|
Turbomixer
A Turbo mixer, also known as a high speed mixer or a tank mixer, is a type of industrial mixer that uses PVC for mixing raw materials to form a free-flowing powder blend. Design It includes a cylindrical tank with a mixing tool assembled on the bottom that typically operates at a peripheral speed of between 20 and 50 m/s, depending on the material to blend. The material is heated inside by a mixer, through the mechanical energy that is produced between the mixing tools and the material which generates mutual impacts of the particles. During the mixing phase, the Turbo-mixer creates an axial vortex. The structure and position of the blades inside the mixer guarantee homogeneous material dispersion. To avoid thermal degradation, it is usually combined with a cooler that cools down the dry blend to the temperature of around 45-55 C. Due to the poor heat conductivity of the cooler, the cooler is usually three times larger than the mixer as the cooling time is proportional ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Industrial Mixer
In industrial process engineering, mixing is a unit operation that involves manipulation of a heterogeneous physical system with the intent to make it more homogeneous. Familiar examples include pumping of the water in a swimming pool to homogenize the water temperature, and the stirring of pancake batter to eliminate lumps (deagglomeration). Mixing is performed to allow heat and/or mass transfer to occur between one or more streams, components or phases. Modern industrial processing almost always involves some form of mixing.Ullmann, Fritz (2005). Ullmann's Chemical Engineering and Plant Design, Volumes 1–2. John Wiley & Sons. http://app.knovel.com/hotlink/toc/id:kpUCEPDV02/ullmanns-chemical-engineering Some classes of chemical reactors are also mixers. With the right equipment, it is possible to mix a solid, liquid or gas into another solid, liquid or gas. A biofuel fermenter may require the mixing of microbes, gases and liquid medium for optimal yield; organic nitration requ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
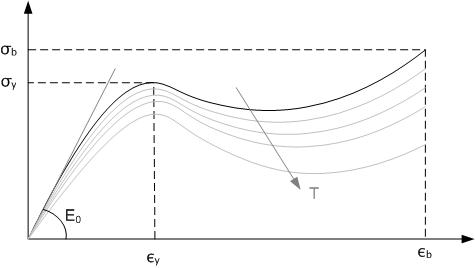
Thermoplastic
A thermoplastic, or thermosoft plastic, is any plastic polymer material that becomes pliable or moldable at a certain elevated temperature and solidifies upon cooling. Most thermoplastics have a high molecular weight. The polymer chains associate by intermolecular forces, which weaken rapidly with increased temperature, yielding a viscous liquid. In this state, thermoplastics may be reshaped and are typically used to produce parts by various polymer processing techniques such as injection molding, compression molding, calendering, and extrusion. Thermoplastics differ from thermosetting polymers (or "thermosets"), which form irreversible chemical bonds during the curing process. Thermosets do not melt when heated, but typically decompose and do not reform upon cooling. Above its glass transition temperature and below its melting point, the physical properties of a thermoplastic change drastically without an associated phase change. Some thermoplastics do not fully crystallize ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |