|
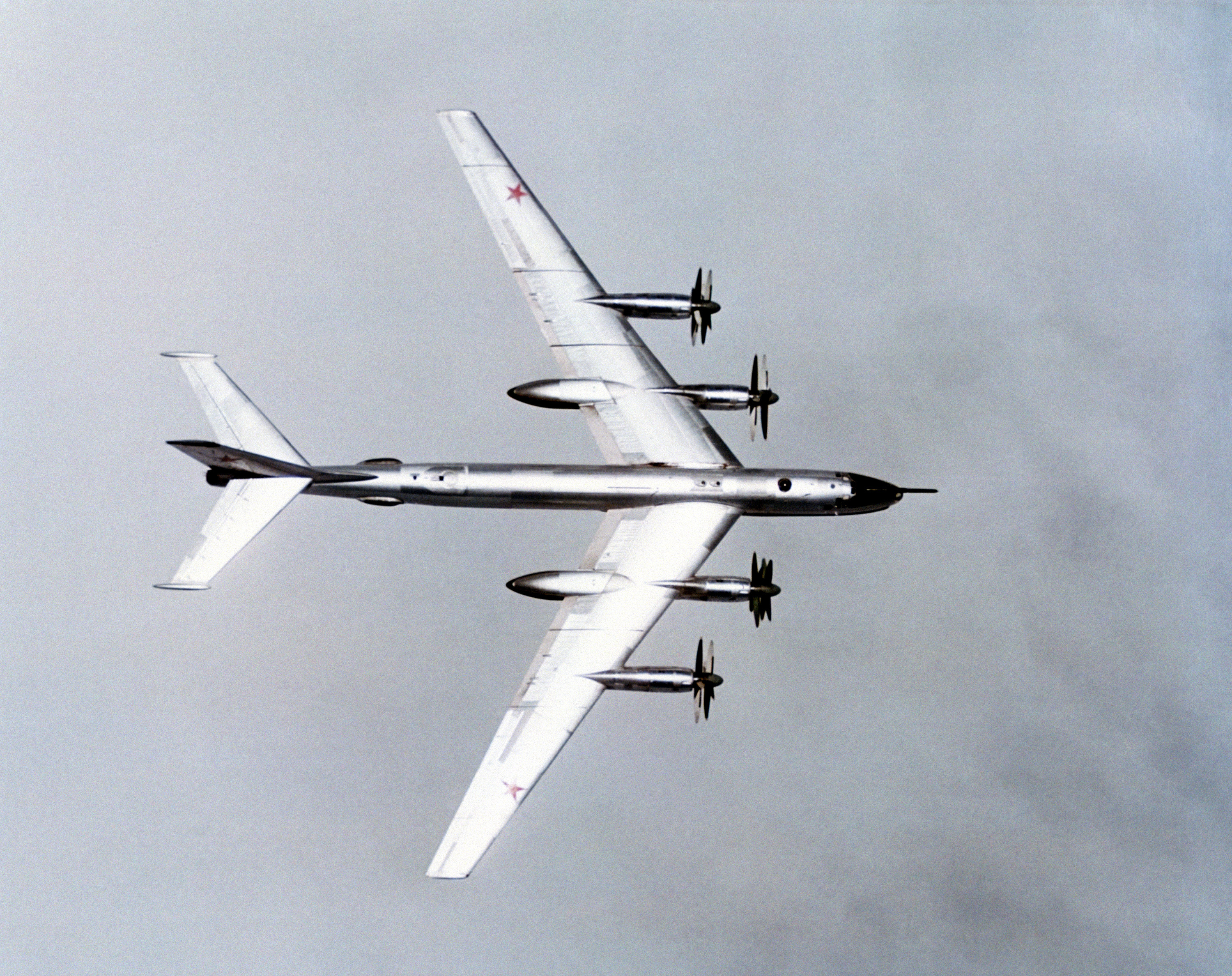
Tu-95MS
The Tupolev Tu-95 (russian: Туполев Ту-95; NATO reporting name: "Bear") is a large, four-engine turboprop-powered strategic bomber and missile platform. First flown in 1952, the Tu-95 entered service with the Long-Range Aviation of the Soviet Air Forces in 1956 and was first used in combat in 2015. It is expected to serve the Russian Aerospace Forces until at least 2040. A development of the bomber for maritime patrol is designated the Tu-142, while a passenger airliner derivative was called the Tu-114. The aircraft has four Kuznetsov NK-12 engines with contra-rotating propellers. It is the only propeller-powered strategic bomber still in operational use today. The Tu-95 is one of the loudest military aircraft, particularly because the tips of the propeller blades move faster than the speed of sound. Its distinctive swept-back wings are set at an angle of 35°. The Tu-95 is the only propeller-driven aircraft with swept wings that has been built in large numbers. Desi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tu-95 Wingspan
The Tupolev Tu-95 (russian: Туполев Ту-95; NATO reporting name: "Bear") is a large, four-engine turboprop-powered strategic bomber and missile platform. First flown in 1952, the Tu-95 entered service with the Long-Range Aviation of the Soviet Air Forces in 1956 and was first used in combat in 2015. It is expected to serve the Russian Aerospace Forces until at least 2040. A development of the bomber for maritime patrol is designated the Tu-142, while a passenger airliner derivative was called the Tu-114. The aircraft has four Kuznetsov NK-12 engines with contra-rotating propellers. It is the only propeller-powered strategic bomber still in operational use today. The Tu-95 is one of the loudest military aircraft, particularly because the tips of the propeller blades move faster than the speed of sound. Its distinctive swept-back wings are set at an angle of 35°. The Tu-95 is the only propeller-driven aircraft with swept wings that has been built in large numbers. Desi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Long-Range Aviation
Long-Range Aviation ( rus, Авиация Дальнего Действия, r=Aviatsiya dal'nego deystviya, abbr. to AДД, or ADD, and literally ''Aviation of Distant Action'') is a branch of the Russian Aerospace Forces responsible for delivering long-range nuclear or conventional strikes by aircraft rather than missiles. The branch was previously part of the Soviet Air Forces and Russian Air Force tasked with long-range bombardment of strategic targets with nuclear weapons. During the Cold War, it was the counterpart to the Strategic Air Command of the United States Air Force. Origins, 1936-1940 The first three Air Armies, designated Air Armies of Specific Purpose (or Particular Purpose) were created between 1936 and 1938. In accordance with the predominant Deep operations doctrine, the Red Army was reorganized into six echelons, of which the long-range aviation was the 1st echelon. The 2nd echelon consisted of: heavy tanks; the 3rd echelon: medium and light tanks; the 4 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tupolev Tu-95LAL
The Tupolev Tu-95LAL (russian: Летающая Атомная Лаборатория, translit=Letayushchaya Atomnaya Laboratoriya, lit=flying atomic laboratory) was an experimental aircraft that was a modified Tupolev Tu-95 Soviet bomber aircraft, which flew from 1961 to 1965, analogous to the United States' earlier Convair NB-36H. It was intended to see whether a nuclear reactor could be used to power an aircraft, primarily testing airborne operation of a reactor and shielding for components and crew. Design and development During the Cold War the USSR had an experimental nuclear aircraft program. Without the need to refuel, a nuclear-powered aircraft would have greatly extended range compared to conventional designs. On 12 August 1955 the Council of Ministers of the USSR issued a directive ordering bomber-related design bureaus to join forces in researching nuclear aircraft. The design bureaus of Andrei Tupolev and Vladimir Myasishchev became the chief design teams, while ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Strategic Bomber
A strategic bomber is a medium- to long-range penetration bomber aircraft designed to drop large amounts of air-to-ground weaponry onto a distant target for the purposes of debilitating the enemy's capacity to wage war. Unlike tactical bombers, penetrators, fighter-bombers, and attack aircraft, which are used in air interdiction operations to attack enemy combatants and military equipment, strategic bombers are designed to fly into enemy territory to destroy strategic targets (e.g., infrastructure, logistics, military installations, factories, etc.). In addition to strategic bombing, strategic bombers can be used for tactical missions. There are currently only three countries that operate strategic bombers: the United States, Russia and China. The modern strategic bomber role appeared after strategic bombing was widely employed, and atomic bombs were first used in combat during World War II. Nuclear strike missions (i.e., delivering nuclear-armed missiles or bombs) can pote ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
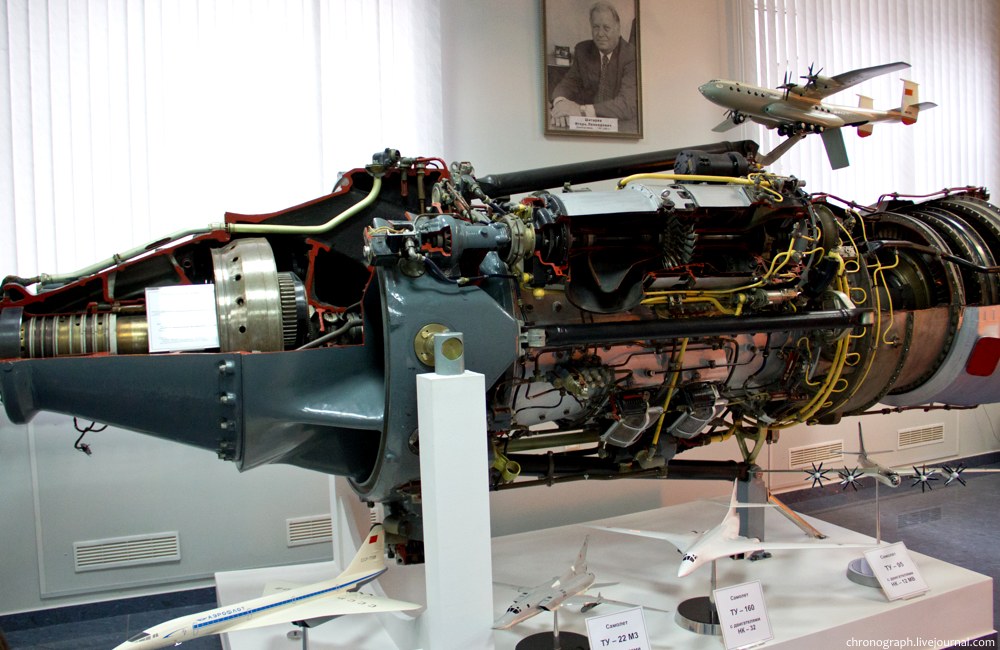
Kuznetsov NK-12
The Kuznetsov NK-12 is a Soviet turboprop engine of the 1950s, designed by the Kuznetsov design bureau. The NK-12 drives two large four-bladed contra-rotating propellers, diameter (NK-12MA), and diameter (NK-12MV). It is the most powerful turboprop engine to enter service. Design and development The design that eventually became the NK-12 turboprop was developed after World War II by a team of Soviet scientists and deported German engineers under Ferdinand Brandner, who had worked for Junkers previously; the design bureau was headed by chief engineer Nikolai D. Kuznetsov. Thus, the NK-12 design evolved from late-war German turboprop studies. This started with the postwar development of the wartime Jumo 022 turboprop design that was designed to develop , weighing . The effort continued with a , weighing , completed by 1947. Evolution to the TV-12 engine required extensive use of new Soviet-developed alloys and was completed in 1951. The NK-12 is the most powerful turboprop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
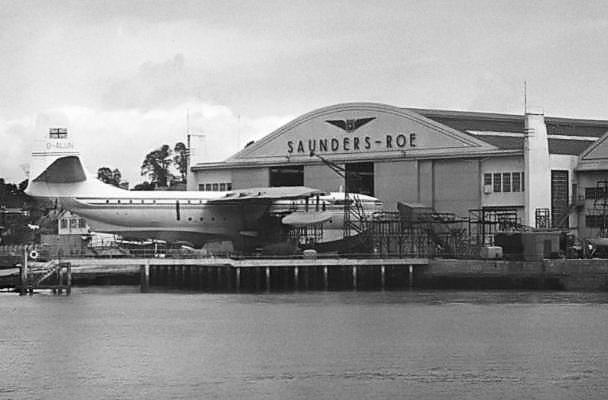
Saunders-Roe Princess
The Saunders-Roe SR.45 Princess was a British flying boat aircraft developed and built by Saunders-Roe at their Cowes facility on the Isle of Wight. It has the distinction of being the largest all-metal flying boat to have ever been constructed. The Princess had been developed to serve as a larger and more luxurious successor to the pre-war commercial flying boats, such as the Short Empire. It was intended to serve the transatlantic route, carrying up to 100 passengers between Southampton, United Kingdom and New York City, United States in spacious and comfortable conditions. To achieve this, it was decided early on to make use of newly developed turboprop technology, opting for the Bristol Proteus engine still in development to power the aircraft. The project suffered delays due to difficulties encountered in the development of the Proteus engine. On 22 August 1952, the first prototype Princess, ''G-ALUN'', conducted its maiden flight. Between 1952 and 1954, the first prototype ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Boeing B-52 Stratofortress
The Boeing B-52 Stratofortress is an American long-range, subsonic, jet-powered strategic bomber. The B-52 was designed and built by Boeing, which has continued to provide support and upgrades. It has been operated by the United States Air Force (USAF) since the 1950s. The bomber is capable of carrying up to 70,000 pounds (32,000 kg) of weapons,"Fact Sheet: B-52 Superfortress." ''Minot Air Force Base'', United States Air Force, October 2005. Retrieved: 12 January 2009. and has a typical combat range of around 8,800 miles (14,080 km) without aerial refueling. Beginning with the successful contract bid in June 1946, the B-52 design evolved from a [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reciprocating Engine
A reciprocating engine, also often known as a piston engine, is typically a heat engine that uses one or more reciprocating pistons to convert high temperature and high pressure into a rotating motion. This article describes the common features of all types. The main types are: the internal combustion engine, used extensively in motor vehicles; the steam engine, the mainstay of the Industrial Revolution; and the Stirling engine for niche applications. Internal combustion engines are further classified in two ways: either a spark-ignition (SI) engine, where the spark plug initiates the combustion; or a compression-ignition (CI) engine, where the air within the cylinder is compressed, thus heating it, so that the heated air ignites fuel that is injected then or earlier.''Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach'' by Yunus A. Cengal and Michael A. Boles Common features in all types There may be one or more pistons. Each piston is inside a cylinder, into which a gas is intr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Myasishchev
V. M. Myasishchev Experimental Design Bureau (Экспериментальный Машиностроительный Завод им. В. М. Мясищева) or OKB-23, founded in 1951 by MGB UdSSR Vladimir Myasishchev, was one of the chief Soviet aerospace design bureaus until its dissolution in 1960. Vladimir Myasishchev went on to head TsAGI. In 1967, Myasishchev left TsAGI and recreated his bureau, which still exists to this day. The bureau prefix was "M." , its workforce is estimated at approximately one thousand. Myasishchev and NPO Molniya intend to use the V-MT or M-55 as launch vehicle for sub-orbital spaceflight. In July 2014, the merger of Myasishchev and Ilyushin to create a single modern production complex was announced by the Board of Directors of OAO Il. Products 1940-1960 * VM-1/DVB-102: prototype long-range, high-altitude bomber, 1940 **VM-2: projected version of VM-1 with M-20 diesel engines, 1940 **VM-3/DVB-102N: projected version ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Boeing B-29 Superfortress
The Boeing B-29 Superfortress is an American four-engined propeller-driven heavy bomber, designed by Boeing and flown primarily by the United States during World War II and the Korean War. Named in allusion to its predecessor, the B-17 Flying Fortress, the Superfortress was designed for high-altitude strategic bombing, but also excelled in low-altitude night incendiary bombing, and in dropping naval mines to blockade Japan. B-29s dropped the atomic bombs on Hiroshima and Nagasaki, the only aircraft ever to drop nuclear weapons in combat. One of the largest aircraft of World War II, the B-29 was designed with state-of-the-art technology, which included a pressurized cabin, dual-wheeled tricycle landing gear, and an analog computer-controlled fire-control system that allowed one gunner and a fire-control officer to direct four remote machine gun turrets. The $3 billion cost of design and production (equivalent to $ billion today), far exceeding the $1.9 b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tupolev Tu-4
The Tupolev Tu-4 (russian: Туполев Ту-4; NATO reporting name: Bull) is a piston-engined Soviet strategic bomber that served the Soviet Air Force from the late 1940s to mid-1960s. It was reverse-engineered from the American Boeing B-29 Superfortress. Design and development Toward the end of World War II, the Soviet Union saw the need for a strategic bombing capability similar to that of the United States Army Air Forces. The Soviet VVS air arm had the locally designed Petlyakov Pe-8 four-engined "heavy" in service at the start of the war, but only 93 had been built by the end of the war and the type had become obsolete. The U.S. regularly conducted bombing raids on Japan, from distant Pacific forward bases using B-29 Superfortresses. Joseph Stalin ordered the development of a comparable bomber. The U.S. twice refused to supply the Soviet Union with B-29s under Lend Lease. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tupolev Tu-85
The Tupolev Tu-85 (russian: Туполев Ту-85; USAF/ DoD reporting name: "Type 31", NATO reporting name: Barge) was a Soviet prototype strategic bomber based on the Tu-4, an unlicensed, reverse engineered copy of the Boeing B-29 Superfortress. It was the ultimate development of the B-29 family, being over 50% heavier than its progenitor and had nearly double the range. Only two prototypes were built before the program was cancelled in favor of the turboprop powered Tupolev Tu-95 bomber which could cover the same range at a far higher speed. Development Neither the Tu-4 nor the Tupolev Tu-80 were true intercontinental strategic bombers as they both lacked the range to attack the United States from bases in the Soviet Union and return. The Tu-85 was designed to achieve the necessary range by use of more powerful and fuel-efficient engines, a redesigned wing to increase the lift/drag ratio and the addition of more fuel. A large number of engines were considered before settling ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |