|
Tropical Storm George (other)
The name George has been used for three tropical cyclones in the Atlantic Ocean and for one in the Australian region of the South-East Indian Ocean. In the Atlantic: * 1947 Fort Lauderdale hurricane, designated "George" by the Weather Bureau office in Miami * Hurricane George (1950), developed southeast of Bermuda, intensified to Category 2 hurricane and became extratropical south of Newfoundland * Tropical Storm George (1951), struck Bay of Campeche and made landfall in Tampico, Mexico In the Australian region: * Cyclone George (2007), developed in the Joseph Bonaparte Gulf, intensified to a Category 5 severe tropical cyclone (Australian scale) and hit the Pilbara coast See also * List of hurricanes named Georges * Hurricane Georgette The name Georgette has been used for eleven tropical cyclones in the Eastern Pacific Ocean. One of these crossed into the Western Pacific Ocean where it degraded into a tropical wave then regenerated into a severe tropical storm. * Tro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tropical Cyclone
A tropical cyclone is a rapidly rotating storm system characterized by a low-pressure center, a closed low-level atmospheric circulation, strong winds, and a spiral arrangement of thunderstorms that produce heavy rain and squalls. Depending on its location and strength, a tropical cyclone is referred to by different names, including hurricane (), typhoon (), tropical storm, cyclonic storm, tropical depression, or simply cyclone. A hurricane is a strong tropical cyclone that occurs in the Atlantic Ocean or northeastern Pacific Ocean, and a typhoon occurs in the northwestern Pacific Ocean. In the Indian Ocean, South Pacific, or (rarely) South Atlantic, comparable storms are referred to simply as "tropical cyclones", and such storms in the Indian Ocean can also be called "severe cyclonic storms". "Tropical" refers to the geographical origin of these systems, which form almost exclusively over tropical seas. "Cyclone" refers to their winds moving in a circle, whirling round ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hurricane George (1950)
The 1950 Atlantic hurricane season was the first year in the Atlantic hurricane database (HURDAT) that storms were given names in the Atlantic basin. Names were taken from the Joint Army/Navy Phonetic Alphabet, with the first named storm being designated "Able", the second "Baker", and so on. It was a very active season with sixteen tropical storms, with eleven of them developing into hurricanes. Six of these hurricanes were intense enough to be classified as major hurricanes—a denomination reserved for storms that attained sustained winds equivalent to a Category 3 or greater on the present-day Saffir–Simpson scale. One storm, the twelfth of the season, was unnamed and was originally excluded from the yearly summary, and three additional storms were discovered in re-analysis. The large quantity of strong storms during the year yielded, prior to modern reanalysis, what was the highest seasonal accumulated cyclone energy (ACE) of the 20th century in the Atlantic basin; 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tropical Storm George (1951)
The 1951 Atlantic hurricane season was the first hurricane season in which tropical cyclones were officially named by the United States Weather Bureau. The season A season is a division of the year based on changes in weather, ecology, and the number of daylight hours in a given region. On Earth, seasons are the result of the axial parallelism of Earth's tilted orbit around the Sun. In temperate and pol ... officially started on June 15, when the NOAA, United States Weather Bureau began its daily monitoring for tropical cyclone activity; the season officially ended on November 15. It was the first year since 1937 Atlantic hurricane season, 1937 in which no hurricanes made landfall (meteorology), landfall on the United States; as Hurricane How was the only tropical storm to hit the nation, the season had the least tropical cyclone damage in the United States since the 1939 Atlantic hurricane season, 1939 season. As in the 1950 Atlantic hurricane season, 1950 season, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
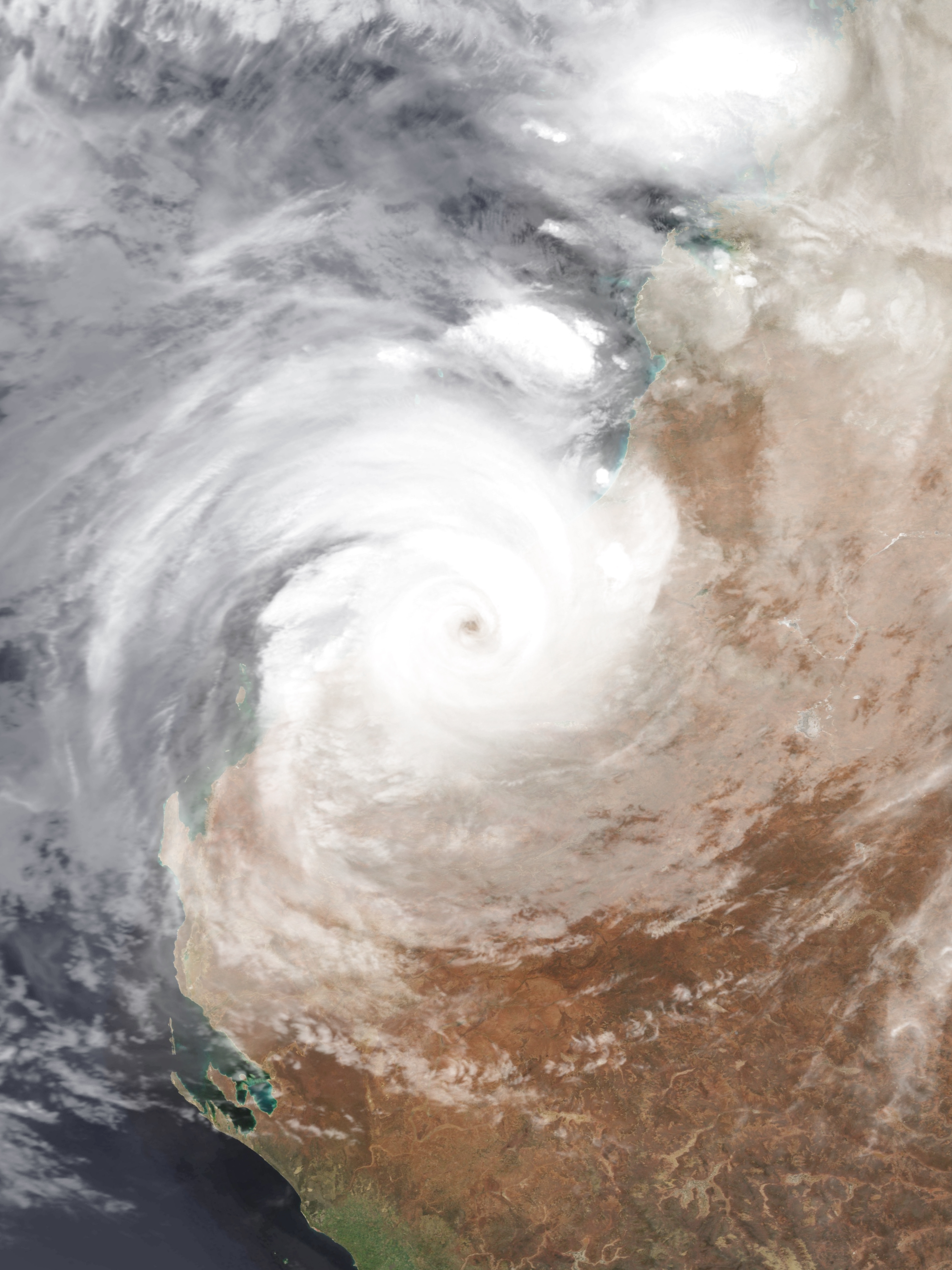
Cyclone George
Severe Tropical Cyclone George was one of the most powerful Australian tropical cyclones on record, attaining a minimum barometric pressure of 902 mbar (hPa; 26.64 inHg). It was also the strongest tropical cyclone worldwide in 2007 and the last Australian region tropical cyclone to achieve this record to date. The cyclone formed on 26 February 2007 in the Northern Territory's Top End, and intensified when it entered the Joseph Bonaparte Gulf, before crossing the northern coast of the Kimberley. It moved over the Indian Ocean, intensifying to a Category 4 cyclone, and eventually crossed the Pilbara coast just east of Port Hedland at peak intensity. After further analysis from the Bureau of Meteorology, George was reclassified to Category 5. The cyclone caused significant damage to the town of Port Hedland and numerous isolated mining camps around the town. Losses in Northern Territory amounted to at least A$12 million (US$9.5 million). Two people died a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Hurricanes Named Georges
The name Georges was used for two tropical cyclones in the Atlantic Ocean. * Hurricane Georges (1980) – Category 1 hurricane looped across the north Atlantic Ocean without causing any reported damage. * Hurricane Georges (1998) – Category 4 hurricane that wrought death and destruction across the Caribbean and Gulf of Mexico. The name "Georges" was retired after the hurricane in 1998 and was replaced by "Gaston" in 2004. See also * Tropical Storm George * Hurricane Georgette The name Georgette has been used for eleven tropical cyclones in the Eastern Pacific Ocean. One of these crossed into the Western Pacific Ocean where it degraded into a tropical wave then regenerated into a severe tropical storm. * Tropical Storm ... {{DEFAULTSORT:Georges, Hurricane Atlantic hurricane set index articles ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hurricane Georgette
The name Georgette has been used for eleven tropical cyclones in the Eastern Pacific Ocean. One of these crossed into the Western Pacific Ocean where it degraded into a tropical wave then regenerated into a severe tropical storm. * Tropical Storm Georgette (1967) – never affected land * Tropical Storm Georgette (1971) – remained over the open ocean * Tropical Storm Georgette (1975) – had no impact on land * Hurricane Georgette (1980) – had no impact * Tropical Storm Georgette (1986) – weak storm that degraded into a tropical wave and crossed into the Western Pacific where it reorganized * Hurricane Georgette (1992) – Category 2 hurricane, remained over the open ocean * Hurricane Georgette (1998) – Category 3 major hurricane, never affected land * Tropical Storm Georgette (2004) – remained over the open ocean * Tropical Storm Georgette (2010) – short-lived storm that struck Baja California Sur * Hurricane Georgette (2016) – Category 4 major hurricane, chur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atlantic Hurricane Set Index Articles
The Atlantic Ocean is the second-largest of the world's five oceans, with an area of about . It covers approximately 20% of Earth's surface and about 29% of its water surface area. It is known to separate the "Old World" of Africa, Europe and Asia from the "New World" of the Americas in the European perception of the World. The Atlantic Ocean occupies an elongated, S-shaped basin extending longitudinally between Europe and Africa to the east, and North and South America to the west. As one component of the interconnected World Ocean, it is connected in the north to the Arctic Ocean, to the Pacific Ocean in the southwest, the Indian Ocean in the southeast, and the Southern Ocean in the south (other definitions describe the Atlantic as extending southward to Antarctica). The Atlantic Ocean is divided in two parts, by the Equatorial Counter Current, with the North(ern) Atlantic Ocean and the South(ern) Atlantic Ocean split at about 8°N. Scientific explorations of the Atlantic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |