|
Triphenylphosphine Phenylimide
Triphenylphosphine phenylimide is the organophosphorus compound with the formula Ph3P=NPh ( Ph = C6H5). It is a white solid that is soluble in organic solvents. The compound is a prototype of a large class of Staudinger reagents, resulting from the Staudinger reaction. The phosphine imides were first prepared in the laboratory of Nobelist Hermann Staudinger. His synthesis involved the direct reaction of triphenylphosphine with phenylazide. :Ph3P + N3Ph → Ph3P=NPh + N2 X-ray crystallography X-ray crystallography is the experimental science determining the atomic and molecular structure of a crystal, in which the crystalline structure causes a beam of incident X-rays to diffract into many specific directions. By measuring the angles ... establishes that the P-N-C angle is bent (130.4°) and the P-N distance is 160 pm.{{cite journal, title=Die Kristallstrukturen von Ph3PNPh, h3PN(H)PhAuI2], und von 2,3-Bis(triphenylphosphoranimino)maleinsäure-N-methylimid (The Cr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Organophosphorus Compound
Organophosphorus compounds are organic compounds containing phosphorus. They are used primarily in pest control as an alternative to chlorinated hydrocarbons that persist in the environment. Some organophosphorus compounds are highly effective insecticides, although some are extremely toxic to humans, including sarin and VX nerve agents. Organophosphorus chemistry is the corresponding science of the properties and reactivity of organophosphorus compounds. Phosphorus, like nitrogen, is in group 15 of the periodic table, and thus phosphorus compounds and nitrogen compounds have many similar properties. The definition of organophosphorus compounds is variable, which can lead to confusion. In industrial and environmental chemistry, an organophosphorus compound need contain only an organic substituent, but need not have a direct phosphorus-carbon (P-C) bond. Thus a large proportion of pesticides (e.g., malathion), are often included in this class of compounds. Phosphorus can adopt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phenyl
In organic chemistry, the phenyl group, or phenyl ring, is a cyclic group of atoms with the formula C6 H5, and is often represented by the symbol Ph. Phenyl group is closely related to benzene and can be viewed as a benzene ring, minus a hydrogen, which may be replaced by some other element or compound to serve as a functional group. Phenyl group has six carbon atoms bonded together in a hexagonal planar ring, five of which are bonded to individual hydrogen atoms, with the remaining carbon bonded to a substituent. Phenyl groups are commonplace in organic chemistry. Although often depicted with alternating double and single bonds, phenyl group is chemically aromatic and has equal bond lengths between carbon atoms in the ring. Nomenclature Usually, a "phenyl group" is synonymous with C6H5− and is represented by the symbol Ph or, archaically, Φ. Benzene is sometimes denoted as PhH. Phenyl groups are generally attached to other atoms or groups. For example, triphenylmethane (Ph3 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
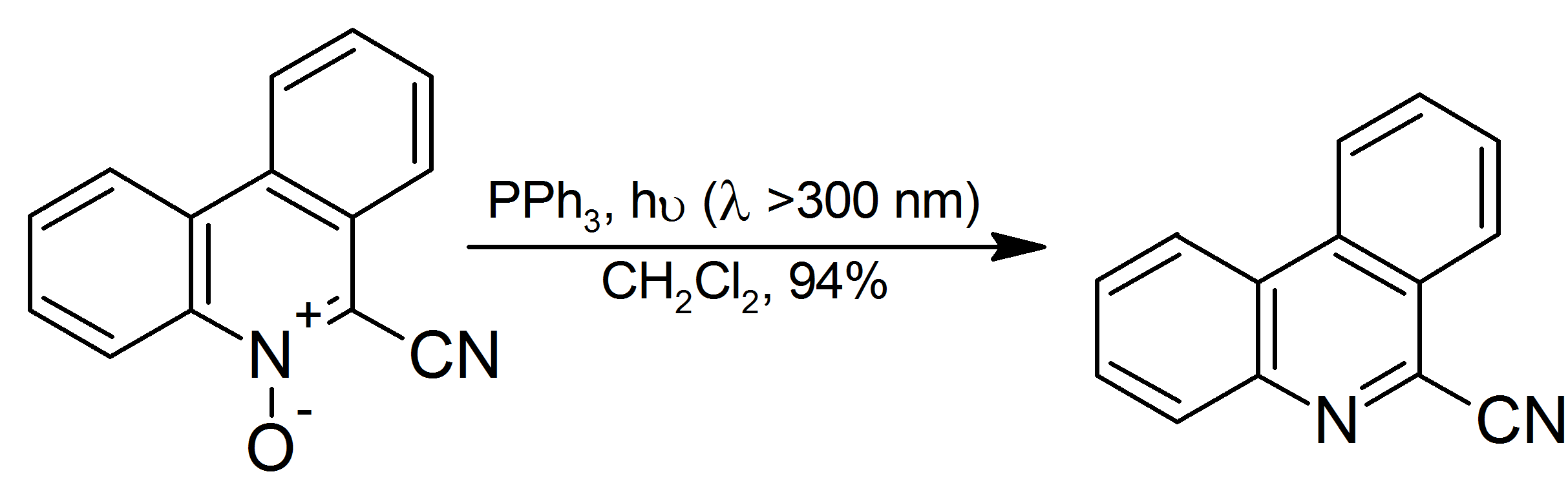
Staudinger Reaction
The Staudinger reaction is a chemical reaction of an organic azide with a phosphine or phosphite produces an iminophosphorane. The reaction was discovered by and named after Hermann Staudinger. The reaction follows this stoichiometry: :R3P + R'N3 → R3P=NR' + N2 Staudinger reduction The Staudinger reduction is conducted in two steps. First phosphine imine-forming reaction is conducted involving treatment of the azide with the phosphine. The intermediate, e.g. triphenylphosphine phenylimide, is then subjected to hydrolysis to produce a phosphine oxide and an amine: :R3P=NR' + H2O → R3P=O + R'NH2 The overall conversion is a mild method of reducing an azide to an amine. Triphenylphosphine or tributylphosphine are most commonly used, yielding tributylphosphine oxide or triphenylphosphine oxide as a side product in addition to the desired amine. An example of a Staudinger reduction is the organic synthesis of the pinwheel compound 1,3,5-tris(aminomethyl)-2,4,6-triethylbenz ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hermann Staudinger
Hermann Staudinger (; 23 March 1881 – 8 September 1965) was a German organic chemist who demonstrated the existence of macromolecules, which he characterized as polymers. For this work he received the 1953 Nobel Prize in Chemistry. He is also known for his discovery of ketenes and of the Staudinger reaction. Staudinger, together with Leopold Ružička, also elucidated the molecular structures of pyrethrin I and II in the 1920s, enabling the development of pyrethroid insecticides in the 1960s and 1970s. Early work Staudinger was born in 1881 in Worms. Staudinger, who initially wanted to become a botanist, studied chemistry at the University of Halle, at the TH Darmstadt and at the LMU Munich. He received his "Verbandsexamen" (comparable to Master's degree) from TH Darmstadt. After receiving his Ph.D. from the University of Halle in 1903, Staudinger qualified as an academic lecturer at the University of Strasbourg in 1907. It was here that he discovered the ketenes, a family ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Triphenylphosphine
Triphenylphosphine (IUPAC name: triphenylphosphane) is a common organophosphorus compound with the formula P(C6H5)3 and often abbreviated to P Ph3 or Ph3P. It is widely used in the synthesis of organic and organometallic compounds. PPh3 exists as relatively air stable, colorless crystals at room temperature. It dissolves in non-polar organic solvents such as benzene and diethyl ether. Preparation and structure Triphenylphosphine can be prepared in the laboratory by treatment of phosphorus trichloride with phenylmagnesium bromide or phenyllithium. The industrial synthesis involves the reaction between phosphorus trichloride, chlorobenzene, and sodium: :PCl3 + 3 PhCl + 6 Na → PPh3 + 6 NaCl Triphenylphosphine crystallizes in triclinic and monoclinic modification. In both cases, the molecule adopts a pyramidal structure with propeller-like arrangement of the three phenyl groups. Principal reactions with chalcogens, halogens, and acids Oxidation Triphenylphosphine undergoes slow ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phenylazide
Phenyl azide is an organic compound with the formula C6H5N3. It is one of the prototypical organic azides. It is a pale yellow oily liquid with a pungent odor. The structure consists of a linear azide substituent bound to a phenyl group. The C−N=N angle is approximately 120°. Preparation Phenyl azide is prepared by the diazotization of phenylhydrazine with nitrous acid: :C6H5NHNH2 + HNO2 → C6H5N3 + 2 H2O Aryl iodides bearing electron-withdrawing substituents undergo metathesis with sodium azide in the presence of Cu(I), sodium ascorbate, and N,N'-dimethylethane-1,2-diamine (DMEDA): :RC6H4I + NaN3 → RC6H4N3 + NaI It can also be prepared by condensation of benzenediazonium salt with toluenesulfonamide, followed by hydrolysis. Chemical reactions Phenyl azide cycloadds to alkenes and especially alkynes, particularly those bearing electronegative substituents. In a classic example of click chemistry, phenyl azide and phenylacetylene react to give diphenyl tr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
X-ray Crystallography
X-ray crystallography is the experimental science determining the atomic and molecular structure of a crystal, in which the crystalline structure causes a beam of incident X-rays to diffract into many specific directions. By measuring the angles and intensities of these diffracted beams, a crystallographer can produce a three-dimensional picture of the density of electrons within the crystal. From this electron density, the mean positions of the atoms in the crystal can be determined, as well as their chemical bonds, their crystallographic disorder, and various other information. Since many materials can form crystals—such as salts, metals, minerals, semiconductors, as well as various inorganic, organic, and biological molecules—X-ray crystallography has been fundamental in the development of many scientific fields. In its first decades of use, this method determined the size of atoms, the lengths and types of chemical bonds, and the atomic-scale differences among various mat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Organophosphorus Compounds
Organophosphorus compounds are organic compounds containing phosphorus. They are used primarily in pest control as an alternative to chlorinated hydrocarbons that persist in the environment. Some organophosphorus compounds are highly effective insecticides, although some are extremely toxic to humans, including sarin and VX (nerve agent), VX nerve agents. Organophosphorus chemistry is the corresponding science of the properties and reactivity of organophosphorus compounds. Phosphorus, like nitrogen, is in pnictogen, group 15 of the periodic table, and thus phosphorus compounds and nitrogen compounds have many similar properties. The definition of organophosphorus compounds is variable, which can lead to confusion. In industrial and environmental chemistry, an organophosphorus compound need contain only an organic substituent, but need not have a direct phosphorus-carbon (P-C) bond. Thus a large proportion of pesticides (e.g., malathion), are often included in this class of compound ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |