|
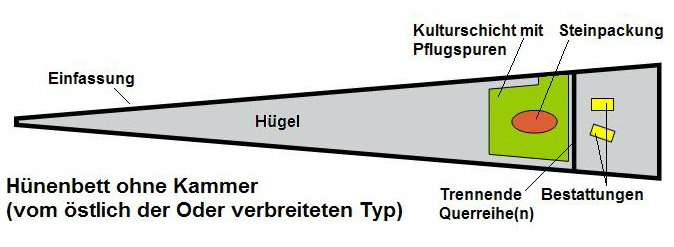
Unchambered Long Barrow
The unchambered long barrowMasset, Claude (1997). ''Les Dolmens'', Errance, pp. 39 and 172 at www.eng-h.gov.uk. Accessed on 18 Aug 2013Lynch (1997), p. 25. earthen long barrow, non-megalithic long barrow or non-megalithic mound (german: kammerloses Hünenbett or ''Hünenbett ohne Kammer''), is a type of found across the , in a belt of land in , and in northern Europe as far east ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Long Barrow
Long barrows are a style of monument constructed across Western Europe in the fifth and fourth millennia BCE, during the Early Neolithic period. Typically constructed from earth and either timber or stone, those using the latter material represent the oldest widespread tradition of stone construction in the world. Around 40,000 long barrows survive today. The structures have a long earthen tumulus, or "barrow", that is flanked on two sides with linear ditches. These typically stretch for between 20 and 70 metres in length, although some exceptional examples are either longer or shorter than this. Some examples have a timber or stone chamber in one end of the tumulus. These monuments often contained human remains interred within their chambers, and as a result, are often interpreted as tombs, although there are some examples where this appears not to be the case. The choice of timber or stone may have arisen from the availability of local materials rather than cultural difference ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Konin
Konin (german: Kunau) is a city in central Poland, on the Warta River. It is the capital of Konin County and is located within the Greater Poland Voivodeship. Prior to 1999, it was the capital of the Konin Voivodeship (1975–1998). In 2021 the population of the city was 71,427, making it the fourth-largest city in Greater Poland after Poznań, Kalisz and Piła. History Prehistory The earliest evidence of human habitation in Konin has been dated to the Paleolithic Era. On the dunes near the Warta, various ancient flint tools and implements have been found, among them being knives, burins, and tanged points. These earliest artifacts are of the Swiderian culture (''Kultura Świderska'') of 9000–8000 BC. Ancient times A permanent settlement arose along the Amber Road, which led from the Roman Empire to the Baltic Sea, traversing the area of present-day Konin. A map drawn by Ptolemy identified the settlement as ''Setidava'' (or ''Getidava''), a probable spot to wade across the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sylt
Sylt (; da, Sild; Sylt North Frisian, Söl'ring North Frisian: ) is an island in northern Germany, part of Nordfriesland district, Schleswig-Holstein, and well known for the distinctive shape of its shoreline. It belongs to the North Frisian Islands and is the largest island in North Frisia. The northernmost island of Germany, it is known for its tourist resorts, notably Westerland, Germany, Westerland, Kampen, Germany, Kampen and Wenningstedt-Braderup, as well as for its sandy beach. It is frequently covered by the media in connection with its exposed situation in the North Sea and its ongoing loss of land during Storm tides of the North Sea, storm tides. Since 1927, Sylt has been connected to the mainland by the Hindenburgdamm causeway. In later years, it has been a resort for the German jet set and tourists in search of occasional celebrity sightings. Geography With , Sylt is the fourth-largest Islands of Germany, German island and the largest German island in the Nort ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alter Hau Barrow
{{disambiguation ...
Alter may refer to: * Alter (name), people named Alter * Alter (automobile) * Alter (crater), a lunar crater * Alter Channel, a Greek TV channel * Archbishop Alter High School, a Roman Catholic high school in Kettering, Ohio * ALTER, a command in older implementations of COBOL * Alter ego, or "alter" in popular usage, a "second self" * Alter (SQL) * ''Alter'' (album), 2002 album by Floater * ''Alter'', a 2006 remix album by Swiss band Knut * "Alter", a song from the 1994 album '' Glow'', by Raven See also * Altar (other) An altar is a religious structure for sacrifices or offerings. Altar may also refer to: Arts and entertainment * ''Altar'' (album), a 2006 album by Sunn O))) and Boris * Altar (Brazilian band), a dance music band * Altar (Dutch band), a death m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Barrows Of Grundoldendorf
Barrow may refer to: Places England * Barrow-in-Furness, Cumbria ** Borough of Barrow-in-Furness, local authority encompassing the wider area ** Barrow and Furness (UK Parliament constituency) * Barrow, Cheshire * Barrow, Gloucestershire * Barrow, Lancashire * Barrow, Rutland * Barrow, Shropshire * Barrow, Somerset * Barrow, Suffolk * Barrow (Lake District), a fell in the county of Cumbria * Barrow upon Humber, Lincolnshire * Barrow upon Soar, Leicestershire * Barrow upon Trent, Derbyshire Ireland * River Barrow, the second-longest river in Ireland * Barrow, a townland in County Kerry, home of Tralee Golf Club United States * Barrow County, Georgia * Barrow, Illinois, an unincorporated community * Utqiaġvik, Alaska (formerly known as Barrow) The Moon * Barrow (crater) People * Barrow (name), a surname, and persons with the name * Barrows (name), a surname, and persons with the name * Musa Barrow, Gambian profession footballer Other uses * Barrow A.F.C., an association foot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vorpommern-Greifswald
Vorpommern-Greifswald is a district in the east of Mecklenburg-Vorpommern, Germany. It is bounded by (from the west and clockwise) the districts of Mecklenburgische Seenplatte and Vorpommern-Rügen, the Baltic Sea, Poland (West Pomeranian Voivodeship) and the state of Brandenburg. The district seat is the University and Hanseatic City of Greifswald. A lake called Berliner See is found in the district. History Vorpommern-Greifswald District was established by merging the former districts of Ostvorpommern and Uecker-Randow; along with the subdivisions of Jarmen-Tutow and Peenetal/Loitz (from the former district of Demmin), and the former district-free town Greifswald, as part of the local government reform of September 2011. The name of the district was decided by referendum on 4 September 2011. The project name for the district was ''Südvorpommern''. Geography The district has a number of lakes including: The island of Usedom Usedom (german: Usedom , pl, Uznam ) is a Bal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sachsenwald
The Sachsenwald () is a forest near Hamburg, Germany. It is an unincorporated area in the amt Hohe Elbgeest. It derives its name (which means 'Saxon woods' in English) from being located in the former Duchy of Saxe-Lauenburg, earlier also called Lower Saxony, now mostly covered by the Herzogtum Lauenburg (Duchy of Lauenburg) district. The Sachsenwald has an area of 68 km2. It was given to Otto von Bismarck in 1871 for his achievements for Germany. Today the managed forest area amounts to about 6,000 hectares, of which 4,500 still belong to the House of Bismarck, residing at Friedrichsruh. From 1989, Ferdinand von Bismarck Ferdinand Herbord Ivar, Prince of Bismarck (German language, German: ''Ferdinand Herbord Ivar Fürst von Bismarck''; 22 November 1930 – 23 July 2019) was a German lawyer and landowner from the family of statesman Otto von Bismarck. He was the he ... sold 2,250 hectares to the shipowner Eberhart von Rantzau, owner of the Deutsche Afrika-Linien. References ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Megalith Of Stralendorf
A megalith is a large stone that has been used to construct a prehistoric structure or monument, either alone or together with other stones. There are over 35,000 in Europe alone, located widely from Sweden to the Mediterranean sea. The word was first used in 1849 by the British antiquarian Algernon Herbert in reference to Stonehenge and derives from the Ancient Greek words "mega" for great and "lithos" for stone. Most extant megaliths were erected between the Neolithic period (although earlier Mesolithic examples are known) through the Chalcolithic period and into the Bronze Age. At that time, the beliefs that developed were dynamism and animism, because Indonesia experienced the megalithic age or the great stone age in 2100 to 4000 BC. So that humans ancient tribe worship certain objects that are considered to have supernatural powers. Some relics of the megalithic era are menhirs (stone monuments) and dolmens (stone tables). Types and definitions While "megalith" is o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Megaliths Of Gnewitz
A megalith is a large stone that has been used to construct a prehistoric structure or monument, either alone or together with other stones. There are over 35,000 in Europe alone, located widely from Sweden to the Mediterranean sea. The word was first used in 1849 by the British antiquarian Algernon Herbert in reference to Stonehenge and derives from the Ancient Greek words "mega" for great and "lithos" for stone. Most extant megaliths were erected between the Neolithic period (although earlier Mesolithic examples are known) through the Chalcolithic period and into the Bronze Age. At that time, the beliefs that developed were dynamism and animism, because Indonesia experienced the megalithic age or the great stone age in 2100 to 4000 BC. So that humans ancient tribe worship certain objects that are considered to have supernatural powers. Some relics of the megalithic era are menhirs (stone monuments) and dolmens (stone tables). Types and definitions While "megalith" is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mecklenburg-Vorpommern
Mecklenburg-Vorpommern (MV; ; nds, Mäkelborg-Vörpommern), also known by its anglicized name Mecklenburg–Western Pomerania, is a state in the north-east of Germany. Of the country's sixteen states, Mecklenburg-Vorpommern ranks 14th in population; it covers an area of , making it the sixth largest German state in area; and it is 16th in population density. Schwerin is the state capital and Rostock is the largest city. Other major cities include Neubrandenburg, Stralsund, Greifswald, Wismar, and Güstrow. It was named after the 2 regions of Mecklenburg and Vorpommern (which means West Pomerania). The state was established in 1945 after World War II through the merger of the historic regions of Mecklenburg and the Prussian Western Pomerania by the Soviet military administration in Allied-occupied Germany. It became part of the German Democratic Republic in 1949, but was dissolved in 1952 during administrative reforms and its territory divided into the districts of R ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ewald Schuldt
Ewald Adolf Ludwig Wilhelm Schuldt (3 January 1914 – 1 June 1987) was a German prehistorian who carried out significant research into the megaliths of northern Germany. Life Early years Schuldt was born on 3 January 1914 in Mechelsdorf near Rerik and grew up as an only child in simple circumstances. He never got to know his father, an agricultural labourer, because he was killed in 1914 as a soldier in France. The second husband of hs mother was to him an understanding stepfather, who initially wanted to Ewald Schuldt to follow him as a gardener.Klaus-Dieter Gralow (ed.): ''Ewald Schuldt: archäologische Expeditionen im eigenen Land (1950–1984).'' Stock & Stein, Schwerin 2005, p. 317. Significance Ewald Schuldt is one of the best known and most successful Mecklenburg archaeologists. He conducted research of lasting importance, particularly in the field of prehistory and early history. His scientific work built on the research begun in 1835 by G.C.F. Lisch, and continu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)



