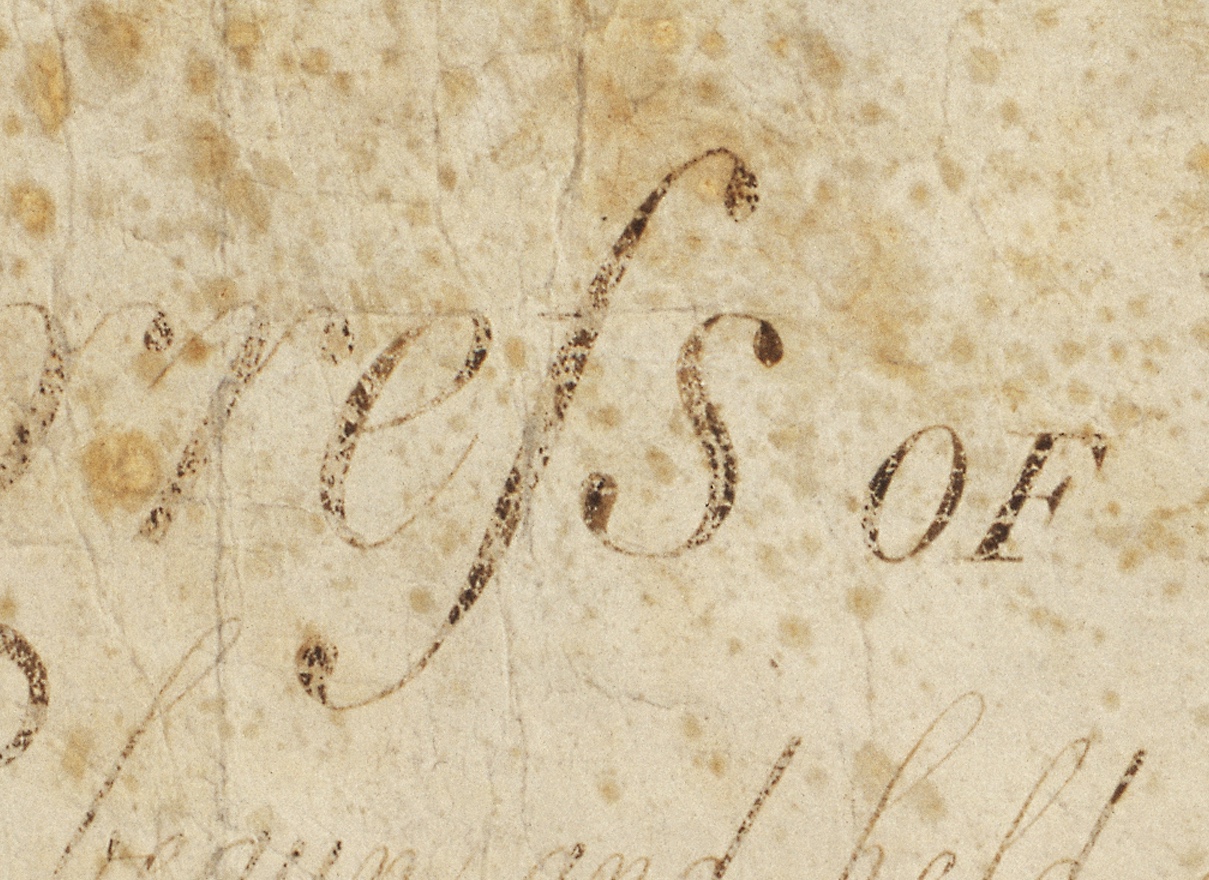|
Uncial Script
Uncial is a majuscule script (written entirely in capital letters) commonly used from the 4th to 8th centuries AD by Latin and Greek scribes. Uncial letters were used to write Greek and Latin, as well as Gothic, and are the current style for Coptic and Nobiin. Development Early uncial script most likely developed from late rustic capitals. Early forms are characterized by broad single-stroke letters using simple round forms taking advantage of the new parchment and vellum surfaces, as opposed to the angular, multiple-stroke letters, which are more suited for rougher surfaces, such as papyrus. In the oldest examples of uncial, such as the fragment of '' De bellis macedonicis'' in the British Library, of the late 1st–early 2nd centuries, all of the letters are disconnected from one another, and word separation is typically not used. Word separation, however, is characteristic of later uncial usage. As the script evolved over the centuries, the characters became more com ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Papyrus Oxyrhynchus 30
Papyrus Oxyrhynchus 30 (P. Oxy. 30) is a historical fragment in Latin. It was discovered by Grenfell and Hunt in 1897 in Oxyrhynchus. The fragment is dated to the third century. It is housed in the Department of Manuscripts of the British Library. The text was published by Grenfell and Hunt in 1898. The manuscript was written on vellum in the form of a codex. The measures of a single leaf are 86 by 50 mm. The text is written in an uncial script. The words are not divided at the end of lines. The subject of the composition was probably the Macedonian wars. See also * Oxyrhynchus Papyri The Oxyrhynchus Papyri are a group of manuscripts discovered during the late nineteenth and early twentieth centuries by papyrology, papyrologists Bernard Pyne Grenfell and Arthur Surridge Hunt at an ancient Landfill, rubbish dump near Oxyrhync ... * Papyrus Oxyrhynchus 29 * Papyrus Oxyrhynchus 31 References {{P.Oxy.I.source 030 3rd-century manuscripts Macedonian Wars Manus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Italy In The Middle Ages
The history of Italy in the Middle Ages can be roughly defined as the time between the collapse of the Western Roman Empire and the Italian Renaissance. Late antiquity in Italy lingered on into the 7th century under the Ostrogothic Kingdom and the Byzantine Empire under the Justinian dynasty, the Byzantine Papacy until the mid 8th century. The "Middle Ages" proper begin as the Byzantine Empire was weakening under the pressure of the Muslim conquests, and most of the Exarchate of Ravenna finally fell under Lombard rule in 751. From this period, former states that were part of the Exarchate and were not conquered by the Lombard Kingdom, such as the Duchy of Naples, became de facto independent states, having less and less interference from the Eastern Roman Empire. Lombard rule ended with the invasion of Charlemagne in 773, who established the Kingdom of Italy and the Papal States in large parts of Northern and Central Italy. This set the precedent for the main political ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
North Africa In The Roman Era
The history of North Africa during the period of classical antiquity (c. 8th century BCE – 5th century CE) can be divided roughly into the history of Egypt in the east, the history of ancient Libya in the middle and the history of Numidia and Mauretania in the west. Initially, in the east, Egypt was under Persian rule during the early phase of classical antiquity, passing to the Ptolemaic dynasty in the Hellenistic era. Libya was inhabited by Berber tribes, while along the coast Phoenician and Greek colonies were set up. The Roman Republic established the province of Africa in 146 BCE after the defeat of Carthage. The Roman Empire eventually controlled the entire Mediterranean coast of Africa, adding Egypt in 30 BCE, Crete and Cyrenaica in 20 BCE, and Mauretania in CE 44. The Western Roman Empire lost most parts of Africa to the Vandals in the 5th century. They were reincorporated into the Roman realm by the Eastern Roman Empire in the 6th century. Later, the empire finall ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Long S
The long s, , also known as the medial ''s'' or initial ''s'', is an Archaism, archaic form of the lowercase letter , found mostly in works from the late 8th to early 19th centuries. It replaced one or both of the letters ''s'' in a double-''s'' sequence (e.g., "ſinfulneſs" for "sinfulness" and "poſſeſs" or "poſseſs" for "possess", but never "poſſeſſ"). The modern letterform is known as the "short", "terminal", or "round" ''s''. In typography, the long ''s'' is known as a type of swash letter, commonly referred to as a "swash ''s''". The long ''s'' is the basis of the first half of the grapheme of the German alphabet Orthographic ligature, ligature letter , ( or , 'sharp ''s'''). As with other letters, the long ''s'' may have a variant appearance depending on typeface: , , , . Rules English This list of rules for the long ''s'' is not exhaustive, and it applies only to books printed during the 17th to early 19th centuries in English-speaking countries. Similar r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
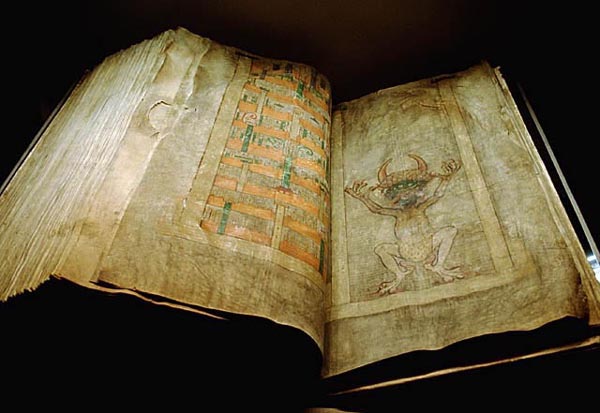
Codex Bezae - Latin Luke 23-47-24-1 (The S
The codex (: codices ) was the historical ancestor format of the modern book. Technically, the vast majority of modern books use the codex format of a stack of pages bound at one edge, along the side of the text. But the term ''codex'' is now reserved for older manuscript books, which mostly used sheets of vellum, parchment, or papyrus, rather than paper. By convention, the term is also used for any Aztec codex (although the earlier examples do not actually use the codex format), Maya codices and other pre-Columbian manuscripts. Library practices have led to many European manuscripts having "codex" as part of their usual name, as with the Codex Gigas, while most do not. Modern books are divided into paperback (or softback) and those bound with stiff boards, called hardbacks. Elaborate historical bindings are called treasure bindings. At least in the Western world, the main alternative to the paged codex format for a long document was the continuous scroll, which was the do ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Irish Language
Irish (Standard Irish: ), also known as Irish Gaelic or simply Gaelic ( ), is a Celtic language of the Indo-European language family. It is a member of the Goidelic languages of the Insular Celtic sub branch of the family and is indigenous language, indigenous to the island of Ireland. It was the majority of the population's first language until the 19th century, when English (language), English gradually became dominant, particularly in the last decades of the century, in what is sometimes characterised as a result of linguistic imperialism. Today, Irish is still commonly spoken as a first language in Ireland's Gaeltacht regions, in which 2% of Ireland's population lived in 2022. The total number of people (aged 3 and over) in Ireland who declared they could speak Irish in April 2022 was 1,873,997, representing 40% of respondents, but of these, 472,887 said they never spoke it and a further 551,993 said they only spoke it within the education system. Linguistic analyses o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Insular Script
Insular script is a Middle Ages, medieval script (styles of handwriting), script system originating in Ireland that spread to England and continental Europe under the influence of Hiberno-Scottish mission, Irish Christianity. Irish missionaries took the script to continental Europe, where they founded monasteries, such as Bobbio Abbey, Bobbio. The scripts were also used in monasteries, like Fulda monastery, Fulda, which were influenced by English missionaries. They are associated with Insular art, of which most surviving examples are illuminated manuscripts. It greatly influenced modern Gaelic type and handwriting. The term "Insular script" is used to refer to a diverse family of scripts used for different functions. At the top of the hierarchy was the Insular half-uncial (or "Insular majuscule"), used for important documents and sacred text. The full uncial, in a version called "English uncial", was used in some English centres. Then "in descending order of formality and increas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ireland
Ireland (, ; ; Ulster Scots dialect, Ulster-Scots: ) is an island in the North Atlantic Ocean, in Northwestern Europe. Geopolitically, the island is divided between the Republic of Ireland (officially Names of the Irish state, named Irelanda sovereign state covering five-sixths of the island) and Northern Ireland (part of the United Kingdomcovering the remaining sixth). It is separated from Great Britain to its east by the North Channel (Great Britain and Ireland), North Channel, the Irish Sea, and St George's Channel. Ireland is the List of islands of the British Isles, second-largest island of the British Isles, the List of European islands by area, third-largest in Europe, and the List of islands by area, twentieth-largest in the world. As of 2022, the Irish population analysis, population of the entire island is just over 7 million, with 5.1 million in the Republic of Ireland and 1.9 million in Northern Ireland, ranking it the List of European islands by population, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bible
The Bible is a collection of religious texts that are central to Christianity and Judaism, and esteemed in other Abrahamic religions such as Islam. The Bible is an anthology (a compilation of texts of a variety of forms) originally written in Hebrew, Aramaic, and Koine Greek. The texts include instructions, stories, poetry, prophecies, and other genres. The collection of materials accepted as part of the Bible by a particular religious tradition or community is called a biblical canon. Believers generally consider it to be a product of divine inspiration, but the way they understand what that means and interpret the text varies. The religious texts were compiled by different religious communities into various official collections. The earliest contained the first five books of the Bible, called the Torah in Hebrew and the Pentateuch (meaning 'five books') in Greek. The second-oldest part was a collection of narrative histories and prophecies (the Nevi'im). The third co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carolingian Renaissance
The Carolingian Renaissance was the first of three medieval renaissances, a period of cultural activity in the Carolingian Empire. Charlemagne's reign led to an intellectual revival beginning in the 8th century and continuing throughout the 9th century, taking inspiration from ancient Roman and Greek culture and the Christian Roman Empire of the fourth century. During this period, there was an increase of literature, writing, visual arts, architecture, music, jurisprudence, liturgical reforms, and scriptural studies. Carolingian schools were effective centers of education, and they served generations of scholars by producing editions and copies of the classics, both Christian and pagan. The movement occurred mostly during the reigns of Carolingian rulers Charlemagne and Louis the Pious. It was supported by the scholars of the Carolingian court, notably Alcuin of York. Charlemagne's '' Admonitio generalis'' (789) and '' Epistola de litteris colendis'' served as manifesto ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lower Case
Letter case is the distinction between the letters that are in larger uppercase or capitals (more formally ''majuscule'') and smaller lowercase (more formally '' minuscule'') in the written representation of certain languages. The writing systems that distinguish between the upper- and lowercase have two parallel sets of letters: each in the majuscule set has a counterpart in the minuscule set. Some counterpart letters have the same shape, and differ only in size (e.g. ), but for others the shapes are different (e.g., ). The two case variants are alternative representations of the same letter: they have the same name and pronunciation and are typically treated identically when sorting in alphabetical order. Letter case is generally applied in a mixed-case fashion, with both upper and lowercase letters appearing in a given piece of text for legibility. The choice of case is often denoted by the grammar of a language or by the conventions of a particular discipline. In ortho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |