|
Treaty Of Paris (1947)
Treaty of Paris may refer to one of many treaties signed in Paris, France: Treaties 1200s and 1300s * Treaty of Paris (1229), which ended the Albigensian Crusade * Treaty of Paris (1259), between Henry III of England and Louis IX of France * Treaty of Paris (1303), between King Philip IV of France and King Edward I of England * Treaty of Paris (1320), peace between King Philip V of France and Robert III, Count of Flanders * Treaty of Paris (1323), in which Count Louis of Flanders relinquished Flemish claims over Zeeland * Treaty of Paris (1355), a land exchange between France and Savoy 1500s to 1700s * Treaty of Paris (1515), planning the marriage of the 15-year old future King Charles I of Spain and 4-year old Renée of France * Treaty of Paris (1623), between France, Savoy, and Venice against Spanish forces in Valtelline * Treaty of Paris (1626), peace between King Louis XIII and the Huguenots of La Rochelle * Treaty of Paris (1657), established a military alliance between Fran ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Treaty Of Paris (1229)
The Treaty of Paris, also known as Treaty of Meaux, was signed on 12 April 1229 between Raymond VII of Toulouse and Louis IX of France in Meaux near Paris. Louis was still a minor, and it was his mother Blanche of Castile, as regent, who was instrumental in forging the treaty. The agreement officially ended the Albigensian Crusade, and according to the terms of the treaty, Raymond's daughter Joan was to be married to Louis' brother Alphonse. Moreover, Raymond ceded the eastern provinces of his lands to Louis and the Marquisat de Provence to the Catholic church. The treaty also gave the Inquisition absolute power regarding searching for, and seizing of, heretics. Raymond ceded more than half his land to the French crown and retained the remainder only during his life, and it would then be inherited by his son-in-law Alphonse, Louis's brother or, if Alphonse had no heir, which occurred, by the French crown. Raymond regained his feudal rights but had to swear allegiance to Louis IX. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Treaty Of Paris (1802)
The Treaty of Paris was signed on 25 June 1802 between the First French Republic, then under First Consul Napoleon Bonaparte, and the Ottoman Empire, then ruled by Sultan Selim III. It was the final form of a preliminary treaty signed at Paris on 9 October 1801 that brought to an end the French campaign in Egypt and Syria and restored Franco-Ottoman relations to their ''status quo ante bellum''. In the treaty the Ottoman Empire also assented to the Treaty of Amiens (25 March 1802), a peace treaty between France and the United Kingdom, which had followed the surrender of French troops in Egypt to the British at the Capitulation of Alexandria. Relations between the Ottoman Empire and France had been strained with the French acquisition of the Ionian Islands in 1797, and the consequent anti-Ottoman propaganda disseminated in the Balkans by French agents. When the French invaded Egypt, the Ottomans declared war (9 September 1798) and subsequently signed a treaty of alliance with Russi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Treaty Of Paris (1900)
The Treaty of Paris was signed on 27 June 1900 between representatives of the Kingdom of Spain and the French Third Republic. The treaty delimited the borders of the Spanish colonies in the Sahara desert (Río de Oro, part of Spanish Sahara) and Equatorial Africa (Spanish Guinea) with respect to the adjoining French colonies on Africa. Moreover, the treaty granted the French the right to pre-emptively seize all territories if Spain decided to abandon its possessions in Río Muni. Gallery File:CostaAOE1896g.jpg, Map detailing the coast of Río de Oro (part of Spanish Sahara colony) in 1896. File:Mapa del Magreb (1956).svg, Borders raised by this treaty after 1900 of the Spanish territories of Spanish West Africa until 1956, including Río de Oro within Spanish Sahara. File:(1897) Golfo de Guinea.jpg, Map of Spanish possessions in the Gulf of Guinea in 1897, before the Treaty of Paris (1900). File:Eq_Guinea_1900_ES.PNG, Borders after the agreement of 1900 on the land what woul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Treaty Of Paris (1898)
The Treaty of Peace between the United States of America and the Kingdom of Spain, commonly known as the Treaty of Paris of 1898 ( fil, Kasunduan sa Paris ng 1898; es, Tratado de París de 1898), was a treaty signed by Spain and the United States on December 10, 1898, that ended the Spanish–American War. Under it, Spain relinquished all claim of sovereignty over and title to territories described there as ''the island of Porto Rico and other islands now under Spanish sovereignty in the West Indies, and the island of Guam in the Marianas or Ladrones'', the archipelago known as the Philippine Islands, and comprehending the islands lying within the following line:'' (details elided), and the Philippines to the United States. The cession of the Philippines involved a compensation of $20 million from the United States to Spain.Puerto Rico is spelled as "Porto Rico" in the treaty. The treaty came into effect on April 11, 1899, when the documents of ratification were exchanged. It w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paris Convention For The Protection Of Industrial Property
The Paris Convention for the Protection of Industrial Property, signed in Paris, France, on 20 March 1883, was one of the first intellectual property treaties. It established a Union for the protection of industrial property. The convention is currently still in force. The substantive provisions of the Convention fall into three main categories: national treatment, priority right and common rules. Contents National treatment According to Articles 2 and 3 of this treaty, juristic and natural persons who are either national of or domiciled in a state party to the Convention shall, as regards the protection of industrial property, enjoy in all the other countries of the Union, the advantages that their respective laws grant to nationals. In other words, when an applicant files an application for a patent or a trademark in a foreign country member of the Union, the application receives the same treatment as if it came from a national of this foreign country. Furthermore, if th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Treaty Of Paris (1857)
The Treaty of Paris (1857) marked the end of the hostilities of the Anglo-Persian War. On the Persian side negotiations were handled by ambassador Ferukh Khan. The two sides signed the peace treaty on 4 March 1857.''The Middle East and North Africa'' 2004 Taylor & Francis Group, Lucy Dean p.36/ref> In the Treaty, the Persians agreed to withdraw from Herat, to apologise to the British ambassador on his return, and to sign a commercial treaty; the British agreed not to shelter opponents of the Shah in the embassy, and they abandoned the demand to replace prime minister as well as one requiring territorial concessions to the Imam of Muscat, a British ally. See also * Greater Iran * Franco-Persian alliance * British Occupation of Bushehr The British Occupation of Bushehr or Bushire under British Occupation refers to the three times British forces entered Bushehr and occupied this area in Iran during the rule of Qajar dynasty, before and during the World War I. The importance o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Treaty Of Paris (1856)
The Treaty of Paris of 1856 brought an end to the Crimean War between the Russian Empire and an alliance of the Ottoman Empire, the United Kingdom, the Second French Empire and the Kingdom of Sardinia. The treaty, signed on 30 March 1856 at the Congress of Paris, made the Black Sea neutral territory, closing it to all warships and prohibiting fortifications and the presence of armaments on its shores. The treaty diminished Russian influence in the region. Conditions for the return of Sevastopol and other towns and cities in the south of Crimea to Russia were severe since no naval or military arsenal could be established by Russia on the coast of the Black Sea. Summary The Treaty of Paris was signed on 30 March 1856 at the Congress of Paris with Russia on one side of the negotiating table and France, Britain, the Ottoman Empire and the Kingdom of Sardinia on the other side. The treaty came about to resolve the Crimean War, which had begun on 23 October 1853, when the Ottoman ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Congress Of Vienna
The Congress of Vienna (, ) of 1814–1815 was a series of international diplomatic meetings to discuss and agree upon a possible new layout of the European political and constitutional order after the downfall of the French Emperor Napoleon Bonaparte. Participants were representatives of all European powers and other stakeholders, chaired by Austrian statesman Klemens von Metternich, and held in Vienna from September 1814 to June 1815. The objective of the Congress was to provide a long-term peace plan for Europe by settling critical issues arising from the French Revolutionary Wars and the Napoleonic Wars without the use of (military) violence. The goal was not simply to restore old boundaries, but to resize the main powers so they could balance each other and remain at peace, being at the same time shepherds for the smaller powers. More fundamentally, strongly generalising, conservative thinking leaders like Von Metternich also sought to restrain or eliminate republicanism, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Treaty Of Paris (1815)
The Treaty of Paris of 1815, also known as the Second Treaty of Paris, was signed on 20 November 1815 following the defeat and second abdication of Napoleon Bonaparte. In February, Napoleon had escaped from his exile on Elba; he entered Paris on 20 March, beginning the Hundred Days of his restored rule. After France's defeat at the hands of the Seventh Coalition in the Battle of Waterloo, Napoleon was persuaded to abdicate again, on 22 June. King Louis XVIII, who had fled the country when Napoleon arrived in Paris, took the throne for a second time on 8 July. The 1815 treaty had more punitive terms than the treaty of the previous year. France was ordered to pay 700 million francs in indemnities, and its borders were reduced to those that had existed on 1 January 1790. France was to pay additional money to cover the cost of providing additional defensive fortifications to be built by neighbouring Coalition countries. Under the terms of the treaty parts of France were to be occup ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
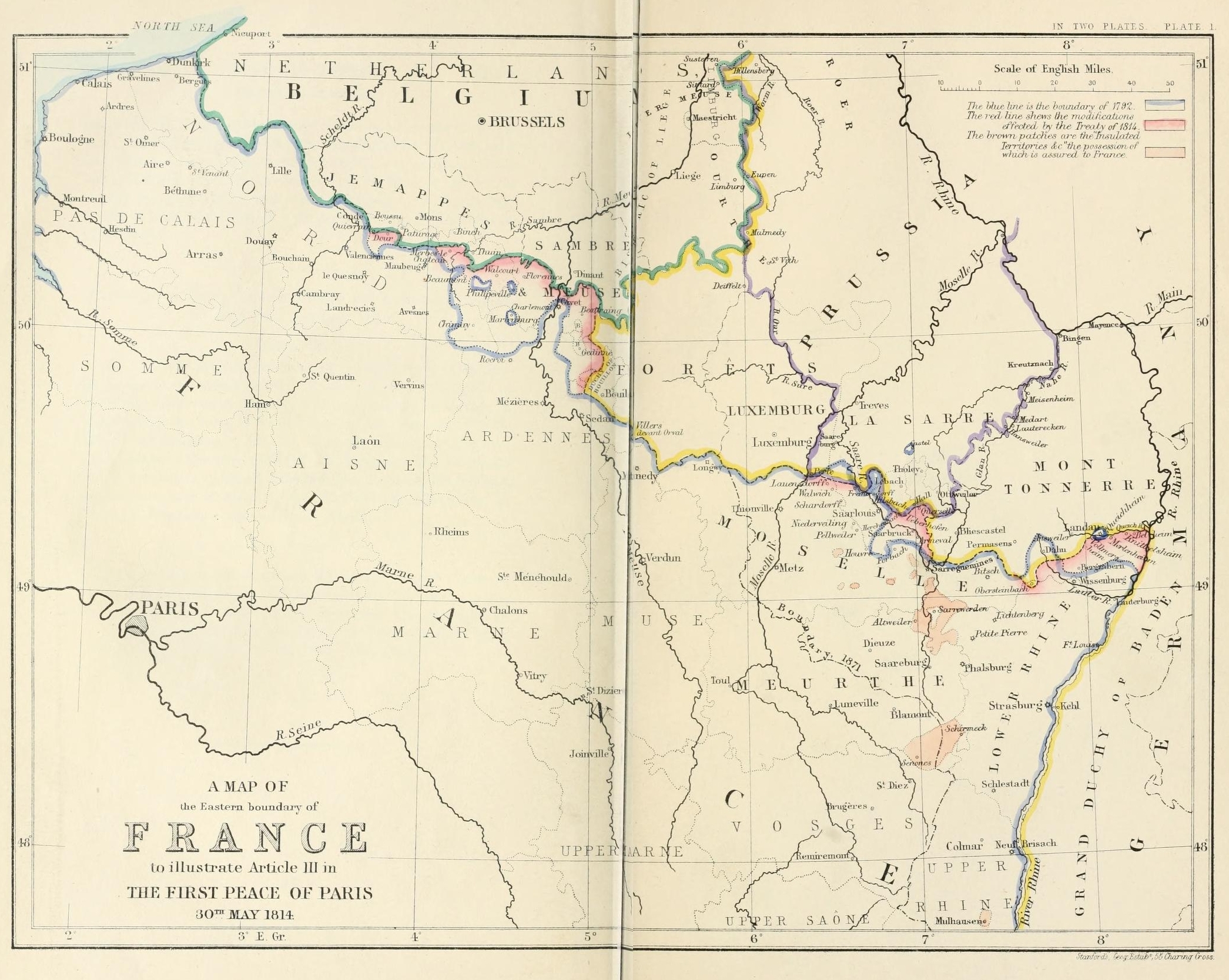
Treaty Of Paris (1814)
The Treaty of Paris, signed on 30 May 1814, ended the war between France and the Sixth Coalition, part of the Napoleonic Wars, following an armistice signed on 23 April between Charles, Count of Artois, and the allies. The treaty set the borders for France under the House of Bourbon and restored territories to other nations. It is sometimes called the First Peace of Paris, as another one followed in 1815. Parties to the treaty This treaty was signed on 30 May 1814, following an armistice signed on 23 April 1814 between Charles, Count of Artois, and the allies. Napoleon had abdicated as Emperor on 6 April, as a result of negotiations at Fontainebleau. Peace talks had started on 9 May between Talleyrand, who negotiated with the allies of Chaumont on behalf of the exiled Bourbon king Louis XVIII of France, and the allies. The Treaty of Paris established peace between France and Great Britain, Russia, Austria, and Prussia, who in March had defined their common war aim in Chaum ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Treaty Of Paris (14 March 1812)
The Treaty of Paris of 14 March 1812 created an alliance between the Austrian Empire and the First French Empire, French Empire against the Russian Empire.The French text of the treaty is in . Austria pledged to provide an auxiliary corps of 30,000 troops under the command of the French emperor, Napoleon Bonaparte, in the event of a war with Russia. The signatory for France was its foreign minister, the Hugues-Bernard Maret, duc de Bassano, Duke of Bassano, and for Austria its ambassador in Paris, the Karl Philipp, Prince of Schwarzenberg, Prince of Schwarzenberg. The treaty had nine public and eleven secret articles. The treaty was published in ''Le Moniteur Universel'' on 5 October 1813. The Franco-Austrian alliance was sought by Austria. On 28 November 1811, the Austrian foreign minister, Klemens von Metternich, informed the Emperor Francis II, Holy Roman Emperor, Francis I that he considered a war between France and Russia likely to come the following year. On 24 February 1812, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Treaty Of Paris (24 February 1812)
The Treaty of Paris of 24 February 1812 between Napoleon I of France and Frederick William III of Prussia established a Franco-Prussian alliance directed against Russia. On 24 June, Prussia joined the French invasion of Russia. The unpopular alliance broke down when the Prussian contingent in French service signed a separate armistice, the Convention of Tauroggen, with Russia on 30 December 1812. On 17 March 1813, Frederick William declared war on France and issued his famous proclamation "To My People". According to East German historiography, the Franco-Prussian alliance strengthened the hand of the monarchy and nobility against social and national movements. In the end, however, the action of the masses—disarming retreating French troops; collecting money, food and clothes for Russian prisoners; clashing with French troops—were definitive in ending it. Background By 1811 both France and Russia were preparing for war. Early in the year a Russian approach to Prussia for an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |