|
Treaty Of Saint-Germain-en-Laye (1919)
The Treaty of Saint-Germain-en-Laye (french: Traité de Saint-Germain-en-Laye) was signed on 10 September 1919 by the victorious Allies of World War I on the one hand and by the Republic of German-Austria on the other. Like the Treaty of Trianon with Hungary and the Treaty of Versailles with Germany, it contained the Covenant of the League of Nations and as a result was not ratified by the United States but was followed by the US–Austrian Peace Treaty of 1921. The treaty signing ceremony took place at the Château de Saint-Germain-en-Laye. Background As a preamble, on 21 October 1918, 208 German-speaking delegates of the Austrian Imperial Council had convened in a "provisional national assembly of German-Austria" at the Lower Austrian Landtag. When the collapse of the Austro-Hungarian Army culminated at the Battle of Vittorio Veneto, the Social Democrat Karl Renner was elected German-Austrian State Chancellor on 30 October. In the course of the Aster Revolution on 31 Oc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
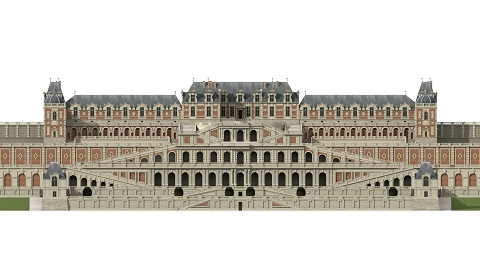
Château De Saint-Germain-en-Laye
The Château de Saint-Germain-en-Laye () is a former royal palace in the commune of Saint-Germain-en-Laye, in the ''département'' of Yvelines, about 19 km west of Paris, France. Today, it houses the ''musée d'Archéologie nationale'' (National Museum of Archaeology). History 12th–13th centuries The first castle, named the ''Grand Châtelet'', was built on the site by Louis VI in 1124. The castle was expanded by Louis IX in the 1230s. Louis IX's chapelle Saint Louis at the castle belongs to the Rayonnant phase of French Gothic architecture. A 1238 charter of Louis IX instituting a regular religious service at the chapel is the first mention of a chapel having been built at the royal castle. This was a ''Sainte Chapelle'', to house a relic of the Crown of Thorns or the True Cross. Its plan and architecture prefigure the major Sainte-Chapelle which Saint Louis built within the Palais de la Cité at Paris between 1240 and 1248. Both buildings were built by Louis's fa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charles I Of Austria
Charles I or Karl I (german: Karl Franz Josef Ludwig Hubert Georg Otto Maria, hu, Károly Ferenc József Lajos Hubert György Ottó Mária; 17 August 18871 April 1922) was Emperor of Austria, King of Hungary (as Charles IV, ), King of Croatia, King of Bohemia (as Charles III, ), and the last of the monarchs belonging to the House of Habsburg-Lorraine to rule over Austria-Hungary. The son of Archduke Otto of Austria and Princess Maria Josepha of Saxony, Charles became heir presumptive of Emperor Franz Joseph when his uncle Archduke Franz Ferdinand of Austria was assassinated in 1914. In 1911, he married Princess Zita of Bourbon-Parma. He is venerated in the Catholic Church, having been beatified by Pope John Paul II on 3 October 2004, and is known to the Catholic Church as Blessed Karl of Austria. Charles succeeded to the thrones in November 1916 following the death of his grand-uncle, Franz Joseph. He began secret negotiations with the Allies, hoping to peacefully end the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Austria-Hungary
Austria-Hungary, often referred to as the Austro-Hungarian Empire,, the Dual Monarchy, or Austria, was a constitutional monarchy and great power in Central Europe between 1867 and 1918. It was formed with the Austro-Hungarian Compromise of 1867 in the aftermath of the Austro-Prussian War and was dissolved shortly after its defeat in the First World War. Austria-Hungary was ruled by the House of Habsburg and constituted the last phase in the constitutional evolution of the Habsburg monarchy. It was a multinational state and one of Europe's major powers at the time. Austria-Hungary was geographically the second-largest country in Europe after the Russian Empire, at and the third-most populous (after Russia and the German Empire). The Empire built up the fourth-largest machine building industry in the world, after the United States, Germany and the United Kingdom. Austria-Hungary also became the world's third-largest manufacturer and exporter of electric home appliances, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Armistice Of Villa Giusti
The Armistice of Villa Giusti or Padua ended warfare between Italy and Austria-Hungary on the Italian Front during World War I. The armistice was signed on 3 November 1918 in the Villa Giusti, outside Padua in the Veneto, Northern Italy, and took effect 24 hours later. Background By the end of October 1918, the Austro-Hungarian Army was so fatigued that its commanders were forced to seek a ceasefire. By 1918 the Austro-Hungarian Empire was tearing itself apart under ethnic lines, and if the Dual Monarchy were to survive, it needed to withdraw from the war. In the final stage of the Battle of Vittorio Veneto, a stalemate was reached, and the troops of Austria-Hungary started a chaotic withdrawal. On 28 October, Austria-Hungary began to negotiate a truce but hesitated to sign the text of the armistice. In the meantime, the Italians reached Trento and Udine, and landed in Trieste. After a threat to break off negotiations, the Austro-Hungarians, on 3 November, accepted the armisti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Real Union
Real union is a union of two or more states, which share some state institutions in contrast to personal unions; however, they are not as unified as states in a political union. It is a development from personal union and has historically been limited to monarchies. Unlike personal unions, real unions almost exclusively led to a reduction of sovereignty for the politically weaker constituent. That was the case with Lithuania and Norway, which came under the influence of stronger neighbors, Poland and Denmark respectively, with whom each of them had shared a personal union previously. Sometimes, however, a real union came about after a period of political union. The most notable example of such a move is the Kingdom of Hungary (Lands of the Crown of Saint Stephen), which achieved equal status to Austria (which exercised control over the " Cisleithanian" crown lands) in Austria-Hungary following the Austro-Hungarian Compromise of 1867. Unions may form for pragmatic reasons, " ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mihály Károlyi
Count Mihály Ádám György Miklós Károlyi de Nagykároly ( hu, gróf nagykárolyi Károlyi Mihály Ádám György Miklós; archaically English: Michael Adam George Nicholas Károlyi, or in short simple form: Michael Károlyi; 4 March 1875 – 19 March 1955) was a Hungarian politician who served as a leader of the short-lived and unrecognized First Hungarian Republic from 1918 to 1919. He served as prime minister between 1 and 16 November 1918 and as president between 16 November 1918 and 21 March 1919. Early life and career Early life The Károlyi family were an illustrious, extremely wealthy, Roman Catholic aristocratic family who had played an important role in Hungarian society since the 17th century. Mihály Károlyi was born on March 4, 1875, in the Károlyi Palace in the aristocratic palace district of Pest. Károlyi’s parents were cousins, and he was born with a cleft lip and cleft palate, which deeply determined his entire childhood and personality development. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
First Hungarian Republic
The First Hungarian Republic ( hu, Első Magyar Köztársaság), until 21 March 1919 the Hungarian People's Republic (), was a short-lived unrecognized country, which quickly transformed into a small rump state due to the foreign and military policy of the doctrinaire pacifist Károlyi government. It existed from 16 November 1918 until 8 August 1919, apart from a 133-day interruption in the form of the Hungarian Soviet Republic. The republic was established in the wake of the dissolution of Austria-Hungary following World War I as a replacement for the Kingdom of Hungary, During the rule of Count Mihály Károlyi's pacifist cabinet, Hungary lost control over approximately 75% of its former pre-World War I territories, which was about , without armed resistance and was subjected to unhindered foreign occupation. It was in turn succeeded by the Hungarian Soviet Republic but re-established following its demise, and ultimately replaced by the Hungarian Republic. Name "Hungarian ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aster Revolution
The Aster Revolution or Chrysanthemum Revolution ( hu, Őszirózsás forradalom) was a revolution in Hungary led by Count Mihály Károlyi in the aftermath of World War I which resulted in the foundation of the short-lived First Hungarian People's Republic. The revolution was brought about by widespread protests as World War I wore on, from which Mihály Károlyi emerged as the leader of the newly proclaimed First Hungarian People's Republic that reigned between 16 November 1918 and 21 March 1919. During this period of time, he served as Prime Minister between 1 and 16 November 1918 and as President between 16 November 1918 and 21 March 1919. The supporters of Károlyi that consisted of citizens and demobilized soldiers adopted aster as the symbol of the revolution, viz., they stuck asters (''őszirózsa'': literally autumn = ''ősz'' and rose = ''rózsa'') in their hats and caps in the streets of Budapest to symbolize their support for the social democratic Hungarian National ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Karl Renner
Karl Renner (14 December 1870 – 31 December 1950) was an Austrian politician and jurist of the Social Democratic Workers' Party of Austria. He is often referred to as the "Father of the Republic" because he led the first government of German-Austria and the First Austrian Republic in 1919 and 1920, and was once again decisive in establishing the present Second Republic after the fall of Nazi Germany in 1945, becoming its first President after World War II (and fourth overall). Early life Renner was born the 18th child of an ethnic German family of poor wine-growers in Unter-Tannowitz (present-day Dolní Dunajovice in the Czech Republic), then part of the Margraviate of Moravia, a crown land of the Austro-Hungarian Empire. Because of his intelligence, he was allowed to attend a selective '' gymnasium'' in nearby Nikolsburg (Mikulov), where one of his teachers was Wilhelm Jerusalem. From 1890 to 1896 he studied law at the University of Vienna. In 1895 he was one of the foundin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Vittorio Veneto
The Battle of Vittorio Veneto was fought from 24 October to 3 November 1918 (with an armistice taking effect 24 hours later) near Vittorio Veneto on the Italian Front during World War I. After having thoroughly defeated Austro-Hungarian troops during the defensive Battle of the Piave River, the Italian army launched a great counter-offensive: the Italian victory marked the end of the war on the Italian Front, secured the dissolution of the Austro-Hungarian Empire and contributed to the end of the First World War just one week later. The battle led to the capture of over 5,000 artillery pieces and over 350,000 Austro-Hungarian troops, including 120,000 Germans, 83,000 Czechs and Slovaks, 60,000 South Slavs, 40,000 Poles, several tens of thousands of Romanians and Ukrainians, and 7,000 Austro-Hungarian loyalist Italians and Friulians. Name When the battle was fought in November 1918, the nearby city was called simply Vittorio, named in 1866 for Vittorio Emanuele II, monarch fro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Austro-Hungarian Army
The Austro-Hungarian Army (, literally "Ground Forces of the Austro-Hungarians"; , literally "Imperial and Royal Army") was the ground force of the Austro-Hungarian Dual Monarchy from 1867 to 1918. It was composed of three parts: the joint army (, "Common Army", recruited from all parts of the country), the Imperial Austrian Landwehr (recruited from Cisleithania), and the Royal Hungarian Honvéd (recruited from Transleithania). In the wake of fighting between the Austrian Empire and the Hungarian Kingdom and the two decades of uneasy co-existence following, Hungarian soldiers served either in mixed units or were stationed away from Hungarian areas. With the Austro-Hungarian Compromise of 1867 the new tripartite army was brought into being. It existed until the disestablishment of the Austro-Hungarian Empire following World War I in 1918. The joint "Imperial and Royal Army" ( or ''k.u.k.'') units were generally poorly trained and had very limited access to new equipment bec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |