|
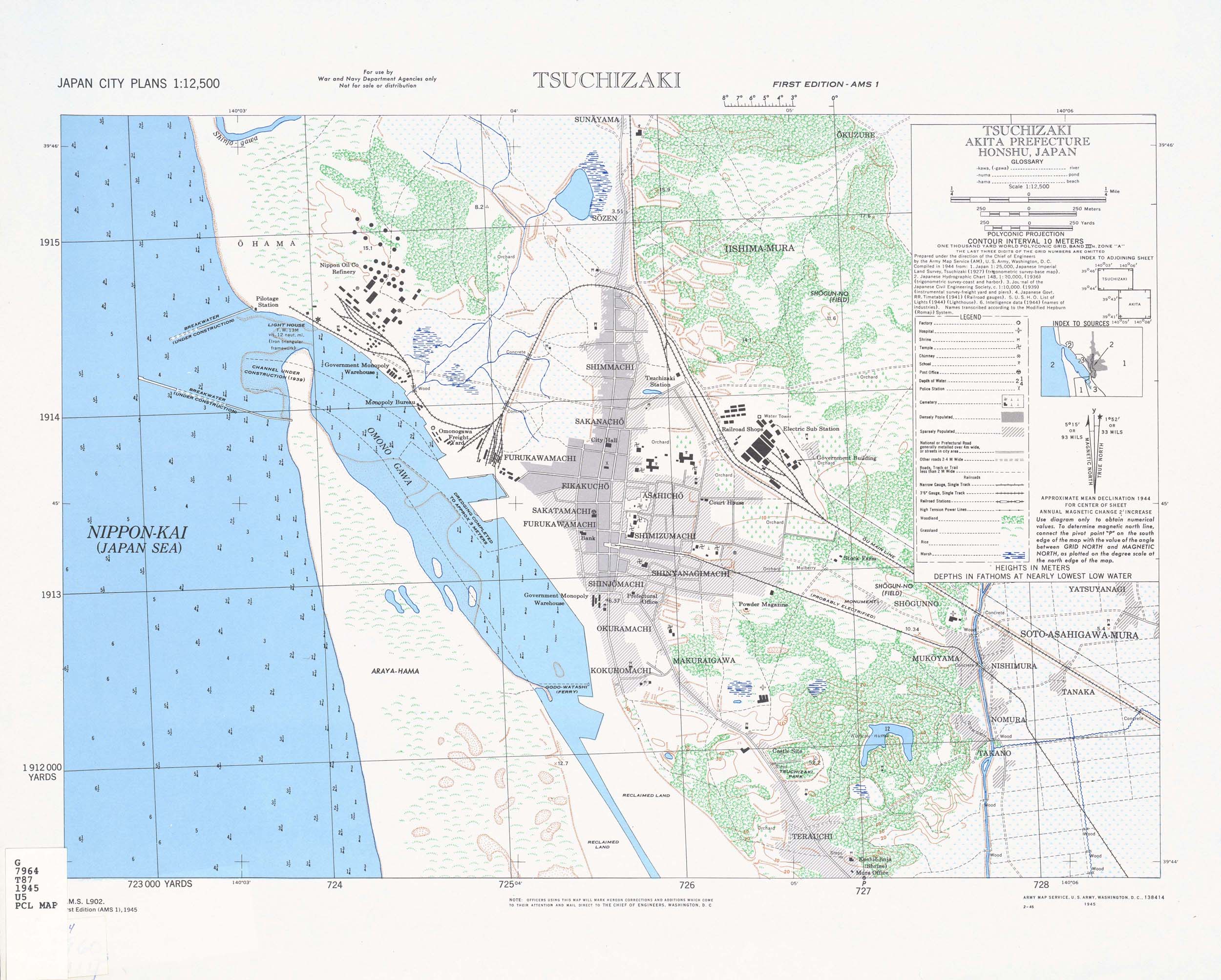
Tsuchizaki Minato
is a neighbourhood located in Akita City, Akita Prefecture, Japan. , the neighbourhood had an estimated population of 21,310 and a population density of 3,400 persons per km². The total area of the neibourhood is . Annexed by the city in 1941, it borders the neighborhoods of Shogunno on the east, Iijima on the north, Mukaihama on the west and Terauchi on the south. The Tsuchizaki area is a port town that developed at the mouth of the Omono River and a place of Port of Akita and Japan Railway Tsuchizaki factory. Tsuchizaki Float Festival is a celebration in the neighbourhood, held every year from July 20 to 21. The Tsuchizaki air raid burned the port facilities and killed more than 250 people on August 14 and 15, 1945. Schools * Tsuchizaki Elementary School * Tsuchizaki Minami Elementary School * Kohoku Elementary School * Tsuchizaki Junior High School * Akita Chuo High School Surrounding area *Port of Akita Nakajima Pier ** Nakajima Pier Ferry Terminal ** Roadside Stat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Akita (city)
'Autumn field' is the capital Cities of Japan, city of Akita Prefecture, Japan, and has been designated a Core cities of Japan, core city since 1 April 1997. , the city has an estimated population of 305,625, 136,628 households and a population density of 340 persons per km2. The total area of the city is . History The area of present-day Akita was part of ancient Dewa Province, and has been inhabited for thousands of years. The Jizōden Site, Jizōden ruins within the city limits are a major archaeological site with artifacts from the Japanese Paleolithic period through the Jōmon period, Jōmon and Yayoi periods. During the Nara period, the Yamato dynasty, Yamato court established Akita Castle in 733 AD to bring the local Emishi tribes under its control. The area was ruled by a succession of local samurai clans in the Sengoku period, before coming under the control of the Satake clan of Kubota Domain during the Edo period. Under the Tokugawa shogunate, a castle town developed ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Port Of Akita
The , formerly known as Port of Tsuchizaki, is a seaport on the Sea of Japan coast of Akita Prefecture, to the west of the city center of Akita in the Tōhoku region of northern Honshū, Japan. It is classified as a by the Japanese government. The port has a total land area of 662.5 hectares. History In 727 the envoys from Bokkai (Balhae) sailed the Sea of Japan and were calling at Akita Port for the first time. In the oldest Japanese marine law Kaisenshikimoku, Tsuchizaki Minato, former name of Akita Port, was referred to as the ten biggest ports in Japan. Tsuchizaki was just mentioned as " Minato (port)" in the Japanese historical references which suggests the harbour was the port of all ports. During the Edo period, Akita was an important port of call on the Kitamaebune route of coastal trade from Osaka to Hokkaido and an important source of revenue for the Satake clan’s Kubota Domain. In modern times, during the Meiji period a breakwater was completed in 1885 and enlar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ōmi Komaki
was the pen-name of a scholar and translator of French literature in Taishō and Shōwa period Japan. His real name was Komaki Ōmiya. Early life Komaki was born in Tsuchizaki-Minato town, Akita prefecture, as the son of a politician. He dropped out of middle school in order to accompany his father to an international conference of legislators in France, and stayed on, working his way through the Law Department of Paris University. He was greatly influenced by the philosophy of Romain Rolland and the '' Clarté'' ("Clarity") movement of the French novelist, Henri Barbusse, which encouraged him to participate in pacifist activities. Literary career Komaki returned to Japan in 1919 and founded the literary magazine '' Tane Maku Hito'' ("The Sowers") in October 1921, named after the famous painting by the French artist Jean-François Millet. He used this as his platform to promote his pacifist and Marxist ideals through poems and essays, many of which he wrote. He was one of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kenzo Futaki
was a Japanese doctor who studied infectious diseases. Futaki was educated at Tokyo Imperial University. He received the prestigious Order of Culture (Bunka Kunshō) from the Emperor for his academic contributions, which included identifying the infectious agents of dysentery and rat bite fever, He was a candidate for the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine The Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine is awarded yearly by the Nobel Assembly at the Karolinska Institute for outstanding discoveries in physiology or medicine. The Nobel Prize is not a single prize, but five separate prizes that, accord .... In addition to his medical research, he had a strong understanding of traditional Japanese folk remedies. References Japanese infectious disease physicians 1873 births 1966 deaths Place of death missing {{Japan-med-bio-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yukiko Ebata
Yukiko Ebata (江畑 幸子 ''Ebata Yukiko'', born November 7, 1989) is a retired Japanese volleyball player who played for the PFU BlueCats and was a member of the Japan women's national volleyball team. She was a member of Japan's bronze medal-winning 2012 Olympic volleyball team. She married to Shun Takahashi who is coach of Victorina Himeji. Career Ebata is from Tsuchizaki-Minato, Akita-shi, Akita prefecture. Her parents are volleyball players, she started playing volleyball when she is in her 3rd year in elementary school. She also has an older brother who also played volleyball. When she entered college, she was offered a scholarship by the director of the Holy Spiritual Women's Junior College, in return for playing volleyball for the school. Ebata has said that this was a major turning point for her. She was then attached to the Holy Spiritual Women's Junior College, she was active in the Spring High Valley and Inter – high as captain. In 2008, she was recruited b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sumo Wrestler
A , or, more colloquially, , is a professional sumo wrestler. follow and live by the centuries-old rules of the sumo profession, with most coming from Japan, the only country where sumo is practiced professionally. Participation in official tournaments () is the only means of marking achievement in sumo, with the rank of an individual based solely on official wins. The number of active peaked at 943 in May 1994, at the height of the "Waka-Taka boom," but had declined to 665 by January 2022. Terminology In popular use, the term can mean any sumo wrestler and be an alternative term to (sumo practitioner) or the more colloquial . The two kanji characters that make up the word are "strength/power" and "gentleman/samurai"; consequently, and more idiomatically, the term can be defined as "a gentleman of strength". Within the world of professional sumo, is used as a catch-all term for wrestlers who are in the lower, un-salaried divisions of , , and . The more prestigious ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dewaminato Rikichi
Dewaminato Rikichi (March 20, 1907, as Rikichi Satō in Tsuchizaki-Minato, Akita Prefecture, Japan – May 17, 1964), was a professional sumo wrestler with Dewanoumi stable. He made his debut in 1928, reaching the top ''makuuchi'' division in 1935. His highest rank was ''sekiwake.'' In January 1939 he won the top division ''yūshō'' or championship with an undefeated 13–0 record, ending a run of five straight championships won by Futabayama. After his retirement in 1944 he worked as a coach at his stable until 1963, when he left the sumo world. He died a year later in 1964. Career He first entered the ring in the Summer 1928 tournament. In 1932, he was one of the few unsalaried wrestlers to be expelled from sumo by the Japan Sumo Association for being involved in a strike called the " Shunjūen Incident" that was largely unsuccessful. He, along with many others, was allowed back in from the Spring 1933 tournament. He was allowed into the ''makushita'' division, but unran ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Daimyo
were powerful Japanese magnates, feudal lords who, from the 10th century to the early Meiji period in the middle 19th century, ruled most of Japan from their vast, hereditary land holdings. They were subordinate to the shogun and nominally to the emperor and the '' kuge''. In the term, means 'large', and stands for , meaning 'private land'. From the ''shugo'' of the Muromachi period through the Sengoku to the ''daimyo'' of the Edo period, the rank had a long and varied history. The backgrounds of ''daimyo'' also varied considerably; while some ''daimyo'' clans, notably the Mōri, Shimazu and Hosokawa, were cadet branches of the Imperial family or were descended from the ''kuge'', other ''daimyo'' were promoted from the ranks of the samurai, notably during the Edo period. ''Daimyo'' often hired samurai to guard their land, and they paid the samurai in land or food as relatively few could afford to pay samurai in money. The ''daimyo'' era ended soon after the Meiji Resto ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Akita Sanesue
was a Japanese daimyo who lived during the Azuchi–Momoyama and early Edo periods. Biography He was the son of daimyo Andō Chikasue, a powerful figure in Dewa Province. Sanesue pledged loyalty to Toyotomi Hideyoshi in 1590 during the Siege of Odawara, and served under him in various campaigns such as the Korean campaign. At the Battle of Sekigahara in 1600, he sided with the eastern army. As Satake Yoshinobu was being moved northward to the Akita's holdings in 1602, the Akita clan, under Sanesue, was moved to Shishido, in Hitachi Province. Sanesue led his sons into combat at the Osaka Campaign in 1615. In 1630, because of discontent against the shogunate, he was exiled to Asama in Ise Province, where he died in 1659. Despite this exile, his son Toshisue survived, and was moved to the Miharu Domain, in Mutsu Province, where his descendants remained in power until the Meiji Restoration. References 1576 births 1660 deaths Akita Sanesue Akita Sanesue was a Japan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tsuchizaki Minato History Tradition Hall
is a neighbourhood located in Akita City, Akita Prefecture, Japan. , the neighbourhood had an estimated population of 21,310 and a population density of 3,400 persons per km². The total area of the neibourhood is . Annexed by the city in 1941, it borders the neighborhoods of Shogunno on the east, Iijima on the north, Mukaihama on the west and Terauchi on the south. The Tsuchizaki area is a port town that developed at the mouth of the Omono River and a place of Port of Akita and Japan Railway Tsuchizaki factory. Tsuchizaki Float Festival is a celebration in the neighbourhood, held every year from July 20 to 21. The Tsuchizaki air raid burned the port facilities and killed more than 250 people on August 14 and 15, 1945. Schools * Tsuchizaki Elementary School * Tsuchizaki Minami Elementary School * Kohoku Elementary School * Tsuchizaki Junior High School * Akita Chuo High School Surrounding area *Port of Akita Nakajima Pier ** Nakajima Pier Ferry Terminal ** Roadside Sta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Akita Port Tower Selion
The is one of the landmarks in the city of Akita, Japan. The sightseeing tower with 6,272 tempered glasses was completed in 1994. It is located in the Tsuchizaki District, Akita, Akita Prefecture, Japan. The steel tower is the tallest structure in the 3 northern Tohoku prefectures with its observation deck at 100 metres (328 ft) and its spire at 143.6 metres (471 ft). The viewing platform provides a 360-degree panorama of the city and the mountains of Oga Peninsula, Taiheizan, and Mt. Chokai are visible. Cable Networks Akita received the TV-U Yamagata broadcast from Takadateyama, Tsuruoka at this landmark in the past.conversation with CNA employee Events * Cue sports at the 2001 World Games Gallery File:Akita Port Tower SELION 20170709.jpg, File:Selion full view.jpg, File:Akita Port Tower SELION at twilight time.jpg, File:Akita Port Tower SELION at night the KANANO purple 01.jpg, File:Selion Lisuta.jpg, Selion Rista File:Selion Plaza 2 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |