|
Trinity Dam
Trinity Dam is an earthfill dam on the Trinity River located about northeast of Weaverville, California in the United States. The dam was completed in the early 1960s as part of the federal Central Valley Project to provide irrigation water to the arid San Joaquin Valley. Standing high, Trinity Dam forms Trinity Lake – California's third largest reservoir, with a capacity of more than . The dam includes a hydroelectric plant, and also provides flood control to the Trinity and Klamath river basins. Below the dam is Lewiston Lake, formed by a second dam, which diverts water through a 10.7 mile tunnel to the Sacramento Valley. Background In response to the Great Depression and drought conditions in California during the early 20th century, the United States Congress passed the 1935 Rivers and Harbors Act, which authorized the Central Valley Project (CVP) – a system of dams and canals to provide a stable supply of irrigation water to California's Central Valley. Among the pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Central Valley (California)
The Central Valley is a broad, elongated, flat valley that dominates the interior of California. It is wide and runs approximately from north-northwest to south-southeast, inland from and parallel to the Pacific coast of the state. It covers approximately , about 11% of California's land area. The valley is bounded by the Coast Ranges The Pacific Coast Ranges (officially gazetted as the Pacific Mountain System in the United States) are the series of mountain ranges that stretch along the West Coast of North America from Alaska south to Northern and Central Mexico. Although th ... to the west and the Sierra Nevada to the east. The Central Valley is a list of regions of California, region known for its agricultural productivity: it provides more than half of the fruits, vegetables, and nuts grown in the United States. More than of the valley are irrigated via reservoirs and canals. The valley hosts many cities, including the state capital Sacramento, California, Sacramento ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
California Department Of Fish And Game
The California Department of Fish and Wildlife (CDFW), formerly known as the California Department of Fish and Game (CDFG), is a state agency under the California Natural Resources Agency. The Department of Fish and Wildlife manages and protects the state's wildlife, wildflowers, trees, mushrooms, algae (kelp) and native habitats (ecosystems). The department is responsible for regulatory enforcement and management of related recreational, commercial, scientific, and educational uses. The department also prevents illegal poaching. History The Game Act was passed in 1852 by the California State Legislature and signed into law by Governor John Bigler. The Game Act closed seasons in 12 counties for quail, partridge, mallard and wood ducks, elk, deer, and antelope. A second legislative action enacted the same year protected salmon runs. In 1854, the Legislature extended the act to include all counties of California. In 1860, protection controls were extended for trout. Lake Merrit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Salmon
Salmon () is the common name for several list of commercially important fish species, commercially important species of euryhaline ray-finned fish from the family (biology), family Salmonidae, which are native to tributary, tributaries of the North Atlantic (genus ''Salmo'') and North Pacific (genus ''Oncorhynchus'') basin. Other closely related fish in the same family include trout, Salvelinus, char, Thymallus, grayling, Freshwater whitefish, whitefish, lenok and Hucho, taimen. Salmon are typically fish migration, anadromous: they hatch in the gravel stream bed, beds of shallow fresh water streams, migrate to the ocean as adults and live like sea fish, then return to fresh water to reproduce. However, populations of several species are restricted to fresh water throughout their lives. Folklore has it that the fish return to the exact spot where they hatched to spawn (biology), spawn, and tracking studies have shown this to be mostly true. A portion of a returning salmon run ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peaking Power
Peaking power plants, also known as peaker plants, and occasionally just "peakers", are power plants that generally run only when there is a high demand, known as peak demand, for electricity. Because they supply power only occasionally, the power supplied commands a much higher price per kilowatt hour than base load power. Peak load power plants are dispatched in combination with base load power plants, which supply a dependable and consistent amount of electricity, to meet the minimum demand. Although historically peaking power plants were frequently used in conjunction with coal baseload plants, peaking plants are now used less commonly. Combined cycle gas turbine plants have two or more cycles, the first of which is very similar to a peaking plant, with the second running on the waste heat of the first. That type of plant is often capable of rapidly starting up, albeit at reduced efficiency, and then over some hours transitioning to a more efficient baseload generation mode. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
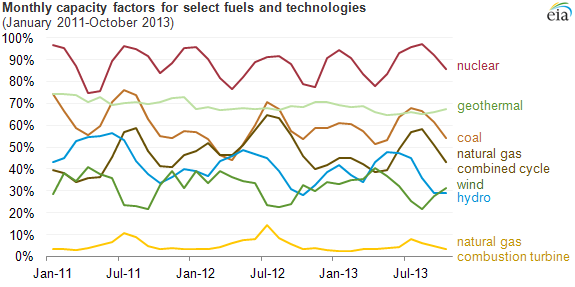
Capacity Factor
The net capacity factor is the unitless ratio of actual electrical energy output over a given period of time to the theoretical maximum electrical energy output over that period. The theoretical maximum energy output of a given installation is defined as that due to its continuous operation at full nameplate capacity over the relevant period. The capacity factor can be calculated for any electricity producing installation, such as a fuel consuming power plant or one using renewable energy, such as wind or the sun. The average capacity factor can also be defined for any class of such installations, and can be used to compare different types of electricity production. The actual energy output during that period and the capacity factor vary greatly depending on a range of factors. The capacity factor can never exceed the availability factor, or uptime during the period. Uptime can be reduced due to, for example, reliability issues and maintenance, scheduled or unscheduled. Other fact ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kilowatt Hour
A kilowatt-hour (unit symbol: kW⋅h or kW h; commonly written as kWh) is a unit of energy: one kilowatt of power for one hour. In terms of SI derived units with special names, it equals 3.6 megajoules (MJ). Kilowatt-hours are a common billing unit for electrical energy delivered to consumers by electric utilities. Definition The kilowatt-hour is a composite unit of energy equal to one kilowatt (kW) sustained for (multiplied by) one hour. Expressed in the standard unit of energy in the International System of Units (SI), the joule (symbol J), it is equal to 3,600 kilojoules or 3.6 MJ."Half-high dots or spaces are used to express a derived unit formed from two or more other units by multiplication.", Barry N. Taylor. (2001 ed.''The International System of Units.'' (Special publication 330). Gaithersburg, MD: National Institute of Standards and Technology. 20. Unit representations A widely used representation of the kilowatt-hour is "kWh", derived from its compone ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Megawatt
The watt (symbol: W) is the unit of Power (physics), power or radiant flux in the International System of Units, International System of Units (SI), equal to 1 joule per second or 1 kg⋅m2⋅s−3. It is used to quantification (science), quantify the rate of Energy transformation, energy transfer. The watt is named after James Watt (1736–1819), an 18th-century Scottish people, Scottish invention, inventor, mechanical engineer, and chemist who improved the Newcomen steam engine, Newcomen engine with his own Watt steam engine, steam engine in 1776. Watt's invention was fundamental for the Industrial Revolution. Overview When an object's velocity is held constant at one metre per second against a constant opposing force of one Newton (unit), newton, the rate at which Work (physics), work is done is one watt. : \mathrm In terms of electromagnetism, one watt is the rate at which electrical work is performed when a current of one ampere (A) flows across an electrical potentia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Outlet Works
A gatehouse, gate house, outlet works or valve house for a dam is a structure housing sluice gates, valves, or pumps (in which case it is more accurately called a pumping station). Many gatehouses are strictly utilitarian, but especially in the nineteenth century, some were very elaborate. Background A set of outlet works is a device used to release and regulate water flow from a dam. Such devices usually consist of one or more pipes or tunnels through the embankment of the dam, directing water usually under high pressure to the river downstream. These structures are usually used when river flow exceeds the capacity of the power plant or diversion capacity of the dam, but do not have flows high enough to warrant the use of the dam spillways. They may also be utilized when river flows must be bypassed due to maintenance work in the power station or diversion gates. Although similar in purpose to spillways, outlet works provide a more controlled release to meet downstream flow requir ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clair Engle
Clair Engle (September 21, 1911July 30, 1964) was an American politician who served as a United States Senator from California from 1959 until his death in 1964. A member of the Democratic Party, he is best remembered for participating in the vote breaking the filibuster of the Civil Rights Act of 1964 in the U.S. Senate while partially paralyzed and unable to speak, shortly before his death from a brain tumor. Engle previously served in the California State Senate from January to August 1943 and U.S. House of Representatives from August 1943 until January 1959. Early life Engle was born in Bakersfield, to Fred Engle, a rancher who had been a teacher and a lawyer, and his wife, Carita. His parents named him after his aunt, who had assisted in his birth, and his name would become the source of many folksy stories over the years. Like his two brothers, he was active in outdoor activities and attended public schools in Shasta and Tehama Counties. His fellow students at Red Blu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oroville Dam
Oroville Dam is an earthfill embankment dam on the Feather River east of the city of Oroville, California, in the Sierra Nevada foothills east of the Sacramento Valley. At 770 feet (235 m) high, it is the tallest dam in the U.S. and serves mainly for water supply, hydroelectricity generation, and flood control. The dam impounds Lake Oroville, the second-largest reservoir in California, capable of storing more than . Built by the California Department of Water Resources, Oroville Dam is one of the key features of the California State Water Project (SWP), one of two major projects passed that set up California's statewide water system. Construction was initiated in 1961, and despite numerous difficulties encountered during its construction, including multiple floods and a major train wreck on the rail line used to transport materials to the dam site, the embankment was topped out in 1967 and the entire project was ready for use in 1968. The dam began to generate electricit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |