|
Typhoon Halola
Typhoon Halola, known in the Philippines as Typhoon Goring, was a small but long-lived tropical cyclone in July 2015 that traveled across the Pacific Ocean. The fifth named storm of the 2015 Pacific hurricane season, Halola originated from a Western Pacific monsoon trough that had expanded into the Central Pacific by July 5. Over the next several days, the system waxed and waned due to changes in wind shear before organizing into a tropical depression on July 10 while well southwest of Hawaii. The depression strengthened into Tropical Storm Halola on the next day as it traveled westward. Halola crossed the International Date Line on July 13 and entered the Western Pacific, where it was immediately recognized as a severe tropical storm. The storm further strengthened into a typhoon over the next day before encountering strong wind shear on July 16, upon which it quickly weakened into a tropical depression as it passed south of Wake Island. However, the she ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wake Island
Wake Island ( mh, Ānen Kio, translation=island of the kio flower; also known as Wake Atoll) is a coral atoll in the western Pacific Ocean in the northeastern area of the Micronesia subregion, east of Guam, west of Honolulu, southeast of Tokyo and north of Majuro. The island is an unorganized, unincorporated territory belonging to (but not a part of) the United States that is also claimed by the Republic of the Marshall Islands. Wake Island is one of the most isolated islands in the world. The nearest inhabited island is Utirik Atoll in the Marshall Islands, to the southeast. The United States took possession of Wake Island in 1899. One of 14 U.S. insular areas, Wake Island is administered by the United States Air Force under an agreement with the U.S. Department of the Interior. The center of activity on the atoll is at Wake Island Airfield, which is primarily used as a mid-Pacific refueling stop for military aircraft and as an emergency landing area. The runway is the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
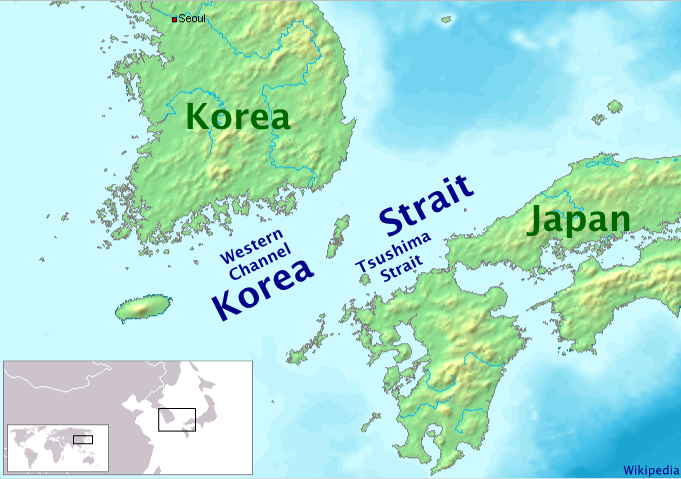
Tsushima Strait
or Eastern Channel (동수로 Dongsuro) is a channel of the Korea Strait, which lies between Korea and Japan, connecting the Sea of Japan, the Yellow Sea, and the East China Sea. The strait is the channel to the east and southeast of Tsushima Island, with the Japanese islands of Honshu to the east and northeast, and Kyushu and the Gotō Islands to the south and southeast. It is narrowest south-east of Shimono-shima, the south end of Tsushima Island proper, constricted there by nearby Iki Island, which lies wholly in the strait near the tip of Honshu. South of that point Japan's Inland Sea mingles its waters through the narrow Kanmon Strait between Honshu and Kyushu, with those of the Eastern Channel, making for some of the busiest sea lanes in the world. The Strait was the site of the decisive naval battle in the Russo-Japanese War, the Battle of Tsushima, between the Japanese and Russian navies in 1905; in which the Russian fleet was virtually destroyed.100 Battles, ''Decisi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Japan Meteorological Agency
The , abbreviated JMA, is an agency of the Ministry of Land, Infrastructure, Transport and Tourism. It is charged with gathering and providing results for the public in Japan that are obtained from data based on daily scientific observation and research into natural phenomena in the fields of meteorology, hydrology, seismology and volcanology, among other related scientific fields. Its headquarters is located in Minato, Tokyo. JMA is responsible for gathering and reporting weather data and forecasts for the general public, as well as providing aviation and marine weather. JMA other responsibilities include issuing warnings for volcanic eruptions, and the nationwide issuance of earthquake warnings of the Earthquake Early Warning (EEW) system. JMA is also designated one of the Regional Specialized Meteorological Centers of the World Meteorological Organization (WMO). It is responsible for forecasting, naming, and distributing warnings for tropical cyclones in the Northwestern ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
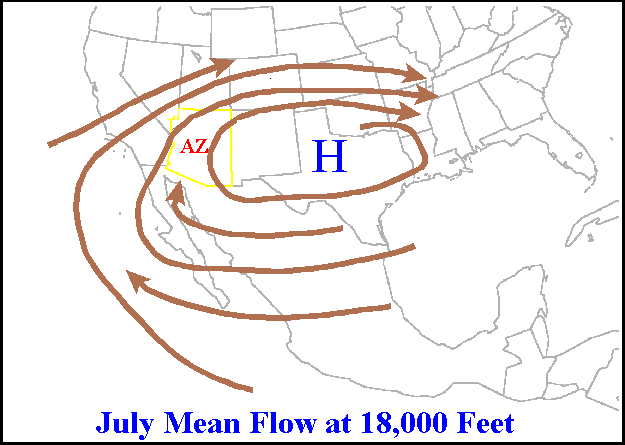
Trough (meteorology)
A trough is an elongated region of relatively low atmospheric pressure without a closed isobaric contour that would define it as a low pressure area. Since low pressure implies a low height on a pressure surface, troughs and ridges refer to features in an identical sense as those on a topographic map. Troughs may be at the surface, or aloft. Near-surface troughs sometimes mark a weather front associated with clouds, showers, and a wind direction shift. Upper-level troughs in the jet stream (as shown in diagram) reflect cyclonic filaments of vorticity. Their motion induces upper-level wind divergence, lifting and cooling the air ahead (downstream) of the trough and helping to produce cloudy and rain conditions there. Unlike fronts, there is not a universal symbol for a trough on a surface weather analysis chart. The weather charts in some countries or regions mark troughs by a line. In the United States, a trough may be marked as a dashed line or bold line. In the UK, Hong Kong ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ridge (meteorology)
A ridge or barometric ridge is a term in meteorology describing an elongated area of relatively high atmospheric pressure compared to the surrounding environment, without being a closed circulation. It is associated with an area of maximum anticyclonic curvature of wind flow. The ridge originates in the center of an anticyclone and sandwiched between two low-pressure areas, and the locus of the maximum curvature is called the ''ridge line''. This phenomenon is the opposite of a trough. Description Ridges can be represented in two ways: * On surface weather maps, the pressure isobars form contours where the maximum pressure is found along the axis of the ridge. * In upper-air maps, geopotential height isohypses form similar contours where the maximum defines the ridge. Related weather Given the direction of the winds around an anticyclonic circulation and the fact that weather systems move from west to east: *ahead of an upper-ridge, the airflow that comes from the polar regi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Central Pacific Hurricane Center
The Central Pacific Hurricane Center (CPHC) of the United States National Weather Service is the official body responsible for tracking and issuing tropical cyclone warnings, watches, advisories, discussions, and statements for the Central Pacific region: from the equator northward, 140°W–180°W, most significantly for Hawai‘i. It is the Regional Specialized Meteorological Center (RSMC) for tropical cyclones in this region, and in this capacity is known as RSMC Honolulu. Based in Honolulu, Hawaii, the CPHC is co-located with the National Weather Service's Honolulu forecast office on the campus of the University of Hawaii at Mānoa. The Honolulu forecast office activates the CPHC when tropical cyclones form in, or move into, the Central Pacific region. The CPHC replaced the previous forecaster, the Joint Hurricane Warning Center, starting in the 1970 season. Area of responsibility The CPHC's area of responsibility is the Central Pacific (CP) region, which is an administra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Honolulu, Hawaii
Honolulu (; ) is the capital and largest city of the U.S. state of Hawaii, which is in the Pacific Ocean. It is an unincorporated county seat of the consolidated City and County of Honolulu, situated along the southeast coast of the island of Oahu, and is the westernmost and southernmost major U.S. city. Honolulu is Hawaii's main gateway to the world. It is also a major hub for business, finance, hospitality, and military defense in both the state and Oceania. The city is characterized by a mix of various Asian, Western, and Pacific cultures, reflected in its diverse demography, cuisine, and traditions. ''Honolulu'' means "sheltered harbor" or "calm port" in Hawaiian; its old name, ''Kou'', roughly encompasses the area from Nuuanu Avenue to Alakea Street and from Hotel Street to Queen Street, which is the heart of the present downtown district. The city's desirability as a port accounts for its historical growth and importance in the Hawaiian archipelago and the broader Pa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coordinated Universal Time
Coordinated Universal Time or UTC is the primary time standard by which the world regulates clocks and time. It is within about one second of mean solar time (such as UT1) at 0° longitude (at the IERS Reference Meridian as the currently used prime meridian) and is not adjusted for daylight saving time. It is effectively a successor to Greenwich Mean Time (GMT). The coordination of time and frequency transmissions around the world began on 1 January 1960. UTC was first officially adopted as CCIR Recommendation 374, ''Standard-Frequency and Time-Signal Emissions'', in 1963, but the official abbreviation of UTC and the official English name of Coordinated Universal Time (along with the French equivalent) were not adopted until 1967. The system has been adjusted several times, including a brief period during which the time-coordination radio signals broadcast both UTC and "Stepped Atomic Time (SAT)" before a new UTC was adopted in 1970 and implemented in 1972. This change also a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anticyclone
An anticyclone is a weather phenomenon defined as a large-scale circulation of winds around a central region of high atmospheric pressure, clockwise in the Northern Hemisphere and counterclockwise in the Southern Hemisphere as viewed from above (opposite to a cyclone). Effects of surface-based anticyclones include clearing skies as well as cooler, drier air. Fog can also form overnight within a region of higher pressure. Mid-tropospheric systems, such as the subtropical ridge, deflect tropical cyclones around their periphery and cause a temperature inversion inhibiting free convection near their center, building up surface-based haze under their base. Anticyclones aloft can form within warm-core lows such as tropical cyclones, due to descending cool air from the backside of upper troughs such as polar highs, or from large-scale sinking such as a subtropical ridge. The evolution of an anticyclone depends upon variables such as its size, intensity, and extent of moist con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atmospheric Convection
Atmospheric convection is the result of a parcel-environment instability, or temperature difference layer in the atmosphere. Different lapse rates within dry and moist air masses lead to instability. Mixing of air during the day which expands the height of the planetary boundary layer leads to increased winds, cumulus cloud development, and decreased surface dew points. Moist convection leads to thunderstorm development, which is often responsible for severe weather throughout the world. Special threats from thunderstorms include hail, downbursts, and tornadoes. Overview There are a few general archetypes of atmospheric instability that are used to explain convection (or lack thereof). A necessary (but not sufficient) condition for convection is that the environmental lapse rate (the rate of decrease of temperature with height) is steeper than the lapse rate experienced by a rising parcel of air. When this condition is met, upward-displaced air parcels can become buoyant and th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Japanese Yen
The is the official currency of Japan. It is the third-most traded currency in the foreign exchange market, after the United States dollar (US$) and the euro. It is also widely used as a third reserve currency after the US dollar and the euro. The New Currency Act of 1871 introduced Japan's modern currency system, with the yen defined as of gold, or of silver, and divided decimally into 100 ''sen'' or 1,000 ''rin''. The yen replaced the previous Tokugawa coinage as well as the various ''hansatsu'' paper currencies issued by feudal ''han'' (fiefs). The Bank of Japan was founded in 1882 and given a monopoly on controlling the money supply. Following World War II, the yen lost much of its prewar value. To stabilize the Japanese economy, the exchange rate of the yen was fixed at ¥360 per US$ as part of the Bretton Woods system. When that system was abandoned in 1971, the yen became undervalued and was allowed to float. The yen had appreciated to a peak of ¥271 per US$ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saccharum Officinarum
''Saccharum officinarum'' is a large, strong-growing species of grass in the genus ''Saccharum''. Its stout stalks are rich in sucrose, a simple sugar which accumulates in the stalk internodes. It originated in New Guinea, and is now cultivated in tropical and subtropical countries worldwide for the production of sugar, ethanol and other products. ''Saccharum officinarum'' is one of the most productive and most intensively cultivated kinds of sugarcane. It can interbreed with other sugarcane species, such as ''Saccharum sinense'' and ''Saccharum barberi''. The major commercial cultivars are complex hybrids. About 70% of the sugar produced worldwide comes from ''S. officinarum'' and hybrids using this species. Description ''Saccharum officinarum'', a perennial plant, grows in clumps consisting of a number of strong unbranched stems. A network of rhizomes forms under the soil which sends up secondary shoots near the parent plant. The stems vary in colour, being green, pinki ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |