|
Tuai
Tuai is a village and rural community located around Lake Whakamarino, in the Wairoa District of the Hawke's Bay Region, on New Zealand's North Island. The local Tuai Power Station was opened in 1929 on the shores of Lake Whakamarino, as part of the Waikaremoana power scheme. Genesis Energy has controlled the power station remotely from Tokaanu power station since the early 2000s. Artist Doris Lusk depicted the power station in a 1948 painting. She described the power station as a “gothic building in the middle of the wild hills”. Lake Whakamarino, also known as Tuai Lake, is popular with anglers. It can be used by fly-fishers, and accessed with small unanchored boats. Demographics Statistics New Zealand describes Tuai as a rural settlement, which covers . It is part of the wider Maungataniwha-Raupunga statistical area. Tuai had a population of 216 at the 2018 New Zealand census, an increase of 3 people (1.4%) since the 2013 census, and a decrease of 27 people (−1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Doris Lusk
Doris More Lusk (5 May 1916 – 14 April 1990) was a New Zealand painter, potter, art teacher, and university lecturer. In 1990 she was posthumously awarded the Governor General Art Award in recognition of her artistic career and contributions. Early life Lusk was born in Dunedin, New Zealand, on 5 May 1916. She was the daughter of Alice Mary (née Coats), and Thomas Younger Lusk, a draughtsman and architect, and had two older siblings, Marion and Paxton. The family moved to Hamilton where she went to primary school. An artist who had a studio near the family's home encouraged Lusk to paint. In 1928, the family returned to Dunedin where her father joined the architectural firm, Mandeno and Frazer. Lusk completed one more year at Arthur Street Primary School before attending Otago Girl's High School in 1930. In 1933, Lusk left high school before she had matriculated, and enrolled in the Dunedin School of Art. Lusk enrolled against her father's wishes and later noted there had ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genesis Energy Limited
Genesis Energy Limited, formerly Genesis Power Limited is a New Zealand publicly listed electricity generation and electricity, natural gas and LPG retailing company. It was formed as part of the 1998–99 reform of the New Zealand electricity sector, taking its generation capacity from the breakup of the Electricity Corporation of New Zealand (ECNZ) and taking retail customers from three local power boards in the Lower North Island. The New Zealand Government owns a 51% share of the company. Genesis Energy is the largest electricity and natural gas retailer in New Zealand with 26% and 39% market share respectively in the 2015–2016 financial year. In 2015, Genesis produced 14% of New Zealand's electricity, and is the third largest electricity generating company in New Zealand in terms of MW capacity, GWh generation and revenue (see comparison table at New Zealand electricity market). History Genesis Energy began business on 1 April 1999, after the reform of the N ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hawke's Bay Region
Hawke's Bay ( mi, Te Matau-a-Māui) is a local government region on the east coast of New Zealand's North Island. The region's name derives from Hawke Bay, which was named by Captain James Cook in honour of Admiral Edward Hawke. The region is governed by Hawke's Bay Regional Council. Geography The region is situated on the east coast of the North Island. It bears the former name of what is now Hawke Bay, a large semi-circular bay that extends for 100 kilometres from northeast to southwest from Māhia Peninsula to Cape Kidnappers. The Hawke's Bay Region includes the hilly coastal land around the northern and central bay, the floodplains of the Wairoa River in the north, the wide fertile Heretaunga Plains around Hastings in the south, and a hilly interior stretching up into the Kaweka and Ruahine Ranges. The prominent peak Taraponui is located inland. Five major rivers flow to the Hawke's Bay coast. From north to south, they are the Wairoa River, Mohaka River, Tutaekuri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Raupunga
Raupunga is a small settlement in the northern Hawke's Bay Region of New Zealand's eastern North Island. It is located close to the country's highest railway bridge, the Mohaka Viaduct, which crosses the Mohaka River. The predominantly Māori village is expected to have a population of 266 people by 2033. The village got running water for the first time in 2017, when a 9 kilometre electric pump system was built from Mangawharangi Stream for $1 million. Until that time, many of the 56 households had got water from buckets. Demographics Maungataniwha-Raupunga statistical area, which includes Mohaka, Kotemaori, Putere and Tuai, covers and had an estimated population of as of with a population density of people per km2. Maungataniwha-Raupunga had a population of 1,188 at the 2018 New Zealand census, an increase of 21 people (1.8%) since the 2013 census, and a decrease of 54 people (−4.3%) since the 2006 census. There were 405 households, comprising 624 males and 564 fe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Māori People
The Māori (, ) are the indigenous Polynesian people of mainland New Zealand (). Māori originated with settlers from East Polynesia, who arrived in New Zealand in several waves of canoe voyages between roughly 1320 and 1350. Over several centuries in isolation, these settlers developed their own distinctive culture, whose language, mythology, crafts, and performing arts evolved independently from those of other eastern Polynesian cultures. Some early Māori moved to the Chatham Islands, where their descendants became New Zealand's other indigenous Polynesian ethnic group, the Moriori. Initial contact between Māori and Europeans, starting in the 18th century, ranged from beneficial trade to lethal violence; Māori actively adopted many technologies from the newcomers. With the signing of the Treaty of Waitangi in 1840, the two cultures coexisted for a generation. Rising tensions over disputed land sales led to conflict in the 1860s, and massive land confiscations, to which ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
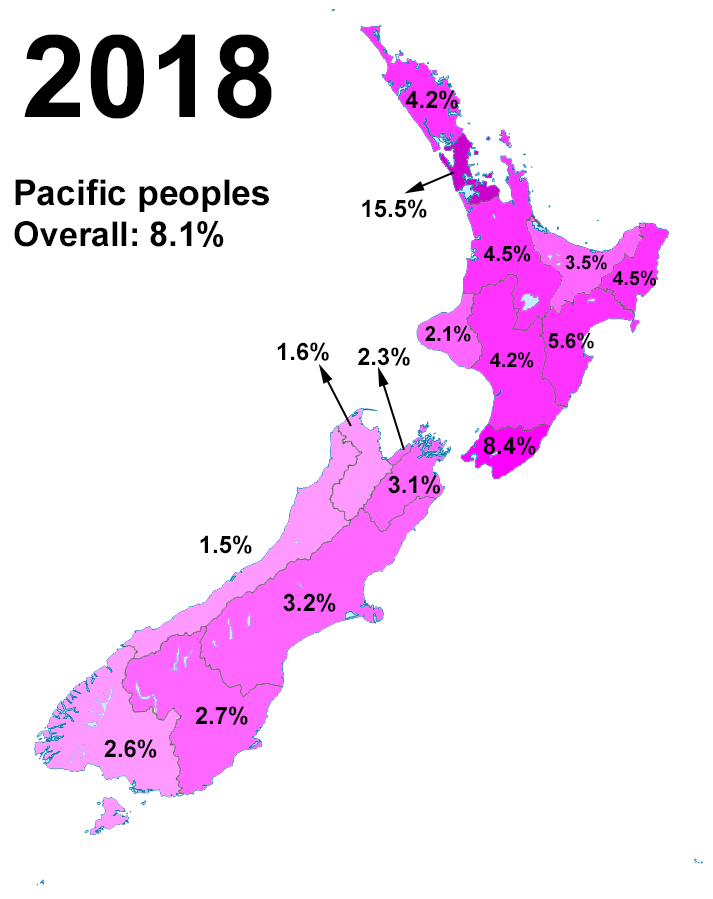
Pasifika New Zealanders
Pasifika New Zealanders are a pan-ethnic group of New Zealanders associated with, and descended from, the indigenous peoples of the Pacific Islands outside of New Zealand itself (also known as Pacific Islanders). They form the fourth-largest ethnic grouping in the country, after European-descended Pākehā, indigenous Māori, and Asian New Zealanders. There are over 380,000 Pasifika people in New Zealand, with the majority living in Auckland. 8% of the population of New Zealand identifies as being of Pacific origin. History Prior to the Second World War Pasifika in New Zealand numbered only a few hundred. Wide-scale Pasifika migration to New Zealand began in the 1950s and 1960s, typically from countries associated with the Commonwealth and the Realm of New Zealand, including Western Samoa (modern-day Samoa), the Cook Islands and Niue. In the 1970s, governments (both Labour and National), migration officials, and special police squads targeted Pasifika illegal overstayers. Paci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Christianity In New Zealand
Christianity in New Zealand dates to the arrival of missionaries from the Church Missionary Society who were welcomed onto the beach at Rangihoua Bay in December 1814. It soon became the predominant belief amongst the indigenous people with an estimated 60% of Māori pledging allegiance to the Christian message within the first 35 years. It remains New Zealand's largest religious group despite there being no official state church. Today, slightly less than half the population identify as Christian. The largest Christian groups are Catholic, Anglican and Presbyterian. Christian organisations are the leading non-government providers of social services in New Zealand. History The first Christian services conducted in New Zealand were carried out by Father Paul-Antoine Léonard de Villefeix, the Dominican chaplain on the ship ''Saint Jean Baptiste'' commanded by the French navigator and explorer Jean-François-Marie de Surville. Villefeix was the first Christian minister to set ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Māori Religion
Māori religion encompasses the various religious beliefs and practices of the Māori, the Polynesian indigenous people of New Zealand. Traditional Māori religion Traditional Māori religion, that is, the pre-European belief-system of the Māori, differed little from that of their tropical Eastern Polynesian homeland ( Hawaiki Nui), conceiving of everything - including natural elements and all living things - as connected by common descent through whakapapa or genealogy. Accordingly, Māori regarded all things as possessing a life force or mauri. Illustrating this concept of connectedness through genealogy are the major personifications dating from before the period of European contact: * Tangaroa was the personification of the ocean and the ancestor or origin of all fish. * Tāne was the personification of the forest and the origin of all birds. * Rongo was the personification of peaceful activities and agriculture and the ancestor of cultivated plants. (Some sources ref ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Regions Of New Zealand
New Zealand is divided into sixteen regions () for local government in New Zealand, local government purposes. Eleven are administered by regional councils (the top tier of local government), and five are administered by Unitary authority#New Zealand, unitary authorities, which are territorial authorities of New Zealand, territorial authorities (the second tier of local government) that also perform the functions of regional councils. The Chatham Islands#Government, Chatham Islands Council is not a region but is similar to a unitary authority, authorised under its own legislation. Current regions History and statutory basis The regional councils are listed in Part 1 of Schedule 2 of the Local Government Act 2002 (New Zealand), Local Government Act 2002, along with reference to the ''New Zealand Gazette, Gazette'' notices that established them in 1989. The Act requires regional councils to promote sustainable developmentthe social, economic, environmental and cultural well-bei ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pākehā
Pākehā (or Pakeha; ; ) is a Māori term for New Zealanders primarily of European descent. Pākehā is not a legal concept and has no definition under New Zealand law. The term can apply to fair-skinned persons, or to any non-Māori New Zealander. Papa'a has a similar meaning in Cook Islands Māori. Historically before the arrival of other ethnic groups the word Māori meant 'ordinary' or 'normal'. The arrival of Europeans led to the formation of a new term to distinguish the self-regarded 'ordinary' or 'normal' Māori from the new arrivals. The etymology of the word ''Pākehā'' remains unclear, but the term was in use by the late-18th century. In December 1814 the Māori children at Rangihoua in the Bay of Islands were "no less eager to see the ''packaha'' than the grown folks". In Māori, plural noun-phrases of the term include (the definite article) and (the indefinite article). When the word was first adopted into English, the usual plural was 'Pakehas'. However, spe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hapū
In Māori and New Zealand English, a ' ("subtribe", or "clan") functions as "the basic political unit within Māori society". A Māori person can belong to or have links to many hapū. Historically, each hapū had its own chief and normally operated independently of its iwi (tribe). Etymology The word literally means "pregnant", and its usage in a socio-political context is a metaphor for the genealogical connection that unites hapū members. Similarly, the Māori word for land, whenua, can also mean "placenta", metaphorically indicating the connection between people and land, and the Māori word for tribe, iwi, can also mean "bones", indicating a link to ancestors. Definition As named divisions of (tribes), hapū membership is determined by genealogical descent; a hapū consists of a number of (extended family) groups. The Māori scholar Hirini Moko Mead states the double meanings of the word hapū emphasise the importance of being born into a hapū group. As a metaphor t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ngāti Hinekura
Iwi () are the largest social units in New Zealand Māori society. In Māori roughly means "people" or "nation", and is often translated as "tribe", or "a confederation of tribes". The word is both singular and plural in the Māori language, and is typically pluralised as such in English. groups trace their ancestry to the original Polynesian migrants who, according to tradition, arrived from Hawaiki. Some cluster into larger groupings that are based on (genealogical tradition) and known as (literally "canoes", with reference to the original migration voyages). These super-groupings generally serve symbolic rather than practical functions. In pre-European times, most Māori were allied to relatively small groups in the form of ("sub-tribes") and ("family"). Each contains a number of ; among the of the Ngāti Whātua iwi, for example, are Te Uri-o-Hau, Te Roroa, Te Taoū, and Ngāti Whātua-o-Ōrākei. Māori use the word ''rohe'' to describe the territory or boundaries ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |