|
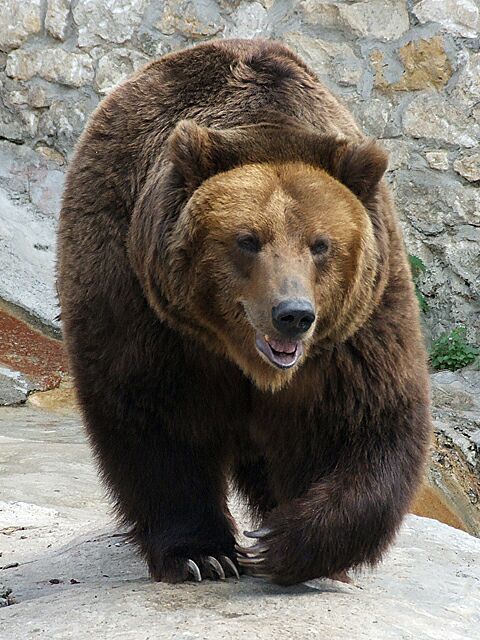
Tundra Wolf
The tundra wolf (''Canis lupus albus''), also known as the Turukhan wolf,Mech, L. David (1981), The Wolf: The Ecology and Behaviour of an Endangered Species', University of Minnesota Press, p. 353, is a subspecies of grey wolf native to Eurasia's tundra and forest-tundra zones from Finland to the Kamchatka Peninsula. It was first described in 1792 by Robert Kerr, who described it as living around the Yenisei, and of having a highly valued pelt.Kerr, R. (1792), The animal kingdom, or zoological system, of the celebrated Sir Charles Linnæus: containing a complete systematic description, arrangement, and nomenclature, of all the known species and varieties of the mammalia, or animals which give suck to their young', Printed for A. Strahan, and T. Cadell, London, and W. Creech, Edinburgh, p. 137 It is a large subspecies, with adult males measuring in body length, and females . Although often written to be larger than '' C. l. lupus'', this is untrue, as heavier members of the lat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Taxidermy
Taxidermy is the art of preserving an animal's body via mounting (over an armature) or stuffing, for the purpose of display or study. Animals are often, but not always, portrayed in a lifelike state. The word ''taxidermy'' describes the process of preserving the animal, but the word is also used to describe the end product, which are called taxidermy mounts or referred to simply as "taxidermy". The word ''taxidermy'' is derived from the Greek words ''taxis'' and ''derma''. ''Taxis'' means "arrangement", and ''derma'' means "skin" (the dermis). The word ''taxidermy'' translates to "arrangement of skin". Taxidermy is practiced primarily on vertebrates (mammals, birds, fish, reptiles, and less commonly on amphibians) but can also be done to larger insects and arachnids under some circumstances. Taxidermy takes on a number of forms and purposes including hunting trophies and natural history museum displays. Museums use taxidermy as a method to record species, including those ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Taymyr Peninsula
The Taymyr Peninsula (russian: Таймырский полуостров, Taymyrsky poluostrov) is a peninsula in the Far North of Russia, in the Siberian Federal District, that forms the northernmost part of the mainland of Eurasia. Administratively it is part of the Krasnoyarsk Krai Federal subject of Russia. Geography The Taymyr Peninsula lies between the Yenisei Gulf of the Kara Sea and the Khatanga Gulf of the Laptev Sea. Lake Taymyr and the Byrranga Mountains are located within the vast Taymyr Peninsula. Cape Chelyuskin, the northernmost point of the Afro-Eurasian continent, is located at the northern end of the Taymyr Peninsula. Population The Nenets people, also known as ''Samoyeds'', are an indigenous people in northern arctic Russia, and some live at the Taymyr Peninsula. The Nganasan people are an indigenous Samoyedic people inhabiting central Siberia, including the Taymyr Peninsula. In the Russian Federation, they are recognized as being one of the Indigenous ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mammals Of The Arctic
Mammals () are a group of vertebrate animals constituting the class Mammalia (), characterized by the presence of mammary glands which in females produce milk for feeding (nursing) their young, a neocortex (a region of the brain), fur or hair, and three middle ear bones. These characteristics distinguish them from reptiles (including birds) from which they diverged in the Carboniferous, over 300 million years ago. Around 6,400 extant species of mammals have been described divided into 29 orders. The largest orders, in terms of number of species, are the rodents, bats, and Eulipotyphla (hedgehogs, moles, shrews, and others). The next three are the Primates (including humans, apes, monkeys, and others), the Artiodactyla (cetaceans and even-toed ungulates), and the Carnivora (cats, dogs, seals, and others). In terms of cladistics, which reflects evolutionary history, mammals are the only living members of the Synapsida (synapsids); this clade, together with Sauropsida ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carnivorans Of Europe
Carnivora is a monophyletic order of placental mammals consisting of the most recent common ancestor of all cat-like and dog-like animals, and all descendants of that ancestor. Members of this group are formally referred to as carnivorans, and have evolved to specialize in eating flesh. The order is the fifth largest order of mammals, comprising at least 279 species. Carnivorans live on every major landmass and in a variety of habitats, ranging from the cold polar regions to the hyper-arid region of the Sahara Desert to the open seas. They come in a very large array of different body plans in contrasting shapes and sizes. Carnivora can be divided into two subclades: the cat-like Feliformia and the dog-like Caniformia, which are differentiated based on the structure of their ear bones and cranial features. The feliforms include families such as the cats, the hyenas, the mongooses and the civets. The majority of feliform species are found in the Old World, though the cats ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mammals Of Russia
This is a list of the mammal species recorded in Russia. There are 266 mammal species in Russia, of which five are critically endangered, thirteen are endangered, twenty-six are vulnerable, and six are near threatened. One of the species listed for Russia is extinct and one can no longer be found in the wild. All the mammals of Russia are in the subclass Theria and infraclass Eutheria, being all placental. The following tags are used to highlight each species' conservation status as assessed by the International Union for Conservation of Nature: Order: Sirenia (manatees and dugongs) Sirenia is an order of fully aquatic, herbivorous mammals that inhabit rivers, estuaries, coastal marine waters, swamps, and marine wetlands. All four species are endangered. *Family: Dugongidae **Genus: ''Hydrodamalis'' *** Steller's sea cow, ''H. gigas'' Order: Rodentia (rodents) Rodents make up the largest order of mammals, with over 40% of mammalian species. They have two incisors in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nenets Autonomous Okrug
The Nenets Autonomous Okrug (russian: Не́нецкий автоно́мный о́круг; Nenets languages, Nenets: Ненёцие автономной ӈокрук, ''Nenjocije awtonomnoj ŋokruk'') is a federal subjects of Russia, federal subject of Russia and an autonomous okrugs of Russia, autonomous okrug of Arkhangelsk Oblast. Its administrative center is the types of inhabited localities in Russia, town of Naryan-Mar. It has an area of and a population of 42,090 as of the Russian Census (2010), 2010 Census, making it the List of federal subjects of Russia by population, least populous federal subject. A plan to merge the autonomous okrug with Arkhangelsk Oblast was presented by the governors of both federal subjects on 13 May 2020, with a referendum planned for September, but was met with opposition by locals, leading to the merger process being scrapped completely. Geography The arctic ecology of this area has a number of unique features derived from the extrem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reindeer
Reindeer (in North American English, known as caribou if wild and ''reindeer'' if domesticated) are deer in the genus ''Rangifer''. For the last few decades, reindeer were assigned to one species, ''Rangifer tarandus'', with about 10 subspecies. A 2022 revision of the genus elevated five of the subspecies to species (see Taxonomy below). They have a circumpolar distribution and are native to the Arctic, sub-Arctic, tundra, boreal forest, and mountainous regions of northern Europe, Siberia, and North America. Reindeer occur in both migratory and sedentary populations, and their herd sizes vary greatly in different regions. The tundra subspecies are adapted for extreme cold, and some are adapted for long-distance migration. Reindeer vary greatly in size and color from the smallest species, the Svalbard reindeer (''R. t. platyrhynchus''), to the largest subspecies, Osborn's caribou (''R. t. osborni''). Although reindeer are quite numerous, some species and subspecies are in d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dudypta River
The Dudypta (russian: Дудыпта) is a river in Krasnoyarsk Krai in Russia, a right tributary of the Pyasina. The river is long, and its drainage basin covers . The Dudypta originates from Lake Makar ( Dudypta Lakes) and flows over the central part of the North Siberian Lowland. The river is navigable for upstream from its estuary. Great Soviet Encyclopedia
The ''Great Soviet Encyclopedia'' (GSE; ) is one of the largest Russian-language encyclopedias, published in the Soviet Union from 1926 to 1990. After 2002, the encyclopedia's data was partially included into the later ''Bolshaya rossiyskaya e ...
References [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
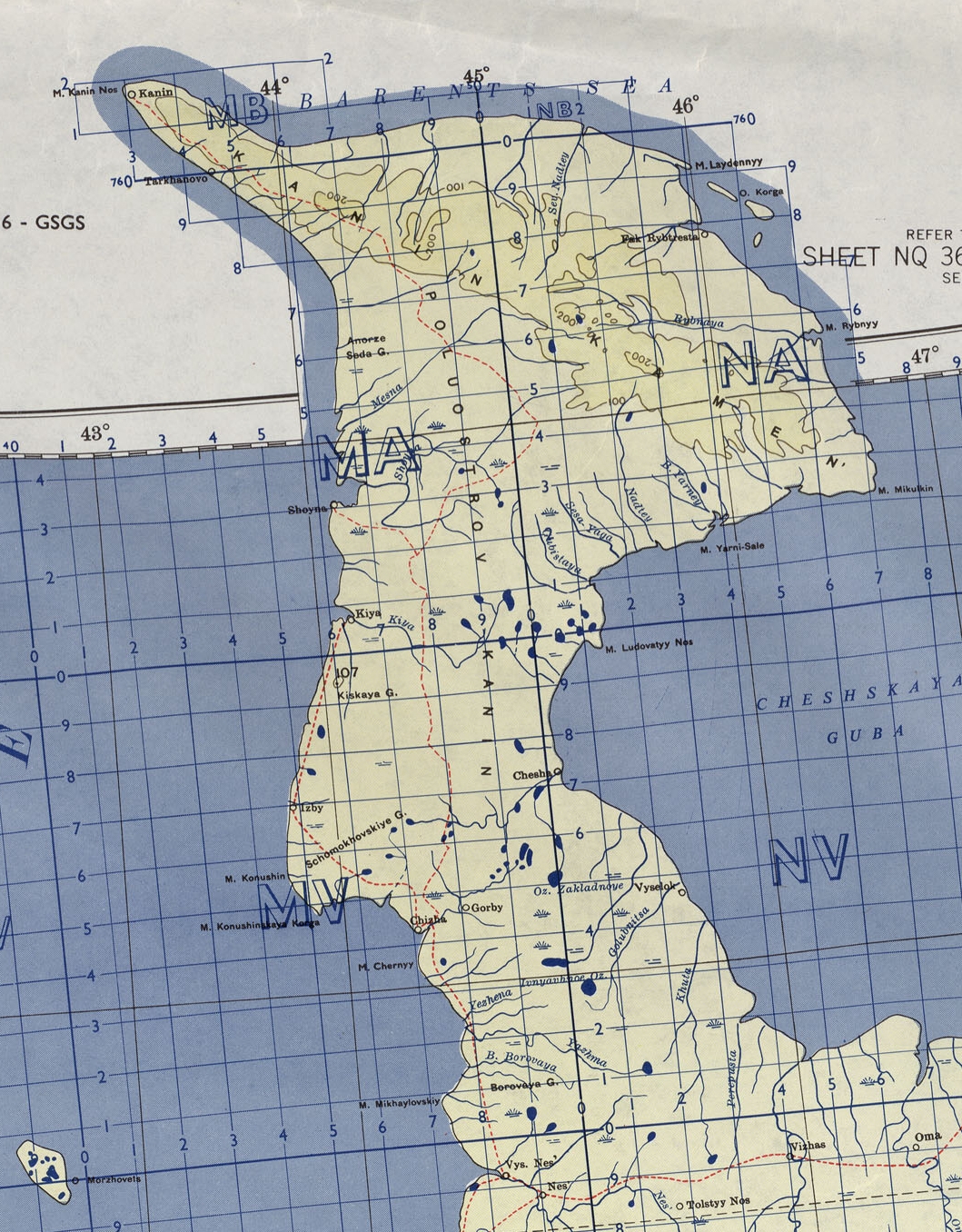
Kanin Peninsula
The Kanin Peninsula () is a large peninsula in Nenets Autonomous Okrug, Russia. It is surrounded by the White Sea to the west and by the Barents Sea to the north and east. Shoyna is one of the few communities on the peninsula. Fauna For cetaceans, beluga whales are most commonly found. Male sperm whales are known to occur as well. Butterflies There are 29 butterfly species in the forest-tundra and 14 species in the hypoarctic tundra. The data on the fauna and distribution of species in the forest-tundra of the Kanin Peninsula are generally typical of this natural zone. The most abundant species are ''Erebia disa'', ''Oeneis norna'', ''Clossiana freija'', ''Pieris napi'', and ''Vacciniina optilete''. The dominant species in southern tundra localities are ''Erebia euryale'', ''Erebia pandrose'', and '' Boloria aquilonaris'', which coincides with the result of the 1903 research. A high abundance of ''E. pandrose'' is a specific feature of the northern part of the Kanin Peninsula an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eurasian Wolf
The Eurasian wolf (''Canis lupus lupus''), also known as the common wolf,Mech, L. David (1981), ''The Wolf: The Ecology and Behaviour of an Endangered Species'', University of Minnesota Press, p. 354, is a subspecies of grey wolf native to Europe and Asia. It was once widespread throughout Eurasia prior to the Middle Ages. Aside from an extensive paleontological record, Indo-European languages typically have several words for "wolf", thus attesting to the animal's abundance and cultural significance.Gamkrelidze, T. V. & Ivanov, V. V. (1995), ''Indo-European and the Indo-Europeans: A Reconstruction and Historical Analysis of a Proto-Language and Proto-Culture'', Walter de Gruyter, pp. 413-417, It was held in high regard in Baltic, Celtic, Slavic, Turkic, ancient Greek, Roman, and Thracian cultures, whilst having an ambivalent reputation in early Germanic cultures. It is the largest of Old World grey wolves, averaging in Europe; however, exceptionally large individuals have w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zoological Museum Of The Zoological Institute Of The Russian Academy Of Sciences
The Zoological Museum of the Zoological Institute of the Russian Academy of Sciences is a Russian museum devoted to zoology. It is located in Saint Petersburg, on Universitetskaya Embankment. It is one of the ten largest nature history museums in the world. Peter the Great's Kunstkamera collections included zoological specimens. In 1724, the museum became a part of the Russian Academy of Sciences. A printed catalogue of the contents was published in 1742. It listed the zoology, botany, geology and anthropology specimens and contained an album of etchings of the building and plan of some of its parts. In 1766, Peter Simon Pallas, a member of the Russian Academy of Sciences, was appointed curator of Zoology. In 1832, the zoological collection was split from the Kunstkamera and, in 1896, moved nearby to its present location in the former southern warehouse of the Saint Petersburg bourse (constructed in 1826-1832). In 1931, the Zoological Institute was established within the Acad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yenisei
The Yenisey (russian: Енисе́й, ''Yeniséy''; mn, Горлог мөрөн, ''Gorlog mörön''; Buryat language, Buryat: Горлог мүрэн, ''Gorlog müren''; Tuvan language, Tuvan: Улуг-Хем, ''Uluğ-Hem''; Khakas language, Khakas: Ким суғ, ''Kim suğ''; Ket language, Ket: Ӄук, ''Quk''; Tundra Nenets language, Nenets: Ензя-ям’, ''Enzja-jam''), also romanised as Yenisei, Enisei, or Jenisej, is the list of rivers by length, fifth-longest river system in the world, and the largest to drain into the Arctic Ocean. Rising in Mungaragiyn-gol in Mongolia, it follows a northerly course before draining into the Yenisey Gulf in the Kara Sea. The Yenisey divides the Western Siberian Plain in the west from the Central Siberian Plateau to the east; it drains a large part of central Siberia. It is the central one of three large Siberian rivers that flow into the Arctic Ocean (the other two being the Ob (river), Ob and the Lena River, Lena). The maximum dept ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)
.jpg)