|
Types Of Earthquake
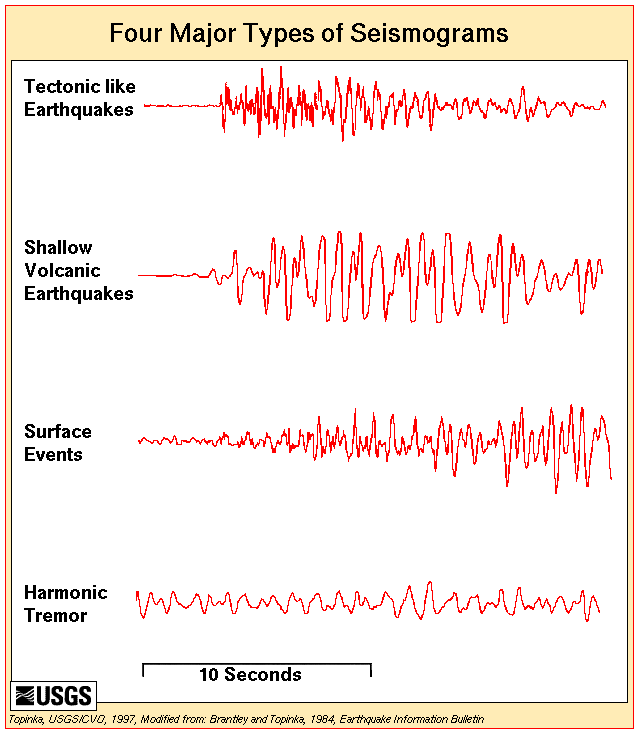
This is a list of different types of earthquake. A * Aftershock, a smaller earthquake that occurs ''after'' a previous large earthquake, in the same area of the main shock B * Blind thrust earthquake, an earthquake which occurs along a thrust fault that does not show signs on the Earth's surface. C * Cryoseism, a seismic event that may be caused by a sudden cracking action in frozen soil or rock saturated with water or ice D * Deep-focus earthquake, also called a plutonic earthquake, an earthquake with a hypocenter depth exceeding * E * Earthquake swarm, events where a local area experiences sequences of many earthquakes striking in a relatively short period of time F * Foreshock, an earthquake that occurs ''before'' a larger seismic event (the mainshock) and is related to it in both time and space H * Harmonic tremor, a sustained release of seismic and infrasonic energy typically associated with the underground movement of magma, the venting of volcanic gas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aftershock
In seismology, an aftershock is a smaller earthquake that follows a larger earthquake, in the same area of the main shock, caused as the displaced crust adjusts to the effects of the main shock. Large earthquakes can have hundreds to thousands of instrumentally detectable aftershocks, which steadily decrease in magnitude and frequency according to a consistent pattern. In some earthquakes the main rupture happens in two or more steps, resulting in multiple main shocks. These are known as doublet earthquakes, and in general can be distinguished from aftershocks in having similar magnitudes and nearly identical seismic waveforms. Distribution of aftershocks Most aftershocks are located over the full area of fault rupture and either occur along the fault plane itself or along other faults within the volume affected by the strain associated with the main shock. Typically, aftershocks are found up to a distance equal to the rupture length away from the fault plane. The pattern ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Megathrust Earthquake
Megathrust earthquakes occur at convergent plate boundaries, where one tectonic plate is forced underneath another. The earthquakes are caused by slip along the thrust fault that forms the contact between the two plates. These interplate earthquakes are the planet's most powerful, with moment magnitudes (''Mw'') that can exceed 9.0. Since 1900, all earthquakes of magnitude 9.0 or greater have been megathrust earthquakes. The thrust faults responsible for megathrust earthquakes often lie at the bottom of oceanic trenches; in such cases, the earthquakes can abruptly displace the sea floor over a large area. As a result, megathrust earthquakes often generate tsunamis that are considerably more destructive than the earthquakes themselves. Teletsunamis can cross ocean basins to devastate areas far from the original earthquake. Terminology and mechanism The term ''megathrust'' refers to an extremely large thrust fault, typically formed at the plate interface along a subduction zone ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Types Of Earthquake
This is a list of different types of earthquake. A * Aftershock, a smaller earthquake that occurs ''after'' a previous large earthquake, in the same area of the main shock B * Blind thrust earthquake, an earthquake which occurs along a thrust fault that does not show signs on the Earth's surface. C * Cryoseism, a seismic event that may be caused by a sudden cracking action in frozen soil or rock saturated with water or ice D * Deep-focus earthquake, also called a plutonic earthquake, an earthquake with a hypocenter depth exceeding * E * Earthquake swarm, events where a local area experiences sequences of many earthquakes striking in a relatively short period of time F * Foreshock, an earthquake that occurs ''before'' a larger seismic event (the mainshock) and is related to it in both time and space H * Harmonic tremor, a sustained release of seismic and infrasonic energy typically associated with the underground movement of magma, the venting of volcanic gas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Volcano Tectonic Earthquake
A volcano tectonic earthquake is caused by the movement of magma beneath the surface of the Earth. The movement results in pressure changes where the rock around the magma has experienced stress. At some point, this stress can cause the rock to break or move. This seismic activity is used by scientists to monitor volcanoes. The earthquakes may also be related to dike intrusion or occur as earthquake swarms. Cause of volcano tectonic earthquakes One possible scenario resulting in a possible volcano tectonic earthquake is tectonic subduction zones. The compression of plates at these subduction zones forces the magma beneath them to move. Magma can not move through the newly compressed crust in as easily a manner. This means it tends to pool in magma chambers beneath the surface and between the converging tectonic plates. Many of the famous and most well known volcanoes fall on this line, including the Ring of Fire. As the plates move, magma underground may be forced in and out ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tsunami Earthquake
In seismology, a tsunami earthquake is an earthquake which triggers a tsunami of significantly greater magnitude, as measured by shorter-period seismic waves. The term was introduced by Japanese seismologist Hiroo Kanamori in 1972. Such events are a result of relatively slow rupture velocities. They are particularly dangerous as a large tsunami may arrive at a coastline with little or no warning. Characteristics The distinguishing feature for a tsunami earthquake is that the release of seismic energy occurs at long periods (low frequencies) relative to typical tsunamigenic earthquakes. Earthquakes of this type do not generally show the peaks of seismic wave activity associated with ordinary events. A tsunami earthquake can be defined as an undersea earthquake for which the surface wave magnitude Ms differs markedly from the moment magnitude Mw, because the former is calculated from surface waves with a period of about 20 seconds, whereas the latter is a measure of the total ene ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Strike-slip Earthquake
In geology, a fault is a planar fracture or discontinuity in a volume of rock across which there has been significant displacement as a result of rock-mass movements. Large faults within Earth's crust result from the action of plate tectonic forces, with the largest forming the boundaries between the plates, such as the megathrust faults of subduction zones or transform faults. Energy release associated with rapid movement on active faults is the cause of most earthquakes. Faults may also displace slowly, by aseismic creep. A ''fault plane'' is the plane that represents the fracture surface of a fault. A ''fault trace'' or ''fault line'' is a place where the fault can be seen or mapped on the surface. A fault trace is also the line commonly plotted on geologic maps to represent a fault. A ''fault zone'' is a cluster of parallel faults. However, the term is also used for the zone of crushed rock along a single fault. Prolonged motion along closely spaced faults can blur the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Supershear Earthquake
In seismology, a supershear earthquake is an earthquake in which the propagation of the rupture along the fault surface occurs at speeds in excess of the seismic shear wave (S-wave) velocity. This causes an effect analogous to a sonic boom. Rupture propagation velocity During seismic events along a fault surface the displacement initiates at the focus and then propagates outwards. Typically for large earthquakes the focus lies towards one end of the slip surface and much of the propagation is unidirectional (e.g. the 2008 Sichuan and 2004 Indian Ocean earthquakes). Theoretical studies have in the past suggested that the upper bound for propagation velocity is that of Rayleigh waves, approximately 0.92 of the shear wave velocity. However, evidence of propagation at velocities between S-wave and compressional wave (P-wave) values have been reported for several earthquakesArchuleta,R.J. 1984A faulting model for the 1979 Imperial Valley earthquake J. Geophys. Res., 89, 4559–4585. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Submarine Earthquake
A submarine, undersea, or underwater earthquake is an earthquake that occurs underwater at the bottom of a body of water, especially an ocean. They are the leading cause of tsunamis. The magnitude can be measured scientifically by the use of the moment magnitude scale and the intensity can be assigned using the Mercalli intensity scale. Understanding plate tectonics helps to explain the cause of submarine earthquakes. The Earth's surface or lithosphere comprises tectonic plates which average approximately 50 miles in thickness, and are continuously moving very slowly upon a bed of magma in the asthenosphere and inner mantle. The plates converge upon one another, and one subducts below the other, or, where there is only shear stress, move horizontally past each other (see transform plate boundary below). Little movements called fault creep are minor and not measurable. The plates meet with each other, and if rough spots cause the movement to stop at the edges, the motion of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Slow Earthquake
A slow earthquake is a discontinuous, earthquake-like event that releases energy over a period of hours to months, rather than the seconds to minutes characteristic of a typical earthquake. First detected using long term strain measurements, most slow earthquakes now appear to be accompanied by fluid flow and related tremor, which can be detected and approximately located using seismometer data filtered appropriately (typically in the 1–5 Hz band). That is, they are quiet compared to a regular earthquake, but not "silent" as described in the past. Slow earthquakes should not be confused with tsunami earthquakes, in which relatively slow rupture velocity produces tsunami out of proportion to the triggering earthquake. In a tsunami earthquake, the rupture propagates along the fault more slowly than usual, but the energy release occurs on a similar timescale to other earthquakes. __TOC__ Causes Earthquakes occur as a consequence of gradual stress increases in a region, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Remotely Triggered Earthquakes
Remotely triggered earthquakes are a result of the effects of large earthquakes at considerable distance, outside of the immediate aftershock zone. The farther one gets from the initiating earthquake in both space and time, the more difficult it is to establish an association. The physics of triggering an earthquake are complex. Most earthquake-generating zones are in a state of being close to failure. If such a zone were to be left completely alone, it would generate significant earthquakes spontaneously. Remote earthquakes, however, are in a position to disturb this critical state, either by shifting the stresses statically, or by dynamic change caused by passing seismic waves. The first type of triggering may be due to static changes in the critical state. For example, after the magnitude 7.3 Landers earthquake struck California in 1992, it is said that "the earthquake map of California lit up like a Christmas tree". This event reinforced the idea of remotely triggered earthqua ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intraplate Earthquake
The term intraplate earthquake refers to a variety of earthquake that occurs ''within the interior'' of a tectonic plate; this stands in contrast to an interplate earthquake, which occurs ''at the boundary'' of a tectonic plate. Intraplate earthquakes are often called "intraslab earthquakes", especially when occurring in microplates. Intraplate earthquakes are relatively rare compared to the more familiar boundary-located interplate earthquakes. Structures far from plate boundaries tend to lack seismic retrofitting, so large intraplate earthquakes can inflict heavy damage. Examples of damaging intraplate earthquakes are the devastating Gujarat earthquake in 2001, the 2012 Indian Ocean earthquakes, the 2017 Puebla earthquake, the 1811–1812 earthquakes in New Madrid, Missouri, and the 1886 earthquake in Charleston, South Carolina. Fault zones within tectonic plates The surface of the Earth is made up of seven primary and eight secondary tectonic plates, plus dozens of terti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
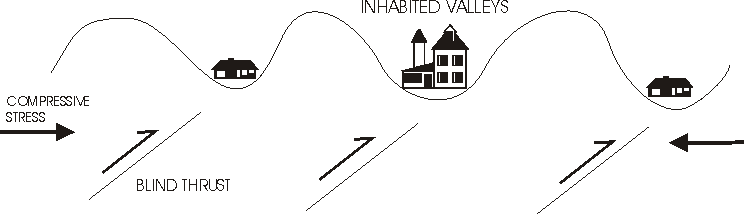
Blind Thrust Earthquake
A blind thrust earthquake occurs along a thrust fault that does not show signs on the Earth's surface, hence the designation "blind". Such faults, being invisible at the surface, have not been mapped by standard surface geological mapping. Sometimes they are discovered as a by-product of oil exploration seismology; in other cases their existence is not suspected. Although such earthquakes are not amongst the most energetic, they are sometimes the most destructive, as conditions combine to form an urban earthquake which greatly affects urban seismic risk. A blind thrust earthquake is quite close, in meaning, to a buried rupture earthquake, if a buried rupture earthquake is not specifically about the fault, but signs the earthquake leaves, on the Earth's surface. Blind thrust faults Blind thrust faults generally exist near tectonic plate margins, in the broad disturbance zone. They form when a section of the Earth's crust is under high compressive stresses, due to plate margin col ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |