|
Tropical Storm Diane (other)
The name Diane has been used for three tropical cyclones worldwide, one in the Atlantic Ocean and two in the South-West Indian Ocean. In the Atlantic: * Hurricane Diane Hurricane Diane was the first Atlantic hurricane to cause more than an estimated $1 billion in damage (in 1955 dollars, which would be $ today), including direct costs and the loss of business and personal revenue. It formed on August 7 ... (1955), caused US$831.7 million (1955 USD) in damage and 184 deaths in the Eastern United States In the South-West Indian: * Tropical Depression Diane (1960) * Tropical Storm Diane (2020) - Caused flooding in Madagascar {{DEFAULTSORT:Diane Atlantic hurricane set index articles South-West Indian Ocean cyclone set index articles ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tropical Cyclone
A tropical cyclone is a rapidly rotating storm system characterized by a low-pressure center, a closed low-level atmospheric circulation, strong winds, and a spiral arrangement of thunderstorms that produce heavy rain and squalls. Depending on its location and strength, a tropical cyclone is referred to by different names, including hurricane (), typhoon (), tropical storm, cyclonic storm, tropical depression, or simply cyclone. A hurricane is a strong tropical cyclone that occurs in the Atlantic Ocean or northeastern Pacific Ocean, and a typhoon occurs in the northwestern Pacific Ocean. In the Indian Ocean, South Pacific, or (rarely) South Atlantic, comparable storms are referred to simply as "tropical cyclones", and such storms in the Indian Ocean can also be called "severe cyclonic storms". "Tropical" refers to the geographical origin of these systems, which form almost exclusively over tropical seas. "Cyclone" refers to their winds moving in a circle, whirling round ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
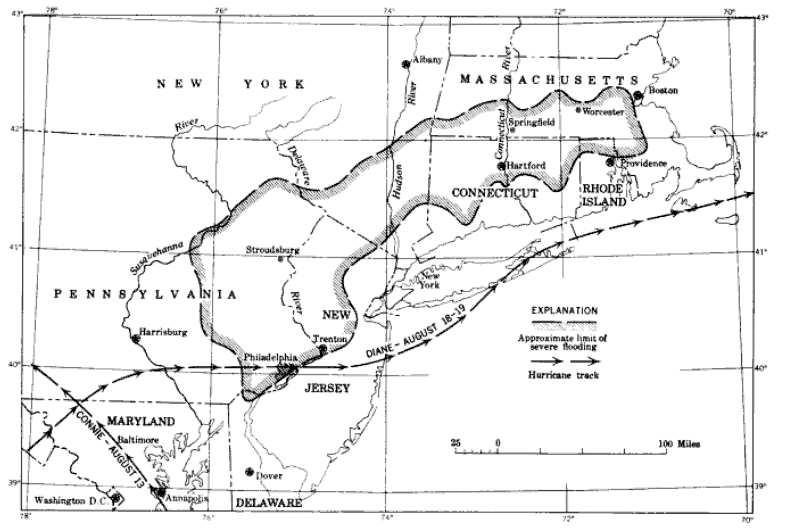
Hurricane Diane
Hurricane Diane was the first Atlantic hurricane to cause more than an estimated $1 billion in damage (in 1955 dollars, which would be $ today), including direct costs and the loss of business and personal revenue. It formed on August 7 from a tropical wave between the Lesser Antilles and Cape Verde. Diane initially moved west-northwestward with little change in its intensity, but began to strengthen rapidly after turning to the north-northeast. On August 12, the hurricane reached peak sustained winds of 105 mph (165 km/h), making it a Category 2 hurricane. Gradually weakening after veering back west, Diane made landfall near Wilmington, North Carolina, as a strong tropical storm on August 17, just five days after Hurricane Connie struck near the same area. Diane weakened further after moving inland, at which point the United States Weather Bureau noted a decreased threat of further destruction. The storm turned to the northeast, and warm waters fr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1959–60 South-West Indian Ocean Cyclone Season
The 1959–60 South-West Indian Ocean cyclone season featured the beginning of tropical cyclone naming in the basin. Systems November tropical cyclone A tropical cyclone was observed northeast of Madagascar on November 26. The storm moved westward, passing north of the island on December 6. Two days later, the storm moved through the Comoros. On December 9, the cyclone struck northeastern Mozambique, dissipating soon after. December tropical cyclone On December 26, a tropical cyclone was first observed west of Diego Garcia. The system moved westward at first, passing north of Tromelin Island on December 30. The track shifted to the southwest, bringing the storm between Madagascar and Réunion. The storm was last observed on January 4, moving southward away from land. Tropical Cyclone Alix A tropical cyclone developed south of Diego Garcia on January 10, which would eventually become Cyclone Alix, the first named storm in the basin. The storm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tropical Storm Diane (2020)
Hurricane Diane was the first Atlantic hurricane to cause more than an estimated $1 billion in damage (in 1955 dollars, which would be $ today), including direct costs and the loss of business and personal revenue. It formed on August 7 from a tropical wave between the Lesser Antilles and Cape Verde. Diane initially moved west-northwestward with little change in its intensity, but began to strengthen rapidly after turning to the north-northeast. On August 12, the hurricane reached peak sustained winds of 105 mph (165 km/h), making it a Category 2 hurricane. Gradually weakening after veering back west, Diane made landfall near Wilmington, North Carolina, as a strong tropical storm on August 17, just five days after Hurricane Connie struck near the same area. Diane weakened further after moving inland, at which point the United States Weather Bureau noted a decreased threat of further destruction. The storm turned to the northeast, and warm waters ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atlantic Hurricane Set Index Articles
The Atlantic Ocean is the second-largest of the world's five oceans, with an area of about . It covers approximately 20% of Earth's surface and about 29% of its water surface area. It is known to separate the "Old World" of Africa, Europe and Asia from the "New World" of the Americas in the European perception of the World. The Atlantic Ocean occupies an elongated, S-shaped basin extending longitudinally between Europe and Africa to the east, and North and South America to the west. As one component of the interconnected World Ocean, it is connected in the north to the Arctic Ocean, to the Pacific Ocean in the southwest, the Indian Ocean in the southeast, and the Southern Ocean in the south (other definitions describe the Atlantic as extending southward to Antarctica). The Atlantic Ocean is divided in two parts, by the Equatorial Counter Current, with the North(ern) Atlantic Ocean and the South(ern) Atlantic Ocean split at about 8°N. Scientific explorations of the Atlantic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |