|
Two Foot Gauge Railways In South Africa
In the early 1900s, narrow-gauge railway lines started playing a significant role in South Africa. They facilitated the transport of various agricultural and mineral produce from locations hardly accessible by road. They therefore enabled many communities to become prosperous. These lines featured the largest and most powerful locomotives ever in existence on two-foot-gauge railways worldwide. All two-foot railways were operated isolated from each other. However, this did not prevent standardization and interchangeability of rolling stock and locomotives. The larger railway lines operated their own workshops performing minor to major maintenance and/or repairs. For the purpose of major overhauls and interchangeability, rolling stock could be transported piggyback on Cape gauge rolling stock by means of a special access ramp on the break of gauge at Cape gauge junctions available on most of the two-foot lines. Their decline started in the 1980s, the last commercial line cease ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CGR NG 4-6-2T 1908
The Cape Government Railways NG 4-6-2T of 1908 was a South African narrow-gauge steam locomotive from the pre-Union era in the Cape of Good Hope. In 1908, the Cape Government Railways placed two Pacific type narrow-gauge steam locomotives in passenger service on the Walmer branch in Port Elizabeth. In 1912, both locomotives were assimilated into the South African Railways and renumbered.Classification of S.A.R. Engines with Renumbering Lists, issued by the Chief Mechanical Engineer’s Office, Pretoria, January 1912, p. 47 (Reprinted in April 1987 by SATS Museum, R.3125-6/9/11-1000)Espitalier, T.J.; Day, W.A.J. (1944). ''The Locomotive in South Africa - A Brief History of Railway Development. Chapter II - The Cape Government Railways'' (Continued). South African Railways and Harbours Magazine, April 1944. pp. 253-257. Manufacturer Two narrow-gauge steam locomotives were built for the Cape Government Railways (CGR) by W.G. Bagnall in 1908. The engines were equally powerfu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
South African Railways
Transnet Freight Rail is a South African rail transport company, formerly known as Spoornet. It was part of the South African Railways and Harbours Administration, a state-controlled organisation that employed hundreds of thousands of people for decades from the first half of the 20th century and was widely referred to by the initials SAR&H (SAS&H in Afrikaans). Customer complaints about serious problems with Transnet Freight Rail's service were reported in 2010. Its head office is in Inyanda House in Parktown, Johannesburg. History Railways were first developed in the area surrounding Cape Town and later in Durban around the 1840s. The first line opened in Durban on 27 June 1850. The initial network was created to serve the agricultural production area between Cape Town and Wellington. The news that there were gold deposits in the Transvaal Republic moved the Cape Colony Government (supported by British Government) to link Kimberley as soon as possible by rail to Cape Town ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
South African Class 91-000
The South African Railways Class of 1973 was a narrow-gauge diesel–electric locomotive. Between September and December 1973, the South African Railways placed 20 Class General Electric type UM6B diesel–electric locomotives in service on its narrow-gauge Avontuur Railway between Port Elizabeth in the Eastern Cape and Avontuur in the Western Cape. Some of them later also worked on the Alfred County Railway out of Port Shepstone in KwaZulu-Natal.South African Railways Index and Diagrams Electric and Diesel Locomotives, 610 mm and 1065 mm Gauges, Ref LXD 14/1/100/20, 28 January 1975, as amendedSoul of A Railway, System 3, Part 1: Cape Midland, based in Port Elizabeth, Part 1, The Port ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
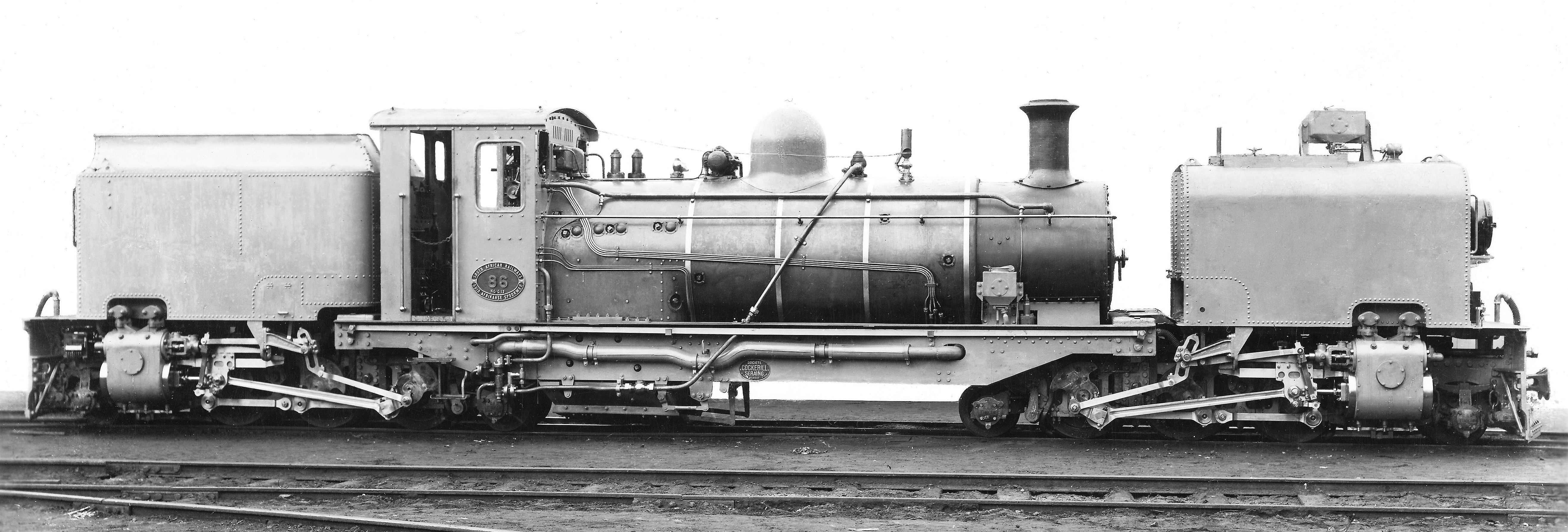
South African Class NG G16 2-6-2+2-6-2
The South African Railways Class NG G16 2-6-2+2-6-2 was a narrow gauge steam locomotive. Between 1937 and 1968, the South African Railways placed 34 Class NG G16 Garratt articulated steam locomotives in service on the Avontuur Railway and on the Natal narrow gauge lines. Manufacturers The success of the Class NG G13 narrow gauge Garratts that were introduced by the South African Railways (SAR) in 1927 led to a decision that any additional narrow gauge articulated locomotives would be of the same design. Altogether 34 more Double Prairie type narrow gauge locomotives were built, spread over five orders from three manufacturers over a span of 32 years.South African Railways and Harbours Locomotive Diagram Book, 2'0" & 3'6" Gauge Steam Locomotives, 15 August 1941, as amended Cockerill In 1937, Société Anonyme John Cockerill of Seraing in Belgium delivered four new locomotives, numbered in the range from NG85 to NG88, which were so similar to the older locomotives tha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
South African Class NG15 2-8-2
The South African Railways Class NG15 2-8-2 is a class of narrow-gauge steam locomotive. In 1931, three narrow-gauge Class NG15 locomotives with a Mikado type wheel arrangement, similar in design to the existing Class Hd and Class NG5 locomotives, were acquired by the South African Railways for the Otavi Mining and Railway Company in South West Africa. More were purchased for the Otavi Railway and the Tsumeb Copper Corporation during the subsequent years, eventually bringing the total number of these locomotives to 21 by 1958.Espitalier, T.J.; Day, W.A.J. (1947). ''The Locomotive in South Africa - A Brief History of Railway Development. Chapter VII - South African Railways (Continued).'' South African Railways and Harbours Magazine, December 1947. pp. 1033-1034. When the narrow-gauge Otavi Railway was regauged to Cape gauge in 1960, all 21 locomotives were taken over by the South African Railways. They were transferred to the Eastern Cape for further service on the narrow-gauge ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
South African Class NG G14 2-6-2+2-6-2
The South African Railways Class NG G14 2-6-2+2-6-2 of 1931 was an articulated narrow gauge steam locomotive. In 1931, the South African Railways (SAR) placed a single lightweight Class Garratt articulated steam locomotive with a Double Prairie type wheel arrangement in service.Espitalier, T.J.; Day, W.A.J. (1946). ''The Locomotive in South Africa - A Brief History of Railway Development. Chapter VII - South African Railways (Continued).'' South African Railways and Harbours Magazine, February 1946. p. 135. Manufacturer A single narrow gauge Garratt locomotive was built for the South African Railways by Hannoversche Maschinenbau AG (Hanomag) in 1930. It was very similar to, but slightly larger and heavier than the Class NG G12 of 1927, the smallest Garratt to ever enter service on the SAR. Upon delivery, it was designated Class NG G14 and numbered NG84.South African Railways and Harbours Locomotive Diagram Book, 2'0" & 3'6" Gauge Steam Locomotives, 15 August 1941, as amended ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
South African Class NG G13 2-6-2+2-6-2
South is one of the cardinal directions or compass points. The direction is the opposite of north and is perpendicular to both east and west. Etymology The word ''south'' comes from Old English ''sūþ'', from earlier Proto-Germanic ''*sunþaz'' ("south"), possibly related to the same Proto-Indo-European root that the word ''sun'' derived from. Some languages describe south in the same way, from the fact that it is the direction of the sun at noon (in the Northern Hemisphere), like Latin meridies 'noon, south' (from medius 'middle' + dies 'day', cf English meridional), while others describe south as the right-hand side of the rising sun, like Biblical Hebrew תֵּימָן teiman 'south' from יָמִין yamin 'right', Aramaic תַּימנַא taymna from יָמִין yamin 'right' and Syriac ܬܰܝܡܢܳܐ taymna from ܝܰܡܝܺܢܳܐ yamina (hence the name of Yemen, the land to the south/right of the Levant). Navigation By convention, the ''bottom or down-facing side'' of a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
South African Class NG G12 2-6-2+2-6-2
South is one of the cardinal directions or compass points. The direction is the opposite of north and is perpendicular to both east and west. Etymology The word ''south'' comes from Old English ''sūþ'', from earlier Proto-Germanic ''*sunþaz'' ("south"), possibly related to the same Proto-Indo-European root that the word ''sun'' derived from. Some languages describe south in the same way, from the fact that it is the direction of the sun at noon (in the Northern Hemisphere), like Latin meridies 'noon, south' (from medius 'middle' + dies 'day', cf English meridional), while others describe south as the right-hand side of the rising sun, like Biblical Hebrew תֵּימָן teiman 'south' from יָמִין yamin 'right', Aramaic תַּימנַא taymna from יָמִין yamin 'right' and Syriac ܬܰܝܡܢܳܐ taymna from ܝܰܡܝܺܢܳܐ yamina (hence the name of Yemen, the land to the south/right of the Levant). Navigation By convention, the ''bottom or down-facing side'' of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
South African Class NG G11 2-6-0+0-6-2
The South African Railways Class NG G11 2-6-0+0-6-2 of 1919 was a narrow gauge steam locomotive. Between 1919 and 1925, the South African Railways (SAR) placed five Class NG G11 Garratt articulated steam locomotives with a 2-6-0+0-6-2 Double Mogul type wheel arrangement in service on the Avontuur narrow gauge line through the Langkloof, and also in Natal. They were the first Garratt locomotives to enter service in South Africa.Espitalier, T.J.; Day, W.A.J. (1945). ''The Locomotive in South Africa - A Brief History of Railway Development. Chapter VII - South African Railways (Continued).'' South African Railways and Harbours Magazine, November 1945. pp. 865-866. Background The challenges of Africa resulted in the regular need for double-heading of steam locomotives on heavy trains. While West Africa found its solution in larger 4-6-2 Pacific and 2-8-2 Mikado locomotives at the beginning of the twentieth century, the steeper gradients and tighter curves in South Africa made a d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
South African Class NG10 4-6-2
The South African Railways Class NG10 4-6-2 of 1916 was a narrow-gauge steam locomotive. In 1916, the South African Railways placed six steam locomotives in service on the Langkloof narrow-gauge line. When a system of grouping narrow-gauge locomotives into classes was eventually introduced somewhere between 1928 and 1930, they were classified as .Espitalier, T.J.; Day, W.A.J. (1945). ''The Locomotive in South Africa – A Brief History of Railway Development. Chapter VII – South African Railways (Continued).'' South African Railways and Harbours Magazine, October 1945. p. 782. Manufacturer During World War I, the usual British locomotive suppliers were hard pressed to satisfy British and foreign requirements. This led to several new locomotive types for the South African Railways (SAR) being ordered from North American builders. In 1915, the SAR placed an order with the Baldwin Locomotive Works in the United States for six narrow-gauge locomotives. They were delivered in 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
South African Class NG9 4-6-0
The South African Railways Class NG9 4-6-0 of 1915 was a narrow-gauge steam locomotive. During 1915 and 1916, the South African Railways placed six steam locomotives in service on the Langkloof narrow-gauge railway. When a system of grouping narrow-gauge locomotives into classes was eventually introduced somewhere between 1928 and 1930, they were classified as Class NG9.Espitalier, T.J.; Day, W.A.J. (1945). ''The Locomotive in South Africa - A Brief History of Railway Development. Chapter VII - South African Railways (Continued).'' South African Railways and Harbours Magazine, October 1945. p. 782. Manufacturer Due to the outbreak of the First World War in 1914, the usual British locomotive suppliers were hard pressed to satisfy British requirements at the time, let alone those of other parts of the world. As a result, the South African Railways (SAR) placed an order with the Baldwin Locomotive Works in the United States of America in 1915 for six narrow-gauge locomotives. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |