|
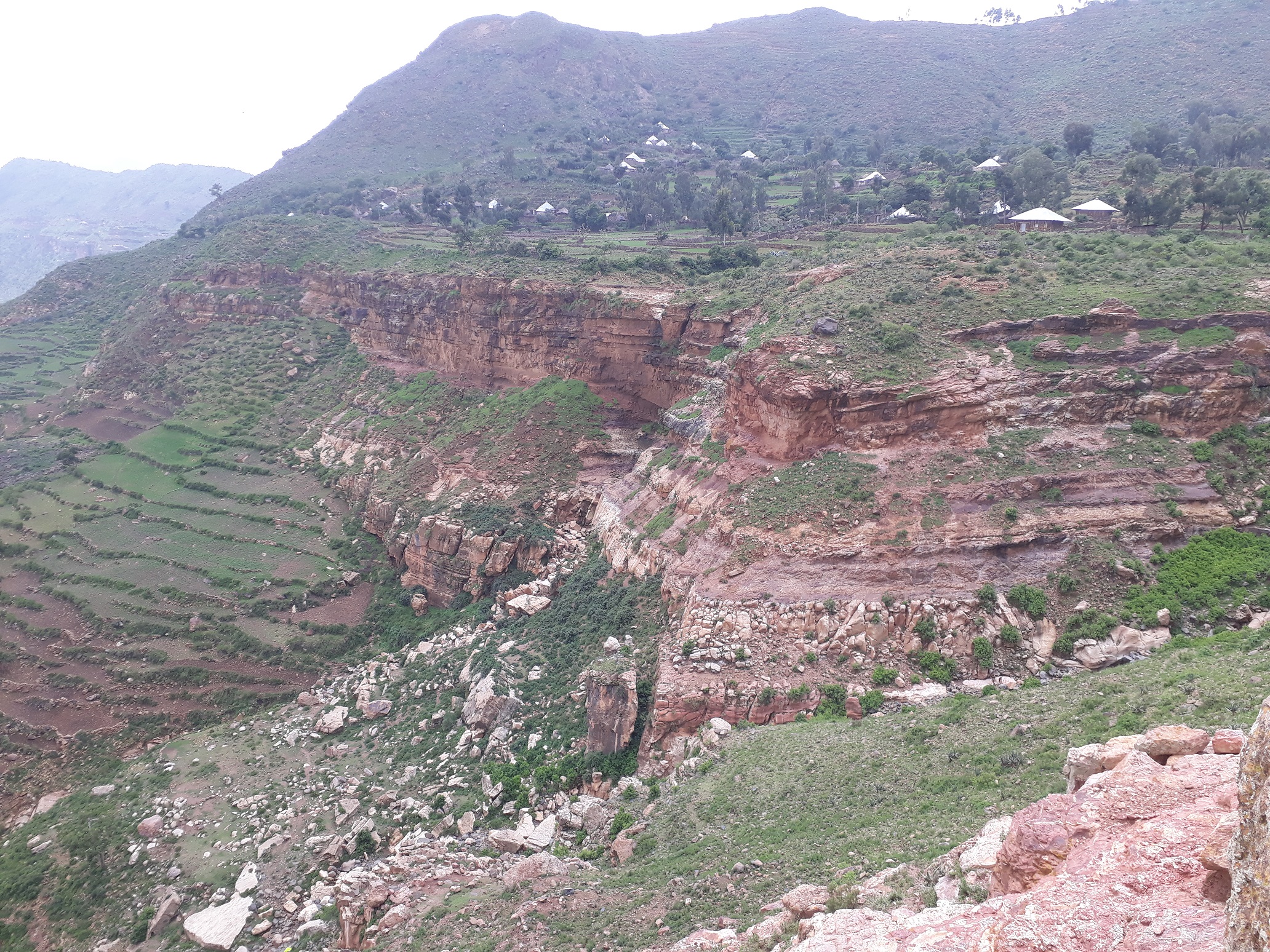
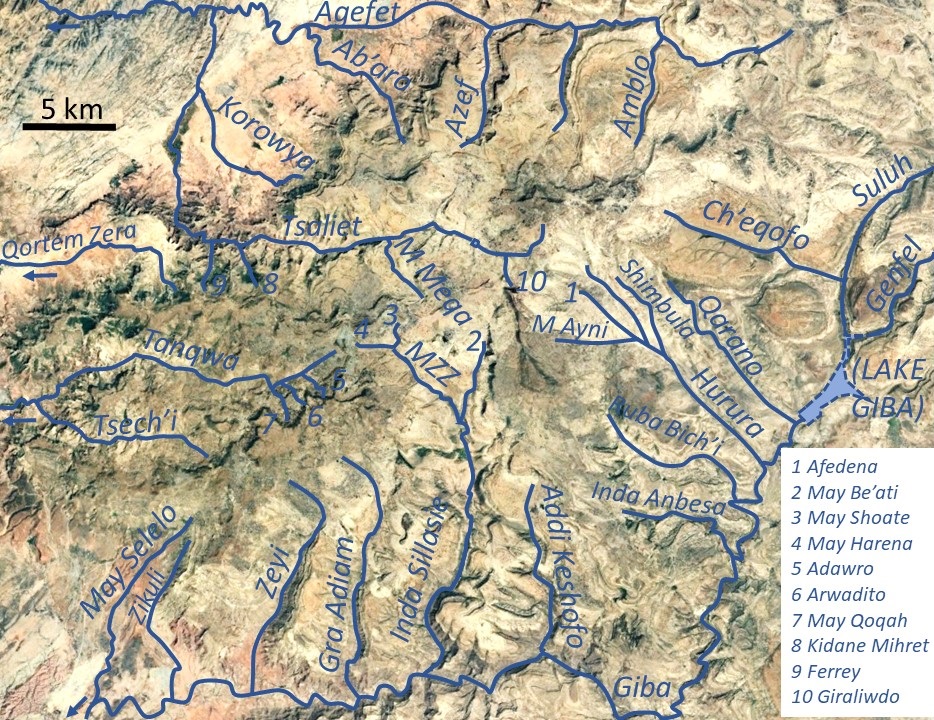
Tsech'i River
Tsech'i is a river of the Nile basin. Rising in the mountains of Dogu’a Tembien in northern Ethiopia, it flows westward to empty finally in Giba and Tekezé River. Characteristics It is a confined ephemeral river, locally meandering in its narrow alluvial plain, with an average slope gradient of 46 metres per kilometre. With its tributaries, the river has cut a deep gorge. Flash floods and flood buffering Runoff mostly happens in the form of high runoff discharge events that occur in a very short period (called flash floods). These are related to the steep topography, often little vegetation cover and intense convective rainfall. The peaks of such flash floods have often a 50 to 100 times larger discharge than the preceding baseflow. The magnitude of floods in this river has however been decreased due to interventions in the catchment. On steep slopes, exclosures have been established; the dense vegetation largely contributes to enhanced infiltration, less flooding and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Menachek
Menachek is a ''tabia'' or municipality in the Tanqua Millash district of the Tigray Region of Ethiopia. The ''tabia'' centre is in Addi Bayro village (also called "Debre Birhan"). Until January 2020 it belonged to the Dogu'a Tembien district. Geography The ''tabia'' occupies the flanks of the valley of the Tsech'i River that drains Dogu'a Tembien to the west. The highest peak is near Welekhlekha (almost 2700 m a.s.l.) and the lowest place in the lower Tsech'i gorge (1920 m a.s.l.). Geology From the higher to the lower locations, the following geological formations are present: * Upper basalt * Interbedded lacustrine deposits * Lower basalt * Amba Aradam Formation * Adigrat Sandstone Geomorphology and soils The main geomorphic units, with corresponding soil types are: * Hagere Selam Highlands, along the central basalt and sandstone ridge ** Associated soil types *** shallow soils with high stone contents (Skeletic Cambisol, Leptic Cambisol, Skeletic R ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Baseflow
Baseflow (also called drought flow, groundwater recession flow, low flow, low-water flow, low-water discharge and sustained or fair-weather runoff) is the portion of the streamflow that is sustained between precipitation events, fed to streams by delayed pathways. It should not be confused with groundwater flow. Fair weather flow is also called base flow. Importance Baseflow is important for sustaining human centers of population and ecosystems. This is especially true for watersheds that do not rely on snowmelt. Different ecological processes will occur at different parts of the hydrograph. During the baseflow ascending limb, there is frequently more stream area and habitat available for water-dependent species, spawning salmon for example. During the recession limb which in California is from May to October, there is increasingly less stream area, indigenous species are more adept at surviving in low flow conditions than introduced species. Geology Baseflow is deri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adigrat Sandstone
The Adigrat Sandstone formation in north Ethiopia, in a wide array of reddish colours, comprises sandstones with coarse to fine grains, and locally conglomerates, silt- and claystones. Given the many lateritic palaeosols and locally fossil wood fragments, the formation is interpreted as a deposit in estuarine, lacustrine-deltaic or continental environments. The upper limit of Adigrat Sandstone is of Middle-Late Jurassic age (around 160 million years or Ma ago) whereas the lower boundary is Triassic (200 Ma). There are numerous rock-hewn churches in this formation. Name and definition The name “Adigrat Sandstone” was coined by geologist William Thomas Blanford, who accompanied the British Expedition to Abyssinia in 1868. The formation is named after the town of Adigrat, on the route of the invading British army. So far the nomenclature was not proposed for recognition to the International Commission on Stratigraphy. Stratigraphic context The Adigrat Sandstone has been deposi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tufa
Tufa is a variety of limestone formed when carbonate minerals precipitate out of water in unheated rivers or lakes. Geothermally heated hot springs sometimes produce similar (but less porous) carbonate deposits, which are known as travertine. Tufa is sometimes referred to as (meteogene) travertine. It should not be confused with hot spring (thermogene) travertine. Tufa, which is calcareous, should also not be confused with tuff, a porous volcanic rock with a similar etymology that is sometimes also called "tufa". Classification and features Modern and fossil tufa deposits abound with wetland plants; as such, many tufa deposits are characterised by their large macrobiological component, and are highly porous. Tufa forms either in fluvial channels or in lacustrine environments. Ford and Pedley (1996) provide a review of tufa systems worldwide. Fluvial deposits Deposits can be classified by their depositional environment (or otherwise by vegetation or petrographically). P ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quaternary
The Quaternary ( ) is the current and most recent of the three period (geology), periods of the Cenozoic era (geology), Era in the geologic time scale of the International Commission on Stratigraphy (ICS). It follows the Neogene Period and spans from 2.58 million years ago to the present. The Quaternary Period is divided into two epochs: the Pleistocene (2.58 million years ago to 11.7 thousand years ago) and the Holocene (11.7 thousand years ago to today, although a third epoch, the Anthropocene, has been proposed but is not yet officially recognised by the ICS). The Quaternary Period is typically defined by the cyclic growth and decay of continental ice sheets related to the Milankovitch cycles and the associated climate and environmental changes that they caused. Research history In 1759 Giovanni Arduino (geologist), Giovanni Arduino proposed that the geological strata of northern Italy could be divided into four successive formations or "orders" ( it, quattro ord ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antalo Limestone
The Antalo Limestone, also known as the Antalo Sequence, is a geological formation in Ethiopia. It is between 300 and 800 metres thick and comprises fossiliferous limestones and marls that were deposited in a reef. Marine microfossils have shown an age between 165 and 150 million years. Name and definition The Antalo Supersequence includes two main stratigraphic units: the Antalo Sequence and the Agula Group. The Antalo Sequence, or Antalo Limestone has been named after the town of Hintalo in Tigray, Ethiopia. The name of the formation was coined by geologist William Thomas Blanford, who accompanied the British Expedition to Abyssinia in 1868. At that time, Hintalo was a major town on the route of the invading British army. So far the nomenclature has not been proposed for recognition to the International Commission on Stratigraphy. Geographical extent The sedimentary succession is found in Ethiopia, in the Mekelle Outlier, in the Blue Nile gorge, in the Harrar Plateau an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amba Aradam Formation
The Amba Aradam Formation is a Cretaceous sandstone formation in Ethiopia. It is up to 200 metres thick, for instance in the Degua Tembien district. As fossils are absent, the age of the Amba Aradam Formation was interpreted based on the age of assumed corresponding sandstones elsewhere in Ethiopia: the Debre Libanos Sandstones in the Blue Nile Basin, and the Upper Sandstone near Harrar in southeast Ethiopia, both of Late Cretaceous age (100–66 million years ago). The lithology of the Amba Aradam Formation makes it less suitable for rock church excavation; caves have however been blasted in this formation to serve as headquarters for the TPLF during the Ethiopian Civil War of the 1980s. Name and definition The name “Amba Aradam Sandstone” was coined by geologist William Thomas Blanford, who accompanied the British invading army in 1868. The formation is named after the Amba Aradam mountain, where the formation widely outcrops. So far the nomenclature was not proposed for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ashangi Basalts
The Ashangi Basalts are the earliest Tertiary volcanic rocks in north Ethiopia, hence they are in the lowest position. These dark porphyritic basalts are separated from the Mesozoic formations below it by basal conglomerates. The basalts hold phenocrysts that developed before the magma reached the earth surface. These basalts are weathered, partially eroded and have a sub-horizontal stratification, particularly at the lower part. This series was created during the first period of the flood basalt eruptions in north Ethiopia, in the Oligocene. Name and definition The name was coined by geologist William Thomas Blanford, who accompanied the British Expedition to Abyssinia in 1868,{{cite book , last1=Blanford , first1=W.T. , title=Observations on the geology and zoology of Abyssinia, made during the progress of the British expedition to that country in 1867-68 , url=https://archive.org/details/cu31924024736666 , date=1870 , publisher=Macmillan and Co. , location=London after Lake Ha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intra-volcanic Sedimentary Rock In North Ethiopia
Between 29 and 27 million years ago, the extrusion of Ethiopia’s flood basalts was interrupted and deposition of continental sediments occurred. Inter-trappean beds outcrop in many places of the Ethiopian highlands. They consist of fluvio-lacustrine deposits, that are generally a few tens of metres thick. Often, these interbedded fluvio-lacustrine deposits are very visible because their bright colours strongly contrast with the basalt environment. Name and definition The formation, also called ''silicified limestone'' and ''interbedded lacustrine deposits'' was first extensively characterised in the 1930s by Merla and Minucci. Stratigraphic context The formation is generally at the interface between the lower Ashangi Basalts, and the upper Alaji Basalts. Environment The sediments were deposited in shallow lakes and marshes in large topographic depressions. The dense vegetation hosted mammals and birds, which found their food between the reeds of the lake shores. The decompos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alaji Basalts
The Alaji (upper) Basalts are the youngest series of the Ethiopian flood basalts. The most recent flows are only 15 million years old. Name and definition The name was coined by geologist William Thomas Blanford, who accompanied the British Expedition to Abyssinia in 1868, after the Imba Alaje mountain. So far the nomenclature has not been proposed for recognition to the International Commission on Stratigraphy. Stratigraphic context Uppermost Tertiary flood basalts in Ethiopia. Locally they are covered by Pliocene shield volcanoes, such as the Simien Mountains, or Mount Guna. These flows have been deposited on the lower Ashangi Basalts and locally on intra-volcanic sedimentary rock. Environment Like all volcanic rocks, the Alaji Basalts originate from initial melting of the Earth's mantle. After extrusion, the magmatic structures form at the surface. Common volcanic structures such as lava tubes or ropy lavas are absent in the Alaji Basalts, but ( columnar joints) are omnipr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transhumance In Ethiopia
Transhumance is a type of pastoralism or nomadism, a seasonal movement of livestock between fixed summer and winter pastures. In montane regions (''vertical transhumance''), it implies movement between higher pastures in summer and lower valleys in winter. Herders have a permanent home, typically in valleys. Generally only the herds travel, with a certain number of people necessary to tend them, while the main population stays at the base. In contrast, ''horizontal transhumance'' is more susceptible to being disrupted by climatic, economic, or political change. Traditional or fixed transhumance has occurred throughout the inhabited world, particularly Europe and western Asia. It is often important to pastoralist societies, as the dairy products of transhumance flocks and herds (milk, butter, yogurt and cheese) may form much of the diet of such populations. In many languages there are words for the higher summer pastures, and frequently these words have been used as place names ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Check Dam
A steel check dam A check dam is a small, sometimes temporary, dam constructed across a swale, drainage ditch, or waterway to counteract erosion by reducing water flow velocity. Check dams themselves are not a type of new technology; rather, they are an ancient technique dating from the second century A.D. Check dams are typically, though not always, implemented in a system of several dams situated at regular intervals across the area of interest. Function A check dam placed in the ditch, swale, or channel interrupts the flow of water and flattens the gradient of the channel, thereby reducing the velocity. In turn, this obstruction induces infiltration and reduces eroding. They can be used not only to slow flow velocity but also to distribute flows across a swale to avoid preferential paths and guide flows toward vegetation. Although some sedimentation may result behind the dam, check dams do not primarily function as sediment-trapping devices. For instance, on the Gra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |