|
Triccianus
Aelius Decius Triccianus was a Roman usurper, who revolted against Emperor Elagabalus. He revolted against Elagabalus using troops still loyal to Macrinus, the previous emperor who Elagabalus had overthrown, and who Triccianus had served under. The revolt was put down, and he was executed. A '' damnatio memoriae'' was issued against him, making it impossible to establish the date of his rebellion or death. History Triccianus was first recorded as being doorkeeper to the legate of Pannonia, before rising to become the ''praefectus legionis'' (legionary commander) of Legio ''II Parthica'' under Caracalla. He became involved in a plot to usurp the throne from Caracalla, with Macrinus. When Macrinus successfully seized the throne, Triccianus was rewarded with the post of provincial governor of Pannonia Inferior. During his time as governor, he used his legio, ''II Parthica'', to repair the military roads in the province. Numerous milestones bore his name, however all of these we ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
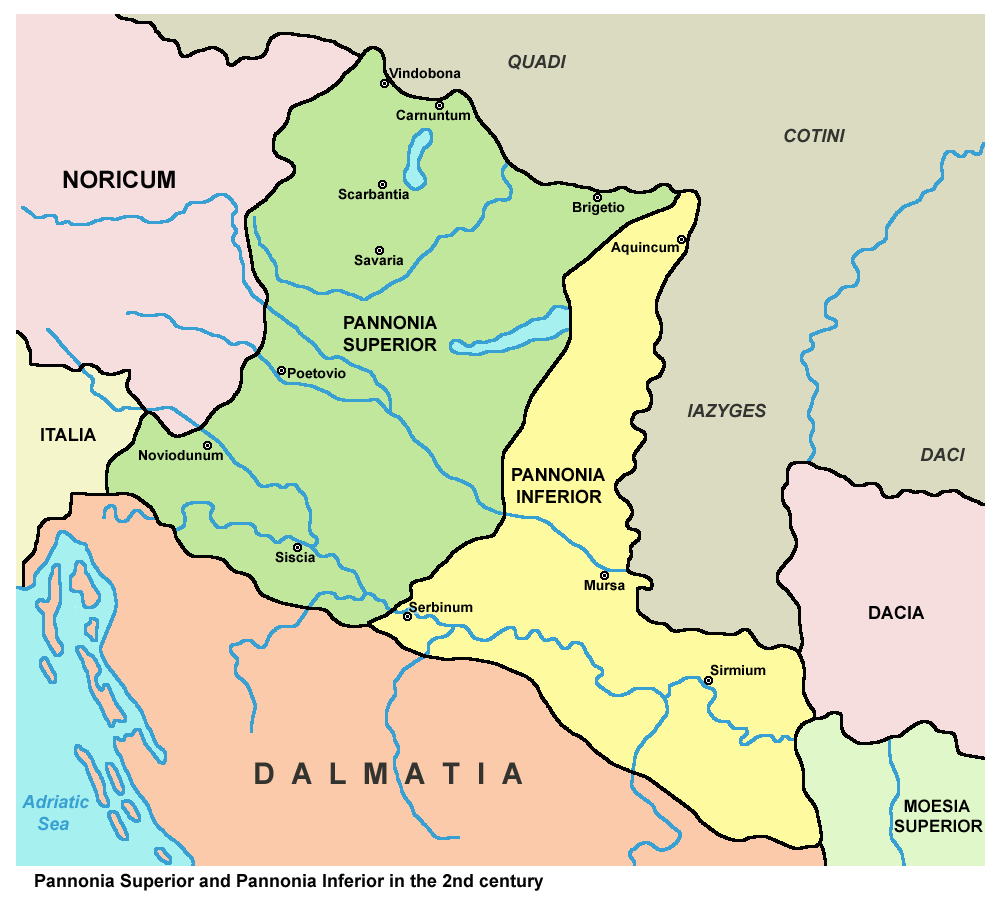
Pannonia Inferior
Pannonia Inferior, lit. Lower Pannonia, was a province of the Roman Empire. Its capital was Sirmium. It was one of the border provinces on the Danube. It was formed in the year 103 AD by Emperor Trajan who divided the former province of Pannonia into two parts: Pannonia Superior and Pannonia Inferior. The province included parts of present-day states of Hungary, Serbia, Croatia, and Bosnia and Herzegovina. The province was bordered to the east (across the Danube) by a Sarmatian tribe—the Iazyges. Later, the Vandals appeared to the north-east. Settlements Major settlements in Pannonia Inferior included: * ''Sirmium'' (Sremska Mitrovica) which several times served as an imperial residence for several emperors. * ''Aquincum'' ( Buda), the provincial capital. * ''Cuccium'' (Ilok) * ''Cibalae'' (Vinkovci) * ''Mursa'' ( Osijek) * ''Certissa'' (Đakovo) * ''Marsonia'' (Slavonski Brod) * ''Sopianae'' (Pécs) Aftermath and legacy The province was yet again split during the reign of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roman Usurper
Roman usurpers were individuals or groups of individuals who obtained or tried to obtain power by force and without legitimate legal authority. Usurpation was endemic during the Roman imperial era, especially from the crisis of the third century onwards, when political instability became the rule. The first dynasty of the Roman Empire, the Julio-Claudians (27 BC – 68 AD), justified the imperial throne by familial ties, namely with the connection (although only through adoption) with Augustus, the first emperor. Eventually, conflicts within the Julio-Claudian family triggered a series of murders, which led to the demise of the line. Nero died with public enemy status, and following his suicide, a short civil war began, known as the Year of the Four Emperors. The Flavian dynasty started with Vespasian, only to end with the assassination of his second son, Domitian. The 2nd century was a period of relative peace that was marked by the rule of the so-called Five Good Emperors, but ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adlection
During the Roman Kingdom, Roman Republic and later, adlecti, or allecti were those who were chosen to fill up a vacancy in any office or collegium (ancient Rome), collegium, and especially those who were chosen to fill up the proper number of the Roman Senate, senate. As these would be generally Equestrian (Roman), equites, Sextus Pompeius Festus, Festus defines the ''adlecti'' to be equites added to the senate: and he appears in this passage to make a distinction between the ''adlecti'' and the ''conscripti''. This distinction is supported by the summons form used to call the senate which reads ''pares'' and ''conscripti'' beginning in 509 BC. Others argue that they were the same; for in another passage, Festus gives the same definition of the conscripti as he had done of the adlecti, and Livy (ii.1) says ''conscriptos in novum senatum appellabant lectos''. The adelecti were also those persons under the Roman Empire, empire who were admitted to the privileges and honours of the pra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
People Executed By The Roman Empire
A person ( : people) is a being that has certain capacities or attributes such as reason, morality, consciousness or self-consciousness, and being a part of a culturally established form of social relations such as kinship, ownership of property, or legal responsibility. The defining features of personhood and, consequently, what makes a person count as a person, differ widely among cultures and contexts. In addition to the question of personhood, of what makes a being count as a person to begin with, there are further questions about personal identity and self: both about what makes any particular person that particular person instead of another, and about what makes a person at one time the same person as they were or will be at another time despite any intervening changes. The plural form "people" is often used to refer to an entire nation or ethnic group (as in "a people"), and this was the original meaning of the word; it subsequently acquired its use as a plural form of per ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Executed Ancient Roman People
Capital punishment, also known as the death penalty, is the state-sanctioned practice of deliberately killing a person as a punishment for an actual or supposed crime, usually following an authorized, rule-governed process to conclude that the person is responsible for violating norms that warrant said punishment. The sentence ordering that an offender is to be punished in such a manner is known as a death sentence, and the act of carrying out the sentence is known as an execution. A prisoner who has been sentenced to death and awaits execution is ''condemned'' and is commonly referred to as being "on death row". Crimes that are punishable by death are known as ''capital crimes'', ''capital offences'', or ''capital felonies'', and vary depending on the jurisdiction, but commonly include serious crimes against the person, such as murder, mass murder, aggravated cases of rape (often including child sexual abuse), terrorism, aircraft hijacking, war crimes, crimes against hum ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Year Of Birth Unknown
A year or annus is the orbital period of a planetary body, for example, the Earth, moving in its orbit around the Sun. Due to the Earth's axial tilt, the course of a year sees the passing of the seasons, marked by change in weather, the hours of daylight, and, consequently, vegetation and soil fertility. In temperate and subpolar regions around the planet, four seasons are generally recognized: spring, summer, autumn and winter. In tropical and subtropical regions, several geographical sectors do not present defined seasons; but in the seasonal tropics, the annual wet and dry seasons are recognized and tracked. A calendar year is an approximation of the number of days of the Earth's orbital period, as counted in a given calendar. The Gregorian calendar, or modern calendar, presents its calendar year to be either a common year of 365 days or a leap year of 366 days, as do the Julian calendars. For the Gregorian calendar, the average length of the calendar year ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
3rd-century Roman Usurpers
The 3rd century was the period from 201 ( CCI) to 300 (CCC) Anno Domini (AD) or Common Era (CE) in the Julian calendar.. In this century, the Roman Empire saw a crisis, starting with the assassination of the Roman Emperor Severus Alexander in 235, plunging the empire into a period of economic troubles, barbarian incursions, political upheavals, civil wars, and the split of the Roman Empire through the Gallic Empire in the west and the Palmyrene Empire in the east, which all together threatened to destroy the Roman Empire in its entirety, but the reconquests of the seceded territories by Emperor Aurelian and the stabilization period under Emperor Diocletian due to the administrative strengthening of the empire caused an end to the crisis by 284. This crisis would also mark the beginning of Late Antiquity. In Persia, the Parthian Empire was succeeded by the Sassanid Empire in 224 after Ardashir I defeated and killed Artabanus V during the Battle of Hormozdgan. The Sassanids ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Valerianus Poetus
Valerian (; la, Publius Licinius Valerianus; c. 199 – 260 or 264) was Roman emperor from 253 to spring 260 AD. He persecuted Christians and was later taken captive by the Persian emperor Shapur I after the Battle of Edessa, becoming the first Roman emperor to be captured as a prisoner of war, causing shock and instability throughout the Roman Empire. The unprecedented event and the unknown fate of the captured emperor generated a variety of different reactions and "new narratives about the Roman Empire in diverse contexts". Biography Origins and rise to power Unlike many of the would-be emperors and rebels who vied for imperial power during the Crisis of the Third Century of the Roman Empire, Valerian was of a noble and traditional senatorial family. Details of his early life are sparse, except for his marriage to Egnatia Mariniana, with whom he had two sons: later emperor Publius Licinius Egnatius Gallienus and Licinius Valerianus. He was Consul for the first time ei ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cassius Dio
Lucius Cassius Dio (), also known as Dio Cassius ( ), was a Roman historian and senator of maternal Greek origin. He published 80 volumes of the history on ancient Rome, beginning with the arrival of Aeneas in Italy. The volumes documented the subsequent founding of Rome (753 BC), the formation of the Republic (509 BC), and the creation of the Empire (27 BC), up until 229 AD. Written in Ancient Greek over 22 years, Dio's work covers approximately 1,000 years of history. Many of his 80 books have survived intact, or as fragments, providing modern scholars with a detailed perspective on Roman history. Biography Lucius Cassius Dio was the son of Cassius Apronianus, a Roman senator and member of the gens Cassia, who was born and raised at Nicaea in Bithynia. Byzantine tradition maintains that Dio's mother was the daughter or sister of the Greek orator and philosopher, Dio Chrysostom; however, this relationship has been disputed. Although Dio was a Roman citizen, he wrote in Gree ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Milestone
A milestone is a numbered marker placed on a route such as a road, railway line, canal or boundary. They can indicate the distance to towns, cities, and other places or landmarks; or they can give their position on the route relative to some datum location. On roads they are typically located at the side or in a median or central reservation. They are alternatively known as mile markers, mileposts or mile posts (sometimes abbreviated MPs). A "kilometric point" is a term used in metricated areas, where distances are commonly measured in kilometres instead of miles. "Distance marker" is a generic unit-agnostic term. Milestones are installed to provide linear referencing points along the road. This can be used to reassure travellers that the proper path is being followed, and to indicate either distance travelled or the remaining distance to a destination. Such references are also used by maintenance engineers and emergency services to direct them to specific points where th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Damnatio Memoriae
is a modern Latin phrase meaning "condemnation of memory", indicating that a person is to be excluded from official accounts. Depending on the extent, it can be a case of historical negationism. There are and have been many routes to , including the destruction of depictions, the removal of names from inscriptions and documents, and even large-scale rewritings of history. The term can be applied to other instances of official scrubbing; in history the practice is seen as long ago as the aftermath of the reign of the Egyptian Pharaohs Akhenaten in the 14th century BC, and Hatshepsut in the 15th century BC. Etymology Although the term is Latin, the phrase was not used by the ancient Romans, and first appeared in a thesis written in Germany in 1689. Ancient world Today's best known examples of ''damnatio memoriae'' from antiquity concern chiselling stone inscriptions or deliberately omitting certain information from them. Ancient Mesopotamia According to Stefan Zawadz ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
_1938.jpg)



_obverse.jpg)

