|
Tropical Storm Emilia (2006)
Tropical Storm Emilia was a rare tropical cyclone that affected the Baja California Peninsula in July 2006. The sixth tropical depression and fifth tropical storm of the 2006 Pacific hurricane season, it developed on July 21 about 400 miles (650 km) off the coast of Mexico. It moved northward toward the coast, reaching peak winds of 65 mph (105 km/h) before turning westward and encountering unfavorable conditions. Emilia later turned to the north, passing near Baja California as a strong tropical storm. Subsequently, the storm moved further away from the coast, and on July 27 it dissipated. The storm brought tropical storm force winds and precipitation to the southwestern Mexican coastline. Later, Emilia produced similar conditions in the southern portion of the Baja California peninsula, where its passage caused minor damage and flooding. Moisture from Emilia reached the southwestern United States, producing thunderstorms and flash flooding in Arizona, as wel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saffir–Simpson Scale
The Saffir–Simpson hurricane wind scale (SSHWS) classifies hurricanes—which in the Western Hemisphere are tropical cyclones that exceed the intensities of tropical depressions and tropical storms—into five categories distinguished by the intensities of their sustained winds. This measuring system was formerly known as the Saffir–Simpson hurricane scale, or SSHS. To be classified as a hurricane, a tropical cyclone must have one-minute-average maximum sustained winds at 10 m above the surface of at least 74 mph (64 kn, 119 km/h; Category 1). The highest classification in the scale, Category 5, consists of storms with sustained winds of at least 157 mph (137 kn, 252 km/h). The classifications can provide some indication of the potential damage and flooding a hurricane will cause upon landfall. The Saffir–Simpson hurricane wind scale is based on the highest wind speed averaged over a one-minute interval 10 m above th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Santa Cruz County, Arizona
Santa Cruz is a County (United States), county in southern Arizona, United States. As of the 2020 United States census, 2020 census, the population is 47,669. The county seat is Nogales, Arizona, Nogales. The county was established in 1899. It borders Pima County, Arizona, Pima County to the north and west, Cochise County, Arizona, Cochise County to the east, and the Mexican state of Sonora (state), Sonora to the south. Santa Cruz County includes the Nogales, Arizona Micropolitan Statistical Area, which is also included in the Tucson, Arizona, Tucson-Nogales, Arizona Combined Statistical Area. History Santa Cruz County, formed on March 15, 1899, out of what was then Pima County, Arizona, Pima County, is named after the Santa Cruz River (Arizona), Santa Cruz River. The river originates in the Canelo Hills in the eastern portion of the county, crosses south into Mexico near the community of Santa Cruz, Sonora and then bends northwards returning into the United States (and Santa C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cabo San Lucas
Cabo San Lucas (, "Saint Luke Cape"), or simply just Cabo, is a resort city at the southern tip of the Baja California Peninsula, in the Mexican state of Baja California Sur. As at the 2020 Census, the population of the city was 202,694 inhabitants.2020 Census of Mexico. Cabo San Lucas together with the famous San José del Cabo are collectively known as Los Cabos. Together, they form a metropolitan area of 351,111 inhabitants.2020 Census of Mexico. Rated as one of Mexico's top five tourist destinations, Cabo is known for its beaches, scuba diving locations, Balnearios, the sea arch El Arco de Cabo San Lucas, and marine life. The Los Cabos Corridor has become a heavily trafficked vacation destination for tourists, with numerous resorts and timeshares along the coast between Cabo San Lucas and San José del Cabo. The waters around Cabo are home to marine wildlife including rays, sharks, mahi-mahi (dorado), and striped marlin. History Archaeological excavations have shown evidenc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magdalena Bay
Magdalena Bay ( es, Bahía Magdalena) is a long bay in Comondú Municipality along the western coast of the Mexican state of Baja California Sur. It is protected from the Pacific Ocean by the unpopulated sandy barrier islands of Isla Magdalena and Isla Santa Margarita. Ecology This bay is particularly noted for the seasonal migration of the California gray whales that come here during winter to calve. The bay is also popular for commercial and sports fishing. Nearby mangrove swamps provide sanctuaries for sea birds. The bay includes the small fishing port of San Carlos, as well as Puerto López Mateos, which provides a good place to observe the whales. Islands Sandy barrier islands Isla Magdalena and Isla Santa Margarita separate the bay from the Pacific Ocean. Magdalena, mostly to the north and facing northwest, is a long, slender, segmented island that parallels the coast a few miles north. There is a small settlement, Puerto Magdalena mostly active during whale wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
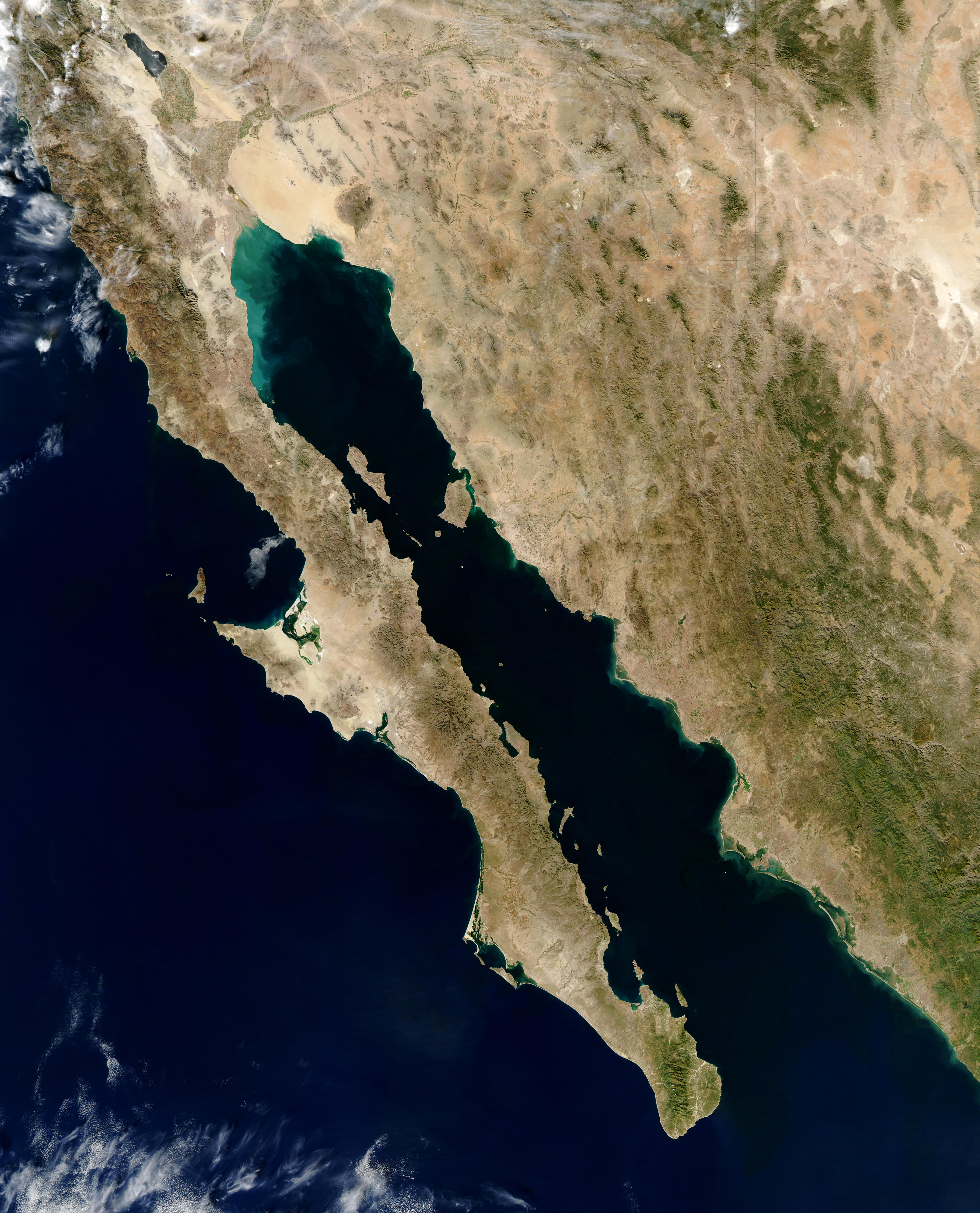
Gulf Of California
The Gulf of California ( es, Golfo de California), also known as the Sea of Cortés (''Mar de Cortés'') or Sea of Cortez, or less commonly as the Vermilion Sea (''Mar Bermejo''), is a marginal sea of the Pacific Ocean that separates the Baja California Peninsula from the Mexico, Mexican mainland. It is bordered by the states of Baja California, Baja California Sur, Sonora, and Sinaloa with a coastline of approximately . Rivers that flow into the Gulf of California include the Colorado River, Colorado, Fuerte River, Fuerte, Mayo River (Mexico), Mayo, Sinaloa River, Sinaloa, Sonora River, Sonora, and the Yaqui River, Yaqui. The surface of the gulf is about . Maximum depths exceed because of the complex geology, linked to plate tectonics. The gulf is thought to be one of the most diverse seas on Earth and is home to more than 5,000 species of micro-invertebrates. Parts of the Gulf of California are a UNESCO World Heritage Site. Geography History The marine expeditions of Fortún ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Buena Vista, Baja California Sur
Buena ( ) is a borough in Atlantic County, New Jersey, United States. As of the 2010 United States Census, the borough's population was 4,603,DP-1 - Profile of General Population and Housing Characteristics: 2010 for Buena borough, Atlantic County, New Jersey . Accessed July 8, 2013. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |