|
Trichlorethylene
The chemical compound trichloroethylene is a halocarbon commonly used as an industrial solvent. It is a clear, colourless non-flammable liquid with a chloroform-like sweet smell. It should not be confused with the similar 1,1,1-trichloroethane, which is commonly known as ''chlorothene''. The IUPAC name is trichloroethene. Industrial abbreviations include TCE, trichlor, Trike, Tricky and tri. It has been sold under a variety of trade names. Under the trade names Trimar and Trilene, trichloroethylene was used as a volatile anesthetic and as an inhaled obstetrical analgesic in millions of patients. Groundwater and drinking water contamination from industrial discharge including trichloroethylene is a major concern for human health and has precipitated numerous incidents and lawsuits. History Pioneered by Imperial Chemical Industries in Britain, its development was hailed as an anesthetic revolution. Originally thought to possess less hepatotoxicity than chloroform, and without the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chloroform
Chloroform, or trichloromethane, is an organic compound with chemical formula, formula Carbon, CHydrogen, HChlorine, Cl3 and a common organic solvent. It is a colorless, strong-smelling, dense liquid produced on a large scale as a precursor to PTFE. It is also a precursor to various refrigerants. It is trihalomethane. It is a powerful anesthetic, euphoriant, anxiolytic, and sedative when inhaled or ingested. Structure The molecule adopts a tetrahedral molecular geometry with C3v symmetry group, symmetry. Natural occurrence The total global flux of chloroform through the environment is approximately tonnes per year, and about 90% of emissions are natural in origin. Many kinds of seaweed produce chloroform, and fungi are believed to produce chloroform in soil. Abiotic processes are also believed to contribute to natural chloroform productions in soils although the mechanism is still unclear. Chloroform volatilizes readily from soil and surface water and undergoes degradation in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Drinking Water Pollution
Water quality refers to the chemical, physical, and biological characteristics of water based on the standards of its usage. It is most frequently used by reference to a set of standards against which compliance, generally achieved through treatment of the water, can be assessed. The most common standards used to monitor and assess water quality convey the health of ecosystems, safety of human contact, extend of water pollution and condition of drinking water. Water quality has a significant impact on water supply and oftentimes determines supply options. Categories The parameters for water quality are determined by the intended use. Work in the area of water quality tends to be focused on water that is treated for potability, industrial/domestic use, or restoration (of an environment/ecosystem, generally for health of human/aquatic life). Human consumption Contaminants that may be in untreated water include microorganisms such as viruses, protozoa and bacteria; inorgani ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
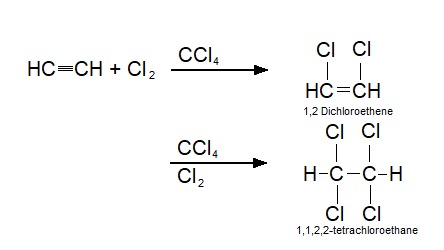
1,1,2,2-Tetrachloroethane
1,1,2,2-tetrachloroethane (TeCA), also known as bonoform, cellon, or westron is a toxic, synthetic halogen rich alkane. It is colorless liquid and has a sweet odor. It is used as an industrial solvent or as a separation agent. TeCA can be inhaled, consumed or absorbed through the skin. After exposure, nausea, dizziness or even liver damage may occur. History 1,1,2,2-tetrachloroethane was used in large amounts to produce other chemicals like trichloroethylene, tetrachloroethylene, and 1,2,-dichloroethylene. It also found its function as a industrial solvent and was used in paint removers and pesticides. Because of its possible carcinogen effects on humans, the production of 1,1,2,2-tetrachloroethane has decreased significantly and is no longer widely used as an end-product. It is however still generated as a byproduct and as an intermediate product during manufacturing, where low levels of the chemical have been detected in the air. Synthesis There are a few different ways ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Catalyst
Catalysis () is the process of increasing the rate of a chemical reaction by adding a substance known as a catalyst (). Catalysts are not consumed in the reaction and remain unchanged after it. If the reaction is rapid and the catalyst recycles quickly, very small amounts of catalyst often suffice; mixing, surface area, and temperature are important factors in reaction rate. Catalysts generally react with one or more reactants to form intermediates that subsequently give the final reaction product, in the process of regenerating the catalyst. Catalysis may be classified as either homogeneous, whose components are dispersed in the same phase (usually gaseous or liquid) as the reactant, or heterogeneous, whose components are not in the same phase. Enzymes and other biocatalysts are often considered as a third category. Catalysis is ubiquitous in chemical industry of all kinds. Estimates are that 90% of all commercially produced chemical products involve catalysts at some s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iron(III) Chloride
Iron(III) chloride is the inorganic compound with the formula . Also called ferric chloride, it is a common compound of iron in the +3 oxidation state. The anhydrous compound is a crystalline solid with a melting point of 307.6 °C. The colour depends on the viewing angle: by reflected light the crystals appear dark green, but by transmitted light they appear purple-red. Structure and properties Anhydrous Anhydrous iron(III) chloride has the structure, with octahedral Fe(III) centres interconnected by two-coordinate chloride ligands. Iron(III) chloride has a relatively low melting point and boils at around 315 °C. The vapor consists of the dimer (like aluminium chloride) which increasingly dissociates into the monomeric (with D3h point group molecular symmetry) at higher temperature, in competition with its reversible decomposition to give iron(II) chloride and chlorine gas. Hydrates In addition to the anhydrous material, ferric chloride forms four hydrates. All ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acetylene
Acetylene (systematic name: ethyne) is the chemical compound with the formula and structure . It is a hydrocarbon and the simplest alkyne. This colorless gas is widely used as a fuel and a chemical building block. It is unstable in its pure form and thus is usually handled as a solution. Pure acetylene is odorless, but commercial grades usually have a marked odor due to impurities such as divinyl sulfide and phosphine.Compressed Gas Association (1995Material Safety and Data Sheet – Acetylene As an alkyne, acetylene is unsaturated because its two carbon atoms are bonded together in a triple bond. The carbon–carbon triple bond places all four atoms in the same straight line, with CCH bond angles of 180°. Discovery Acetylene was discovered in 1836 by Edmund Davy, who identified it as a "new carburet of hydrogen". It was an accidental discovery while attempting to isolate potassium metal. By heating potassium carbonate with carbon at very high temperatures, he produced a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Human Exposure
Humans (''Homo sapiens'') are the most abundant and widespread species of primate, characterized by bipedalism and exceptional cognitive skills due to a large and complex brain. This has enabled the development of advanced tools, culture, and language. Humans are highly social and tend to live in complex social structures composed of many cooperating and competing groups, from families and kinship networks to political states. Social interactions between humans have established a wide variety of values, social norms, and rituals, which bolster human society. Its intelligence and its desire to understand and influence the environment and to explain and manipulate phenomena have motivated humanity's development of science, philosophy, mythology, religion, and other fields of study. Although some scientists equate the term ''humans'' with all members of the genus ''Homo'', in common usage, it generally refers to ''Homo sapiens'', the only extant member. Anatomically mode ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Groundwater
Groundwater is the water present beneath Earth's surface in rock and soil pore spaces and in the fractures of rock formations. About 30 percent of all readily available freshwater in the world is groundwater. A unit of rock or an unconsolidated deposit is called an aquifer when it can yield a usable quantity of water. The depth at which soil pore spaces or fractures and voids in rock become completely saturated with water is called the water table. Groundwater is recharged from the surface; it may discharge from the surface naturally at springs and seeps, and can form oases or wetlands. Groundwater is also often withdrawn for agricultural, municipal, and industrial use by constructing and operating extraction wells. The study of the distribution and movement of groundwater is hydrogeology, also called groundwater hydrology. Typically, groundwater is thought of as water flowing through shallow aquifers, but, in the technical sense, it can also contain soil moisture, perma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
N-Propyl Bromide
1-Bromopropane (''n''-propylbromide or nPB) is an organobromine compound with the chemical formula CH3CH2CH2Br. It is a colorless liquid that is used as a solvent. It has a characteristic hydrocarbon odor. Its industrial applications increased dramatically in the 21st century due to the phasing out of chlorofluorocarbons, perchloroethylene, and chloroalkanes such as 1,1,1-Trichloroethane under the Montreal Protocol. Preparation Industrial routes to 1-bromopropane involve free-radical additions to the corresponding alkenes. In this way, the anti-Markovnikov product is obtained.David Ioffe, Arieh Kampf "Bromine, Organic Compounds" in Kirk-Othmer Encyclopedia of Chemical Technology 2002 by John Wiley & Sons. . A laboratory synthesis involves treating propanol with a mixture of hydrobromic and sulfuric acids: :CH3CH2CH2OH + HBr → CH3CH2CH2Br + H2O Alternate synthetic routes include treating propanol with phosphorus tribromide. or via a Hunsdiecker reaction with buty ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of R-phrases
R-phrases (short for risk phrases) are defined in Annex III of European Union Directive 67/548/EEC: ''Nature of special risks attributed to dangerous substances and preparations''. The list was consolidated and republished in Directive 2001/59/EC, where translations into other EU languages may be found. These risk phrases are used internationally, not just in Europe, and there is an ongoing effort towards complete international harmonization using the Globally Harmonized System of Classification and Labelling of Chemicals (GHS) which now generally replaces these risk phrases. Risk phrases Missing R-numbers indicate phrases that have been deleted or replaced by other phrases. Combinations R-phrases no longer in use * : Extremely flammable liquefied gas. * : May cause birth defects. See also * List of S-phrases * Material safety data sheet * Risk and Safety Statements {{short description, System of hazard codes and phrases for labeling dangerous chemicals and compounds Risk a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Halothane
Halothane, sold under the brand name Fluothane among others, is a general anaesthetic. It can be used to induce or maintain anaesthesia. One of its benefits is that it does not increase the production of saliva, which can be particularly useful in those who are difficult to intubate. It is given by inhalation. Side effects include an irregular heartbeat, respiratory depression, and hepatotoxicity. Like all volatile anesthetics, it should not be used in people with a personal or family history of malignant hyperthermia. It appears to be safe in porphyria. It is unclear whether use during pregnancy is harmful to the baby, and it is not generally recommended for use during a C-section. Halothane is a chiral molecule that is used as a racemic mixture. Halothane was discovered in 1955. It was approved for medical use in the United States in 1958. It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines. Its use in developed countries has been mostly replaced by newer ane ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Soda Lime
Soda lime is a mixture of NaOH and CaO chemicals, used in granular form in closed breathing environments, such as general anaesthesia, submarines, rebreathers and recompression chambers, to remove carbon dioxide from breathing gases to prevent CO2 retention and carbon dioxide poisoning. It is made by treating slaked lime with concentrated sodium hydroxide solution. Chemical components The main components of soda lime are * Calcium oxide, CaO (about 75%) * Water, H2O (about 20%) * Sodium hydroxide, NaOH (about 3%) * Potassium hydroxide, KOH (about 0.1%). Anaesthetic use During the administration of general anaesthesia, the gases expired by a patient, which contain carbon dioxide, are passed through an anaesthetic machine breathing circuit filled with soda lime granules. Medical-grade soda lime includes an indicating dye that changes color when the soda lime reaches its carbon dioxide absorbing capacity. To ensure that a soda lime canister (CO2 absorber) is functioning properly ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |