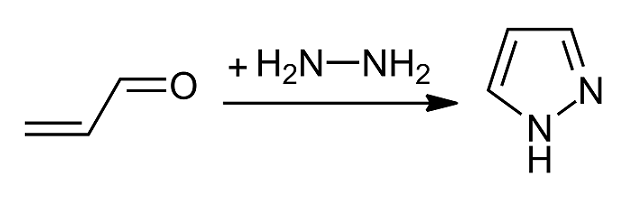|
Trispyrazolylborate
In inorganic chemistry, the trispyrazolylborate ligand, abbreviated Tp−, is an anionic tridentate and tripodal ligand. Trispyrazolylborate refers specifically to the anion B(C3N2H3)3sup>−, but the term trispyrazolylborate refers to derivatives substituted at on the pyrazolyl rings. This family of compounds are sometimes called scorpionate ligands. Tp ligands As suggested by the resonance structures, the nitrogen centers that are not bonded to boron are basic. These centers bind to three adjacent sites of a metal such that the simple adducts have C3v symmetry. The facial bonding mode is reminiscent of cyclopentadienyl ligands, although the ligand field stabilization energy of Tp− is weaker as indicated by the fact that Fe(Tp)2 is a spin-crossover complex whereas ferrocene is low-spin. The Tp ligands are usually prepared from the reaction of pyrazole with potassium borohydride: :KBH4 + 3 C3H3N2H → K B(C3N2H3)3 + 3H2 Intermediates include the monopyrazolylborate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tp Dicarbonyl Nitrosyl Complex Of Mo
TP may refer to: Arts and entertainment Music * Test pressing, of a vinyl record * Tonic parallel (Tp and tP), in music theory * TP (Teddy Pendergrass album), ''TP'' (Teddy Pendergrass album), 1980 * TP (Tony Parker album), ''TP'' (Tony Parker album), 2007 * Tonus Peregrinus (vocal ensemble), a British group * Either of two R&B albums by R. Kelly: ** ''TP-2.com'', 2000 ** ''TP.3 Reloaded'', 2005 Other media * ''The Legend of Zelda: Twilight Princess'', a Nintendo video game * Test pattern or test card, a broadcast television signal * ''The Tomorrow People'', a British science fiction television series Businesses and organizations Technology brands and businesses * TP-Link, a global manufacturer of computer networking products * TP Vision, a subsidiary of TPV Technology, Amsterdam, Netherlands * Telekomunikacja Polska (now ''Orange Polksa''), a Polish telecommunications provider * ThinkPad, Lenovo's line of business laptop computers and tablets Transport businesses * TAP Air P ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pyrazole
Pyrazole is an organic compound with the formula C3H3N2H. It is a heterocycle characterized by a 5-membered ring of three carbon Carbon () is a chemical element with the symbol C and atomic number 6. It is nonmetallic and tetravalent In chemistry, the valence (US spelling) or valency (British spelling) of an element is the measure of its combining capacity with o ... atoms and two adjacent nitrogen atoms, which are in Arene substitution pattern, ortho-substitution. Pyrazole is a weak base, with p''K''b 11.5 (p''K''a of the conjugate acid 2.49 at 25 °C). Pyrazoles are also a class of compounds that have the ring C3N2 with adjacent nitrogen atoms. Notable drugs containing a pyrazole ring are celecoxib (celebrex) and the anabolic steroid stanozolol. Preparation and reactions Pyrazoles are synthesized by the reaction of α,β-unsaturated aldehydes with hydrazine and subsequent dehydrogenation: : Substituted pyrazoles are prepared by condensation of 1,3-diketones ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acetonitrile
Acetonitrile, often abbreviated MeCN (methyl cyanide), is the chemical compound with the formula and structure . This colourless liquid is the simplest organic nitrile (hydrogen cyanide is a simpler nitrile, but the cyanide anion is not classed as organic). It is produced mainly as a byproduct of acrylonitrile manufacture. It is used as a polar aprotic solvent in organic synthesis and in the purification of butadiene. The skeleton is linear with a short distance of 1.16 Å. Acetonitrile was first prepared in 1847 by the French chemist Jean-Baptiste Dumas. Applications Acetonitrile is used mainly as a solvent in the purification of butadiene in refineries. Specifically, acetonitrile is fed into the top of a distillation column filled with hydrocarbons including butadiene, and as the acetonitrile falls down through the column, it absorbs the butadiene which is then sent from the bottom of the tower to a second separating tower. Heat is then employed in the separatin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Organometallic Chemistry
Organometallic chemistry is the study of organometallic compounds, chemical compounds containing at least one chemical bond between a carbon atom of an organic molecule and a metal, including alkali, alkaline earth, and transition metals, and sometimes broadened to include metalloids like boron, silicon, and selenium, as well. Aside from bonds to organyl fragments or molecules, bonds to 'inorganic' carbon, like carbon monoxide (metal carbonyls), cyanide, or carbide, are generally considered to be organometallic as well. Some related compounds such as transition metal hydrides and metal phosphine complexes are often included in discussions of organometallic compounds, though strictly speaking, they are not necessarily organometallic. The related but distinct term " metalorganic compound" refers to metal-containing compounds lacking direct metal-carbon bonds but which contain organic ligands. Metal β-diketonates, alkoxides, dialkylamides, and metal phosphine complexes are repres ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, responding to stimuli, providing structure to cells and organisms, and transporting molecules from one location to another. Proteins differ from one another primarily in their sequence of amino acids, which is dictated by the nucleotide sequence of their genes, and which usually results in protein folding into a specific 3D structure that determines its activity. A linear chain of amino acid residues is called a polypeptide. A protein contains at least one long polypeptide. Short polypeptides, containing less than 20–30 residues, are rarely considered to be proteins and are commonly called peptides. The individual amino acid residues are bonded together by peptide bonds and adjacent amino acid residues. The sequence of amino acid residue ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Imidazole
Imidazole (ImH) is an organic compound with the formula C3N2H4. It is a white or colourless solid that is soluble in water, producing a mildly alkaline solution. In chemistry, it is an aromatic heterocycle, classified as a diazole Diazole refers to either one of a pair of isomeric chemical compounds with molecular formula C3H4N2, having a five-membered ring consisting of three carbon atoms and two nitrogen atoms. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
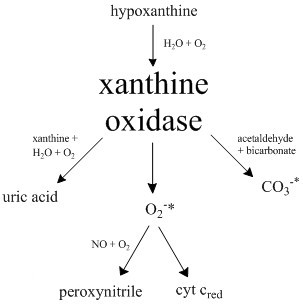
Xanthine Oxidase
Xanthine oxidase (XO, sometimes XAO) is a form of xanthine oxidoreductase, a type of enzyme that generates reactive oxygen species. These enzymes catalyze the oxidation of hypoxanthine to xanthine and can further catalyze the oxidation of xanthine to uric acid. These enzymes play an important role in the catabolism of purines in some species, including humans. Xanthine oxidase is defined as an ''enzyme activity'' (EC 1.17.3.2). The same protein, which in humans has the HGNC approved gene symbol ''XDH'', can also have xanthine dehydrogenase activity (EC 1.17.1.4). Most of the protein in the liver exists in a form with xanthine dehydrogenase activity, but it can be converted to xanthine oxidase by reversible sulfhydryl oxidation or by irreversible proteolytic modification. Reaction The following chemical reactions are catalyzed by xanthine oxidase: * hypoxanthine + H2O + O2 \rightleftharpoons xanthine + H2O2 * xanthine + H2O + O2 \rightleftharpoons uric acid + H2O2 * Xanthine o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hemerythrin
Hemerythrin (also spelled haemerythrin; grc, αἷμα, haîma, blood, grc, ἐρυθρός, erythrós, red) is an oligomeric protein responsible for oxygen (O2) transport in the marine invertebrate phyla of sipunculids, priapulids, brachiopods, and in a single annelid worm genus, ''Magelona''. Myohemerythrin is a monomeric O2-binding protein found in the muscles of marine invertebrates. Hemerythrin and myohemerythrin are essentially colorless when deoxygenated, but turn a violet-pink in the oxygenated state. Hemerythrin does not, as the name might suggest, contain a heme. The names of the blood oxygen transporters hemoglobin, hemocyanin, hemerythrin, do not refer to the heme group (only found in globins), instead these names are derived from the Greek word for blood. Hemerythrin may also contribute to innate immunity and anterior tissue regeneration in certain worms. O2 binding mechanism The mechanism of dioxygen binding is unusual. Most O2 carriers operate via formation of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bioinorganic Chemistry
Bioinorganic chemistry is a field that examines the role of metals in biology. Bioinorganic chemistry includes the study of both natural phenomena such as the behavior of metalloproteins as well as artificially introduced metals, including those that are non-essential, in medicine and toxicology. Many biological processes such as respiration depend upon molecules that fall within the realm of inorganic chemistry. The discipline also includes the study of inorganic models or mimics that imitate the behaviour of metalloproteins. As a mix of biochemistry and inorganic chemistry, bioinorganic chemistry is important in elucidating the implications of electron-transfer proteins, substrate bindings and activation, atom and group transfer chemistry as well as metal properties in biological chemistry. The successful development of truly interdisciplinary work is necessary to advance bioinorganic chemistry. Composition of living organisms About 99% of mammals' mass are the elements carb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nitrosyl
In organic chemistry, nitroso refers to a functional group in which the nitric oxide () group is attached to an organic moiety. As such, various nitroso groups can be categorized as ''C''-nitroso compounds (e.g., nitrosoalkanes; ), ''S''-nitroso compounds ( nitrosothiols; ), ''N''-nitroso compounds (e.g., nitrosamines, ), and ''O''-nitroso compounds (alkyl nitrites; ). Synthesis Nitroso compounds can be prepared by the reduction of nitro compounds or by the oxidation of hydroxylamines. Ortho-nitrosophenols may be produced by the Baudisch reaction. In the Fischer–Hepp rearrangement aromatic 4-nitrosoanilines are prepared from the corresponding nitrosamines. Properties Nitrosoarenes typically participate in a monomer–dimer equilibrium. The dimers, which are often pale yellow, are often favored in the solid state, whereas the deep-green monomers are favored in dilute solution or at higher temperatures. They exist as ''cis'' and ''trans'' isomers. Due to the stability o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |