|
Trust Anchor
In cryptographic systems with hierarchical structure, a trust anchor is an authoritative entity for which trust is assumed and not derived. In the X.509 architecture, a root certificate would be the trust anchor from which the whole chain of trust is derived. The trust anchor must be in the possession of the trusting party beforehand to make any further certificate path validation possible. Most operating systems provide a built-in list of self-signed root certificates to act as trust anchors for applications. The Firefox Mozilla Firefox, or simply Firefox, is a free and open-source web browser developed by the Mozilla Foundation and its subsidiary, the Mozilla Corporation. It uses the Gecko rendering engine to display web pages, which implements current and ... web browser also provides its own list of trust anchors. The end-user of an operating system or web browser is implicitly trusting in the correct operation of that software, and the software manufacturer in turn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cryptography
Cryptography, or cryptology (from grc, , translit=kryptós "hidden, secret"; and ''graphein'', "to write", or ''-logia'', "study", respectively), is the practice and study of techniques for secure communication in the presence of adversarial behavior. More generally, cryptography is about constructing and analyzing protocols that prevent third parties or the public from reading private messages. Modern cryptography exists at the intersection of the disciplines of mathematics, computer science, information security, electrical engineering, digital signal processing, physics, and others. Core concepts related to information security ( data confidentiality, data integrity, authentication, and non-repudiation) are also central to cryptography. Practical applications of cryptography include electronic commerce, chip-based payment cards, digital currencies, computer passwords, and military communications. Cryptography prior to the modern age was effectively synonymo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
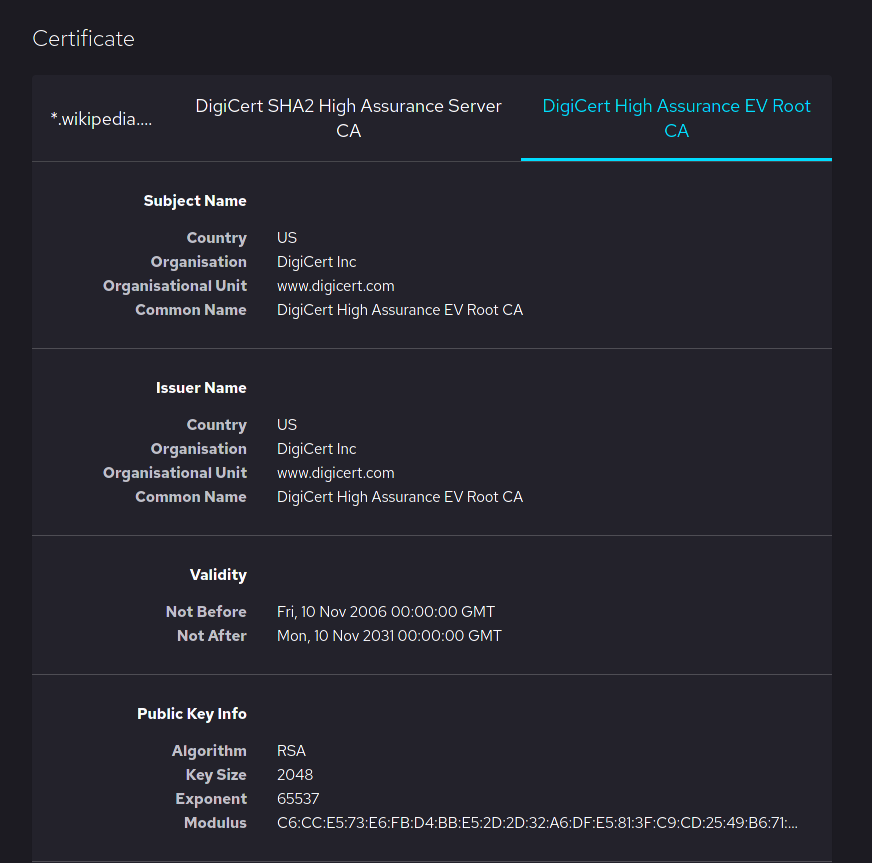
Root Certificate
In cryptography and computer security, a root certificate is a public key certificate that identifies a root certificate authority (CA). Root certificates are self-signed (and it is possible for a certificate to have multiple trust paths, say if the certificate was issued by a root that was cross-signed) and form the basis of an X.509-based public key infrastructure (PKI). Either it has matched Authority Key Identifier with Subject Key Identifier, in some cases there is no Authority Key identifier, then Issuer string should match with Subject string (). For instance, the PKIs supporting HTTPS for secure web browsing and electronic signature schemes depend on a set of root certificates. A certificate authority can issue multiple certificates in the form of a tree structure. A root certificate is the top-most certificate of the tree, the private key which is used to "sign" other certificates. All certificates signed by the root certificate, with the "CA" field set to true, inherit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chain Of Trust
In computer security, a chain of trust is established by validating each component of hardware and software from the end entity up to the root certificate. It is intended to ensure that only trusted software and hardware can be used while still retaining flexibility. Introduction A chain of trust is designed to allow multiple users to create and use software on the system, which would be more difficult if all the keys were stored directly in hardware. It starts with hardware that will only boot from software that is digitally signed. The signing authority will only sign boot programs that enforce security, such as only running programs that are themselves signed, or only allowing signed code to have access to certain features of the machine. This process may continue for several layers. This process results in a chain of trust. The final software can be trusted to have certain properties, because if it had been illegally modified its signature would be invalid, and the previou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Certification Path Validation Algorithm
The certification path validation algorithm is the algorithm which verifies that a given certificate path is valid under a given public key infrastructure (PKI). A path starts with the Subject certificate and proceeds through a number of intermediate certificates up to a trusted root certificate, typically issued by a trusted certificate authority (CA). Path validation is necessary for a relying party to make an informed trust decision when presented with any certificate that is not already explicitly trusted. For example, in a hierarchical PKI, a certificate chain starting with a web server certificate might lead to a small CA, then to an intermediate CA, then to a large CA whose trust anchor is present in the relying party's web browser. In a bridged PKI, a certificate chain starting with a user at Company A might lead to Company A's CA certificate, then to a bridge CA, then to company B's CA certificate, then to company B's trust anchor, which a relying party at company B coul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Root Certificate
In cryptography and computer security, a root certificate is a public key certificate that identifies a root certificate authority (CA). Root certificates are self-signed (and it is possible for a certificate to have multiple trust paths, say if the certificate was issued by a root that was cross-signed) and form the basis of an X.509-based public key infrastructure (PKI). Either it has matched Authority Key Identifier with Subject Key Identifier, in some cases there is no Authority Key identifier, then Issuer string should match with Subject string (). For instance, the PKIs supporting HTTPS for secure web browsing and electronic signature schemes depend on a set of root certificates. A certificate authority can issue multiple certificates in the form of a tree structure. A root certificate is the top-most certificate of the tree, the private key which is used to "sign" other certificates. All certificates signed by the root certificate, with the "CA" field set to true, inherit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Firefox
Mozilla Firefox, or simply Firefox, is a free and open-source web browser developed by the Mozilla Foundation and its subsidiary, the Mozilla Corporation. It uses the Gecko rendering engine to display web pages, which implements current and anticipated web standards. In November 2017, Firefox began incorporating new technology under the code name "Quantum" to promote parallelism and a more intuitive user interface. Firefox is available for Windows 7 and later versions, macOS, and Linux. Its unofficial ports are available for various Unix and Unix-like operating systems, including FreeBSD, OpenBSD, NetBSD, illumos, and Solaris Unix. It is also available for Android and iOS. However, as with all other iOS web browsers, the iOS version uses the WebKit layout engine instead of Gecko due to platform requirements. An optimized version is also available on the Amazon Fire TV as one of the two main browsers available with Amazon's Silk Browser. Firefox was created in 2002 under ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Certificate Authority
In cryptography, a certificate authority or certification authority (CA) is an entity that stores, signs, and issues digital certificates. A digital certificate certifies the ownership of a public key by the named subject of the certificate. This allows others (relying parties) to rely upon signatures or on assertions made about the private key that corresponds to the certified public key. A CA acts as a trusted third party—trusted both by the subject (owner) of the certificate and by the party relying upon the certificate. The format of these certificates is specified by the X.509 or EMV standard. One particularly common use for certificate authorities is to sign certificates used in HTTPS, the secure browsing protocol for the World Wide Web. Another common use is in issuing identity cards by national governments for use in electronically signing documents. Overview Trusted certificates can be used to create secure connections to a server via the Internet. A certificate is e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |