|
True Polar Wander On Mars
For some time, scientists have thought that the location of the poles of Mars shifted due to the great mass of volcanic material in the Tharsis dome which includes Olympus Mons, the highest volcano in the Solar System. For a period early in the history of Mars, the poles were about 20 degrees away from their present geographic positions. At that time ice was deposited in a region called Dorsa Argentea Formation. Also, the Martian dichotomy was aligned along the equator. A band of rivers formed at around 25 degrees south carried water from the southern highlands to the northern lowlands. After the polar shift, the location of the dichotomy boundary and the band of river valleys shifted. Dorsa Argentea was no longer at the pole. To produce the change in the pole location, the tilt of the planet remained unchanged, rather the crust and mantle moved. They rotated around the core. This study suggests that the volcanoes and the movement of the poles occurred at about the same time. V ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tharsis - Valles Marineris MOLA Shaded Colorized Zoom 32
Tharsis () is a vast volcanic plateau centered near the equator in the western hemisphere of Mars. The region is home to the largest volcanoes in the Solar System, including the three enormous shield volcanoes Arsia Mons, Pavonis Mons, and Ascraeus Mons, which are collectively known as the Tharsis Montes. The tallest volcano on the planet, Olympus Mons, is often associated with the Tharsis region but is actually located off the western edge of the plateau. The name Tharsis is the Greco-Latin transliteration of the biblical Tarshish, the land at the western extremity of the known world. Location and size Tharsis can have many meanings depending on historical and scientific context. The name is commonly used in a broad sense to represent a continent-sized region of anomalously elevated terrain centered just south of the equator around longitude 265°E.Carr, M.H. (2006). ''The Surface of Mars;'' Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, p. 46. . Called the Tharsis bulge or Thar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tharsis
Tharsis () is a vast volcanic plateau centered near the equator in the western hemisphere of Mars. The region is home to the largest volcanoes in the Solar System, including the three enormous shield volcanoes Arsia Mons, Pavonis Mons, and Ascraeus Mons, which are collectively known as the Tharsis Montes. The tallest volcano on the planet, Olympus Mons, is often associated with the Tharsis region but is actually located off the western edge of the plateau. The name Tharsis is the Greco-Latin transliteration of the biblical Tarshish, the land at the western extremity of the known world. Location and size Tharsis can have many meanings depending on historical and scientific context. The name is commonly used in a broad sense to represent a continent-sized region of anomalously elevated terrain centered just south of the equator around longitude 265°E.Carr, M.H. (2006). ''The Surface of Mars;'' Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, p. 46. . Called the Tharsis bulge or Thar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Olympus Mons
Olympus Mons (; Latin for Mount Olympus) is a large shield volcano on Mars. The volcano has a height of over 21.9 km (13.6 mi or 72,000 ft) as measured by the Mars Orbiter Laser Altimeter (MOLA). Olympus Mons is about two and a half times Mount Everest's height above sea level. It is one of the largest volcanoes, the tallest planetary mountain, and approximately tied with Rheasilvia as the tallest mountain currently discovered in the Solar System. It is associated with the Tharsis Montes, a large volcanic region on Mars. Olympus Mons is the youngest of the large volcanoes on Mars, having formed during Mars's Hesperian Period with eruptions continuing well into the Amazonian. It had been known to astronomers since the late 19th century as the albedo feature Nix Olympica (Latin for "Olympic Snow"). Its mountainous nature was suspected well before space probes confirmed its identity as a mountain. The volcano is located in Mars's western hemisphere, with the cent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Solar System
The Solar SystemCapitalization of the name varies. The International Astronomical Union, the authoritative body regarding astronomical nomenclature, specifies capitalizing the names of all individual astronomical objects but uses mixed "Solar System" and "solar system" structures in theinaming guidelines document. The name is commonly rendered in lower case ('solar system'), as, for example, in the ''Oxford English Dictionary'' an''Merriam-Webster's 11th Collegiate Dictionary''. is the gravity, gravitationally bound system of the Sun and the objects that orbit it. It Formation and evolution of the Solar System, formed 4.6 billion years ago from the gravitational collapse of a giant interstellar molecular cloud. The solar mass, vast majority (99.86%) of the system's mass is in the Sun, with most of the Jupiter mass, remaining mass contained in the planet Jupiter. The four inner Solar System, inner system planets—Mercury (planet), Mercury, Venus, Earth and Mars—are terrest ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dorsa Argentea Formation
The Dorsa Argentea Formation (DAF) is thought to be a large system of eskers that were under an ancient ice cap in the south polar region of Mars. The ancient ice cap was at least twice the size of the present ice cap and may have been 1500–2000 meters thick. Later research suggests that the area of this polar ice sheet is believed to have covered about 1.5 million square kilometers, roughly twice the size of France or the American state of Texas. This group of ridges extends from 270–100 E and 70–90 S, around the south pole of Mars. It sits under the Late Amazonian South Polar Layered Deposits (SPLD), in the Mare Australe quadrangle. The combined length of these ridges is huge, one study studied seven different ridge systems which contained almost 4,000 ridges that had a total length 51,000 km. Most eskers are thought to be formed inside ice-walled tunnels by streams which flowed within and under glaciers. After the retaining ice walls melted away, stream deposits re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Martian Dichotomy
The most conspicuous feature of Mars is a sharp contrast, known as the Martian dichotomy, between the Southern and the Northern hemispheres. The two hemispheres' geography differ in elevation by 1 to 3 km. The average thickness of the Martian crust is 45 km, with 32 km in the northern lowlands region, and 58 km in the southern highlands. The boundary between the two regions is quite complex in places. One distinctive type of topography is called fretted terrain. It contains mesas, knobs, and flat-floored valleys having walls about a mile high. Around many of the mesas and knobs are lobate debris aprons that have been shown to be rock glaciers. Many large valleys formed by the lava erupted from the volcanoes of Mars cut through the dichotomy. The Martian dichotomy boundary includes the regions called Deuteronilus Mensae, Protonilus Mensae, and Nilosyrtis Mensae. All three regions have been studied extensively because they contain landforms believed to hav ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amazonis Quadrangle
The Amazonis quadrangle is one of a series of 30 quadrangle maps of Mars used by the United States Geological Survey (USGS) Astrogeology Research Program. The Amazonis quadrangle is also referred to as MC-8 (Mars Chart-8). The quadrangle covers the area from 135° to 180° west longitude and 0° to 30° north latitude on Mars. The Amazonis quadrangle contains the region called Amazonis Planitia. This area is thought to be among the youngest parts of Mars because it has a very low density of craters. The Amazonian Epoch is named after this area. This quadrangle contains special, unusual features called the Medusae Fossae Formation and Sulci. Medusae Fossae Formation The Amazonis quadrangle is of great interest to scientists because it contains a big part of a formation, called the Medusae Fossae Formation. It is a soft, easily eroded deposit that extends for nearly 1,000 km along the equator of Mars. The surface of the formation has been eroded by the wind into a series ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tharsis Quadrangle
The Tharsis quadrangle is one of a series of 30 quadrangle maps of Mars used by the United States Geological Survey (USGS) Astrogeology Research Program. The Tharsis quadrangle is also referred to as MC-9 (Mars Chart-9). The name Tharsis refers to a land mentioned in the Bible. It may be at the location of the old town of Tartessus at the mouth of Guadalquivir. The quadrangle covers the area from 90° to 135° west longitude and 0° to 30° north latitude on Mars and contains most of the Tharsis Rise. The plateau is about as high as Earth's Mount Everest and about as big in area as all of Europe. Tharsis contains a group of large volcanoes. Olympus Mons is the tallest. Within the quadrangle, the two largest impact craters are Poynting and Paros. Volcanoes Tharsis is a land of great volcanoes. Olympus Mons is the tallest known volcano in the Solar System; it is 100 times larger than any volcano on Earth. Ascraeus Mons and Pavonis Mons are at least 200 miles across a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
True Polar Wander
True polar wander is a solid-body rotation of a planet or moon with respect to its spin axis, causing the geographic locations of the north and south poles to change, or "wander". Unless the body is totally rigid (which the Earth is not) its stable state rotation has the largest moment of inertia axis aligned with the spin axis, with the smaller two moments of inertia axes lying in the plane of the equator. If the body is not in this steady state, true polar wander will occur: the planet or moon will rotate as a rigid body to realign the largest moment of inertia axis with the spin axis. (See .) If the body is near the steady state but with the angular momentum not exactly lined up with the largest moment of inertia axis, the pole position will oscillate. Weather and water movements can also induce small changes. These subjects are covered in the article ''Polar motion''. Description in the context of Earth The mass distribution of the Earth is not spherically symmetric, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geography Of Mars
Areography, also known as the geography of Mars, is a subfield of planetary science that entails the delineation and characterization of regions on Mars. Areography is mainly focused on what is called physical geography on Earth; that is the distribution of physical features across Mars and their cartographic representations. History The first detailed observations of Mars were from ground-based telescopes. The history of these observations are marked by the oppositions of Mars, when the planet is closest to Earth and hence is most easily visible, which occur every couple of years. Even more notable are the perihelic oppositions of Mars which occur approximately every 16 years, and are distinguished because Mars is closest to earth and Jupiter perihelion making it even closer to Earth. In September 1877, (a perihelic opposition of Mars occurred on September 5), Italian astronomer Giovanni Schiaparelli published the first detailed map of Mars. These maps notably contained feat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
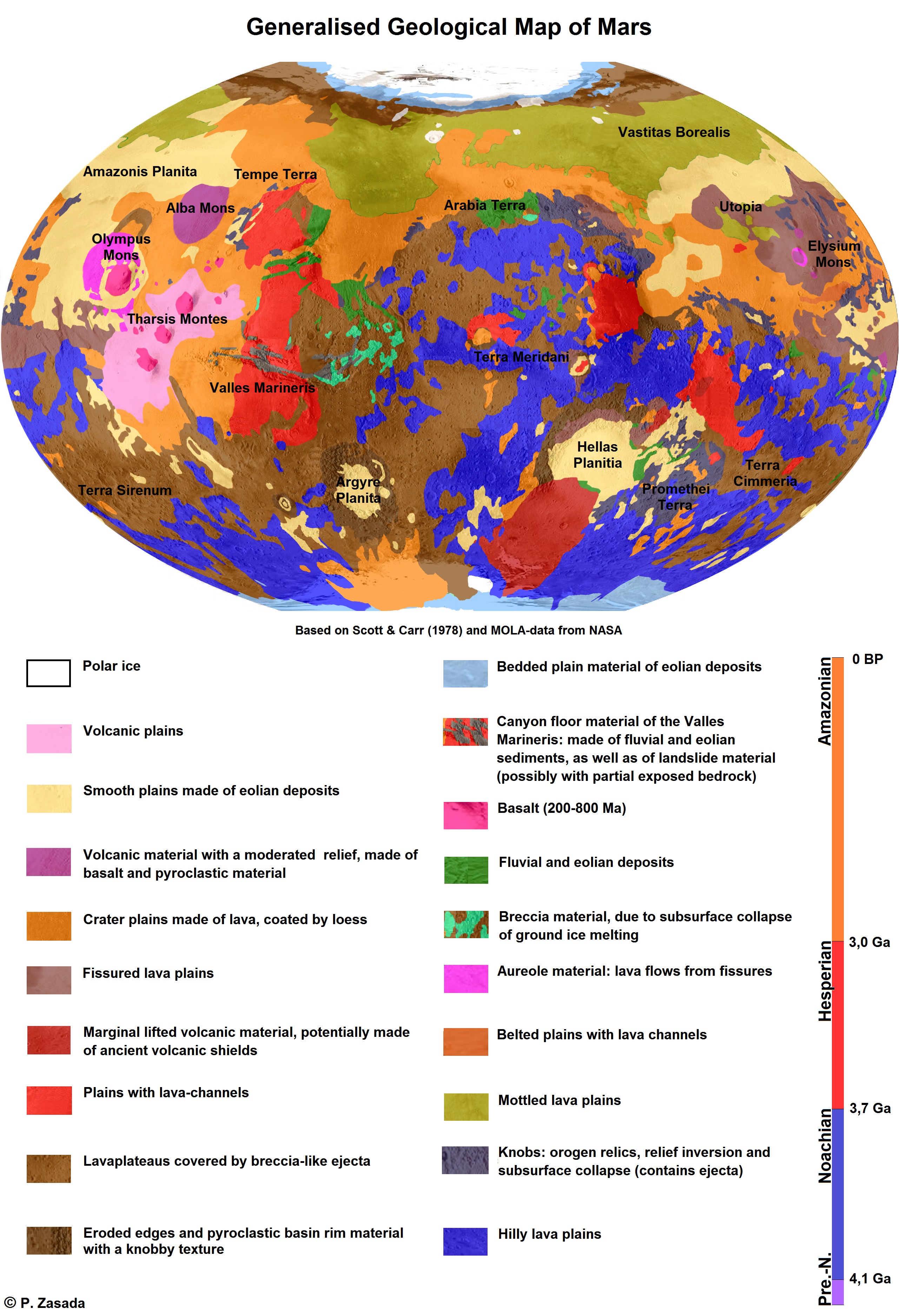
Geology Of Mars
The geology of Mars is the scientific study of the surface, crust, and interior of the planet Mars. It emphasizes the composition, structure, history, and physical processes that shape the planet. It is analogous to the field of terrestrial geology. In planetary science, the term ''geology'' is used in its broadest sense to mean the study of the solid parts of planets and moons. The term incorporates aspects of geophysics, geochemistry, mineralogy, geodesy, and cartography. A neologism, areology, from the Greek word ''Arēs'' (Mars), sometimes appears as a synonym for Mars's geology in the popular media and works of science fiction (e.g. Kim Stanley Robinson, Kim Stanley Robinson's Mars trilogy). The term areology is also used by the Areological Society. Geological map of Mars (2014) File:Geologic Map of Mars figure2.pdf, Figure 2 for the geologic map of Mars Global Martian topography and large-scale features Composition of Mars Mars is a terrestrial planet, whic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Volcanism On Mars
Volcanic activity, or volcanism, has played a significant role in the geologic evolution of Mars. Scientists have known since the Mariner 9 mission in 1972 that volcanic features cover large portions of the Martian surface. These features include extensive lava flows, vast lava plains, and the largest known volcanoes in the Solar System. Martian volcanic features range in age from Noachian (>3.7 billion years) to late Amazonian (< 500 million years), indicating that the planet has been volcanically active throughout its history, and some speculate it probably still is so today. Both and Mars are large, differentiated |




_with_poles_HiRes.jpg)