|
Typhoon Phyllis (1975)
Typhoon Phyllis was one of seven tropical cyclones in 1975 to pass within range of the Japan Meteorological Agency's (JMA) radar surveillance. A tropical disturbance developed in the monsoon trough just west of Guam on August 11. The disturbance was classified as a tropical depression the next day. Tracking northward, the depression intensified into Tropical Storm Phyllis later on August 12. On the next day, Phyllis, after developing an eye, attained typhoon intensity. The typhoon accelerated north while rapidly intensifying, and on the evening of August 14, Phyllis reached its peak intensity of . Typhoon Phyllis turned northwest, making landfall over Shikoku on August 17, with winds of . Phyllis weakened to a tropical storm later the same day. Its remnants were last observed on August 20. Phyllis, along with Typhoon Rita, were accountable for the bulk of tropical cyclone casualties in Japan during the 1975 Pacific typhoon season. From Phyllis alone, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Japan
Japan ( ja, 日本, or , and formally , ''Nihonkoku'') is an island country in East Asia. It is situated in the northwest Pacific Ocean, and is bordered on the west by the Sea of Japan, while extending from the Sea of Okhotsk in the north toward the East China Sea, Philippine Sea, and Taiwan in the south. Japan is a part of the Ring of Fire, and spans Japanese archipelago, an archipelago of List of islands of Japan, 6852 islands covering ; the five main islands are Hokkaido, Honshu (the "mainland"), Shikoku, Kyushu, and Okinawa Island, Okinawa. Tokyo is the Capital of Japan, nation's capital and largest city, followed by Yokohama, Osaka, Nagoya, Sapporo, Fukuoka, Kobe, and Kyoto. Japan is the List of countries and dependencies by population, eleventh most populous country in the world, as well as one of the List of countries and dependencies by population density, most densely populated and Urbanization by country, urbanized. About three-fourths of Geography of Japan, the c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tropical Cyclone Naming
Tropical cyclones and subtropical cyclones are named by various warning centers to simplify communication between forecasters and the general public regarding forecasts, watches and warnings. The names are intended to reduce confusion in the event of concurrent storms in the same basin. Once storms develop sustained wind speeds of more than , names are generally assigned to them from predetermined lists, depending on the basin in which they originate. Some tropical depressions are named in the Western Pacific; while tropical cyclones must contain a significant amount of gale-force winds before they are named in the Southern Hemisphere. Before it became standard practice to give personal (first) names to tropical cyclones, they were named after places, objects, or the saints' feast days on which they occurred. Credit for the first usage of personal names for weather systems is generally given to Queensland Government Meteorologist Clement Wragge, who named systems between 18 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
All Nippon Airways
, also known as ANA (''Ē-enu-ē'') or is an airline in Japan. Its headquarters are located in Shiodome City Center in the Shiodome area of Minato ward of Tokyo. It operates services to both domestic and international destinations and had more than 20,000 employees as of March 2016. In addition to its mainline operations, ANA controls several subsidiary passenger carriers, including its regional airline, ANA Wings, Air Nippon, Air Do (a low-cost carrier operating scheduled service between Tokyo and cities in Hokkaido), and Allex Cargo (ANA Cargo - the freighter division operated by Air Japan). ANA is also the largest shareholder in Peach, a low-cost carrier joint venture with Hong Kong company First Eastern Investment Group. In October 1999, the airline became a member of Star Alliance. On 29 March 2013, ANA was named a 5-Star Airline by Skytrax. On 27 April 2018, ANA announced ANA Business Jet Co., Ltd., a joint venture with Sojitz to offer private jet charter flights. H ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kōchi Prefecture
is a prefecture of Japan located on the island of Shikoku. Kōchi Prefecture has a population of 757,914 (1 December 2011) and has a geographic area of 7,103 km2 (2,742 sq mi). Kōchi Prefecture borders Ehime Prefecture to the northwest and Tokushima Prefecture to the northeast. Kōchi is the capital and largest city of Kōchi Prefecture, with other major cities including Nankoku, Shimanto, and Kōnan. Kōchi Prefecture is located on Japan's Pacific coast surrounding a large bay in the south of Shikoku, with the southernmost point of the island located at Cape Ashizuri in Tosashimizu. Kōchi Prefecture is home to Kōchi Castle, considered the most intact Japanese castle, and the Shimanto River, one of the few undammed rivers in Japan. History Kōchi Prefecture was historically known as Tosa Province and was controlled by the Chōsokabe clan in the Sengoku period and the Yamauchi clan during the Edo period. Kōchi city is also the birthplace of noted revolutiona ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tosashimizu, Kōchi
270px, Tosashimizu City Hall 270px, AerialView of central Tosashimizu City is a city located in the southwest of Kōchi Prefecture, Japan. , the city had an estimated population of 12,407 in 7004 households, and a population density of 47 persons per km². The total area of the city is . Geography Tosashimizu is located in far western Kochi Prefecture on the island of Shikoku. Parts of the city are within the borders of the Ashizuri-Uwakai National Park. Neighbouring municipalities Kōchi Prefecture * Sukumo * Shimanto City * Ōtsuki * Mihara Climate Tosashimizu has a humid subtropical climate (Köppen climate classification ''Cfa'') with hot, humid summers and cool winters. There is significant precipitation throughout the year, especially during June and July. The average annual temperature in Tosashimizu is . The average annual rainfall is with June as the wettest month. The temperatures are highest on average in August, at around , and lowest in January, at around ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shimizu, Shizuoka
is a town in Suntō District of Shizuoka Prefecture, Japan. , the town had an estimated population of 32,453 in 14058 households, and a population density of 3,700 persons per km2. The total area of the town was . Geography Shimizu is located at the northern end of Izu Peninsula. Both the Kakita River and the Kano River flow through the town. The area has a temperate maritime climate with hot, humid summers and mild, cool winters. Neighboring municipalities *Shizuoka Prefecture **Numazu **Mishima **Nagaizumi Demographics Per Japanese census data, the population of Shimizu has been increasing over the past 70 years. Climate The city has a climate characterized by hot and humid summers, and relatively mild winters (Köppen climate classification ''Cfa''). The average annual temperature in Shimizu is 15.8 °C. The average annual rainfall is 1925 mm with September as the wettest month. The temperatures are highest on average in August, at around 26.6 °C, and l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Regional Specialized Meteorological Center
A Regional Specialized Meteorological Centre (RSMC) is responsible for the distribution of information, advisories, and warnings regarding the specific program they have a part of, agreed by consensus at the World Meteorological Organization as part of the World Weather Watch. Environmental emergency response programme As a result of the poor communications between countries following the Chernobyl disaster in the Spring of 1986, the World Meteorological Organization (WMO) was requested by the International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA) and other international organizations to arrange for early warning messages about nuclear accidents to be transmitted over the Global Telecommunications System (GTS). In addition some WMO member countries that lacked extensive forecasting capability requested that specialized pollutant transport and dispersion forecasts be provided during these emergencies. As a result, during 1989 Meteo-France (MF), Environment Canada (EC) and the United Kingdom's M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
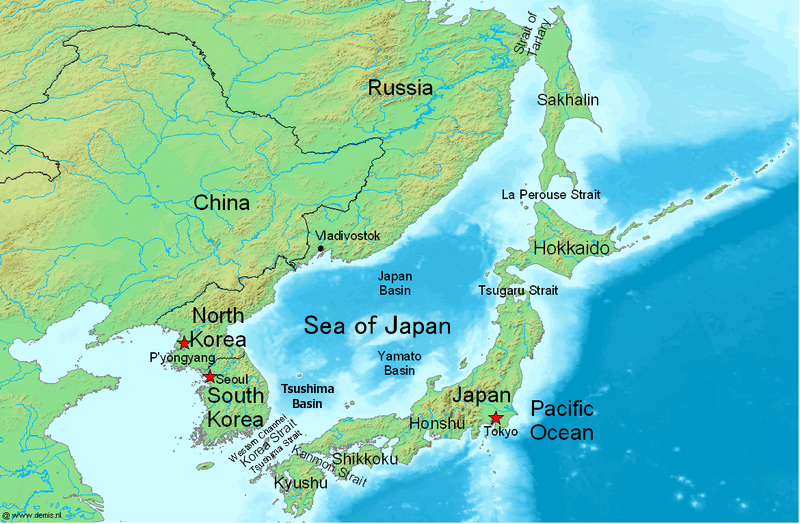
Sea Of Japan
The Sea of Japan is the marginal sea between the Japanese archipelago, Sakhalin, the Korean Peninsula, and the mainland of the Russian Far East. The Japanese archipelago separates the sea from the Pacific Ocean. Like the Mediterranean Sea, it has almost no tides due to its nearly complete enclosure from the Pacific Ocean. This isolation also affects faunal diversity and salinity, both of which are lower than in the open ocean. The sea has no large islands, bays or capes. Its water balance is mostly determined by the inflow and outflow through the straits connecting it to the neighboring seas and the Pacific Ocean. Few rivers discharge into the sea and their total contribution to the water exchange is within 1%. The seawater has an elevated concentration of dissolved oxygen that results in high biological productivity. Therefore, fishing is the dominant economic activity in the region. The intensity of shipments across the sea has been moderate owing to political issues, but it ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Extratropical Cyclone
Extratropical cyclones, sometimes called mid-latitude cyclones or wave cyclones, are low-pressure areas which, along with the anticyclones of high-pressure areas, drive the weather over much of the Earth. Extratropical cyclones are capable of producing anything from cloudiness and mild showers to severe gales, thunderstorms, blizzards, and tornadoes. These types of cyclones are defined as large scale (synoptic) low pressure weather systems that occur in the middle latitudes of the Earth. In contrast with tropical cyclones, extratropical cyclones produce rapid changes in temperature and dew point along broad lines, called weather fronts, about the center of the cyclone. Terminology The term " cyclone" applies to numerous types of low pressure areas, one of which is the extratropical cyclone. The descriptor ''extratropical'' signifies that this type of cyclone generally occurs outside the tropics and in the middle latitudes of Earth between 30° and 60° latitude. They are term ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Barometric Pressure
Atmospheric pressure, also known as barometric pressure (after the barometer), is the pressure within the atmosphere of Earth. The standard atmosphere (symbol: atm) is a unit of pressure defined as , which is equivalent to 1013.25 millibars, 760mm Hg, 29.9212 inchesHg, or 14.696psi.International Civil Aviation Organization. ''Manual of the ICAO Standard Atmosphere'', Doc 7488-CD, Third Edition, 1993. . The atm unit is roughly equivalent to the mean sea-level atmospheric pressure on Earth; that is, the Earth's atmospheric pressure at sea level is approximately 1 atm. In most circumstances, atmospheric pressure is closely approximated by the hydrostatic pressure caused by the weight of air above the measurement point. As elevation increases, there is less overlying atmospheric mass, so atmospheric pressure decreases with increasing elevation. Because the atmosphere is thin relative to the Earth's radius—especially the dense atmospheric layer at low altitudes—the Earth's gravi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rapid Deepening
In meteorology, rapid intensification is a situation where a tropical cyclone intensifies dramatically in a short period of time. The United States National Hurricane Center defines rapid intensification as an increase in the maximum sustained winds of a tropical cyclone of at least in a 24-hour period. Necessary conditions External In order for rapid intensification to occur, several conditions must be in place. Water temperatures must be extremely warm (near or above ), and water of this temperature must be sufficiently deep such that waves do not churn deeper cooler waters up to the surface. Wind shear must be low; when wind shear is high, the convection and circulation in the cyclone will be disrupted. Dry air can also limit the strengthening of tropical cyclones. Internal Usually, an anticyclone in the upper layers of the troposphere above the storm must also be present for extremely low surface pressures to develop. This is because air must be converging towards the low ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |