|
Traveling Wave Antenna
In radio and telecommunication, a traveling-wave antenna is a class of antenna that uses a traveling wave on a guiding structure as the main radiating mechanism. Its distinguishing feature is that the radio-frequency current that generates the radio waves travels through the antenna in one direction. This is in contrast to a ''resonant antenna'', such as the monopole or dipole, in which the antenna acts as a resonator, with radio currents traveling in both directions, bouncing back and forth between the ends of the antenna. An advantage of traveling wave antennas is that since they are nonresonant they often have a wider bandwidth than resonant antennas. Common types of traveling wave antenna are the Beverage antenna, axial-mode helical antenna, and rhombic antenna. Traveling-wave antennas fall into two general categories: ''slow-wave antennas'', and ''fast-wave antennas''. Fast-wave antennas are often referred to as leaky wave antenna. See also * Axial mode helical ante ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radio
Radio is the technology of signaling and communicating using radio waves. Radio waves are electromagnetic waves of frequency between 30 hertz (Hz) and 300 gigahertz (GHz). They are generated by an electronic device called a transmitter connected to an antenna which radiates the waves, and received by another antenna connected to a radio receiver. Radio is very widely used in modern technology, in radio communication, radar, radio navigation, remote control, remote sensing, and other applications. In radio communication, used in radio and television broadcasting, cell phones, two-way radios, wireless networking, and satellite communication, among numerous other uses, radio waves are used to carry information across space from a transmitter to a receiver, by modulating the radio signal (impressing an information signal on the radio wave by varying some aspect of the wave) in the transmitter. In radar, used to locate and track objects like aircraft, ships, spacecraf ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rhombic Antenna
A rhombic antenna is made of four sections of wire suspended parallel to the ground in a diamond or "rhombus" shape. Each of the four sides is the same length – about a quarter-wavelength to one wavelength per section – converging but not touching at an angle of about 42° at the fed end and at the far end. The length is not critical, typically from one to two wavelengths ( λ), but there is an optimum angle for any given length and frequency. A horizontal rhombic antenna radiates horizontally polarized radio waves at a low elevation angle off the pointy ends of the antenna. If the sections are joined by a resistor at either of the acute (pointy) ends, then the antenna will receive from and transmit to only the direction the end with the resistor points at. Its principal advantages over other types of antenna are its simplicity, high forward gain, wide bandwidth, and the ability to operate over a wide range of frequencies. Description A rhombic antenna consists of one to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shortwave Broadband Antenna
A shortwave broadband antenna is a radio antenna that can be used for transmission (and reception) of any shortwave radio band from among the greater part of the shortwave radio spectrum, without requiring any band-by-band adjustment of the antenna. Generally speaking, there is no difficulty in building an adequate receiving antenna; the challenge is designing an antenna which can be used for transmission without an adjustable impedance matching network. An ideal “broadband” shortwave antenna would work continuously across much of, if not all of, the shortwave spectrum with good radiation efficiency and minimal compromise of the radiation pattern. Most practical broadband antennas compromise on one of the above: Either they only work on a few relatively narrow slices of the HF radio spectrum, or they work across the complete spectrum, without gaps, but are inefficient radiators on some or all of the frequencies. Other antennas provide adequate efficiency on some frequencies, bu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rhombic Antenna
A rhombic antenna is made of four sections of wire suspended parallel to the ground in a diamond or "rhombus" shape. Each of the four sides is the same length – about a quarter-wavelength to one wavelength per section – converging but not touching at an angle of about 42° at the fed end and at the far end. The length is not critical, typically from one to two wavelengths ( λ), but there is an optimum angle for any given length and frequency. A horizontal rhombic antenna radiates horizontally polarized radio waves at a low elevation angle off the pointy ends of the antenna. If the sections are joined by a resistor at either of the acute (pointy) ends, then the antenna will receive from and transmit to only the direction the end with the resistor points at. Its principal advantages over other types of antenna are its simplicity, high forward gain, wide bandwidth, and the ability to operate over a wide range of frequencies. Description A rhombic antenna consists of one to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leaky Wave Antenna
Leaky-wave antenna (LWA) belong to the more general class of traveling wave antenna, that use a traveling wave on a guiding structure as the main radiating mechanism. Traveling-wave antenna fall into two general categories, slow-wave antennas and fast-wave antennas, which are usually referred to as leaky-wave antennas. Introduction The traveling wave on a Leaky-Wave Antenna is a fast wave, with a phase velocity greater than the speed of light. This type of wave radiates continuously along its length, and hence the propagation wavenumber kz is complex, consisting of both a phase and an attenuation constant. Highly directive beams at an arbitrary specified angle can be achieved with this type of antenna, with a low sidelobe level. The phase constant β of the wave controls the beam angle (and this can be varied changing the frequency), while the attenuation constant α controls the beamwidth. The aperture distribution can also be easily tapered to control the sidelobe level or beam s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
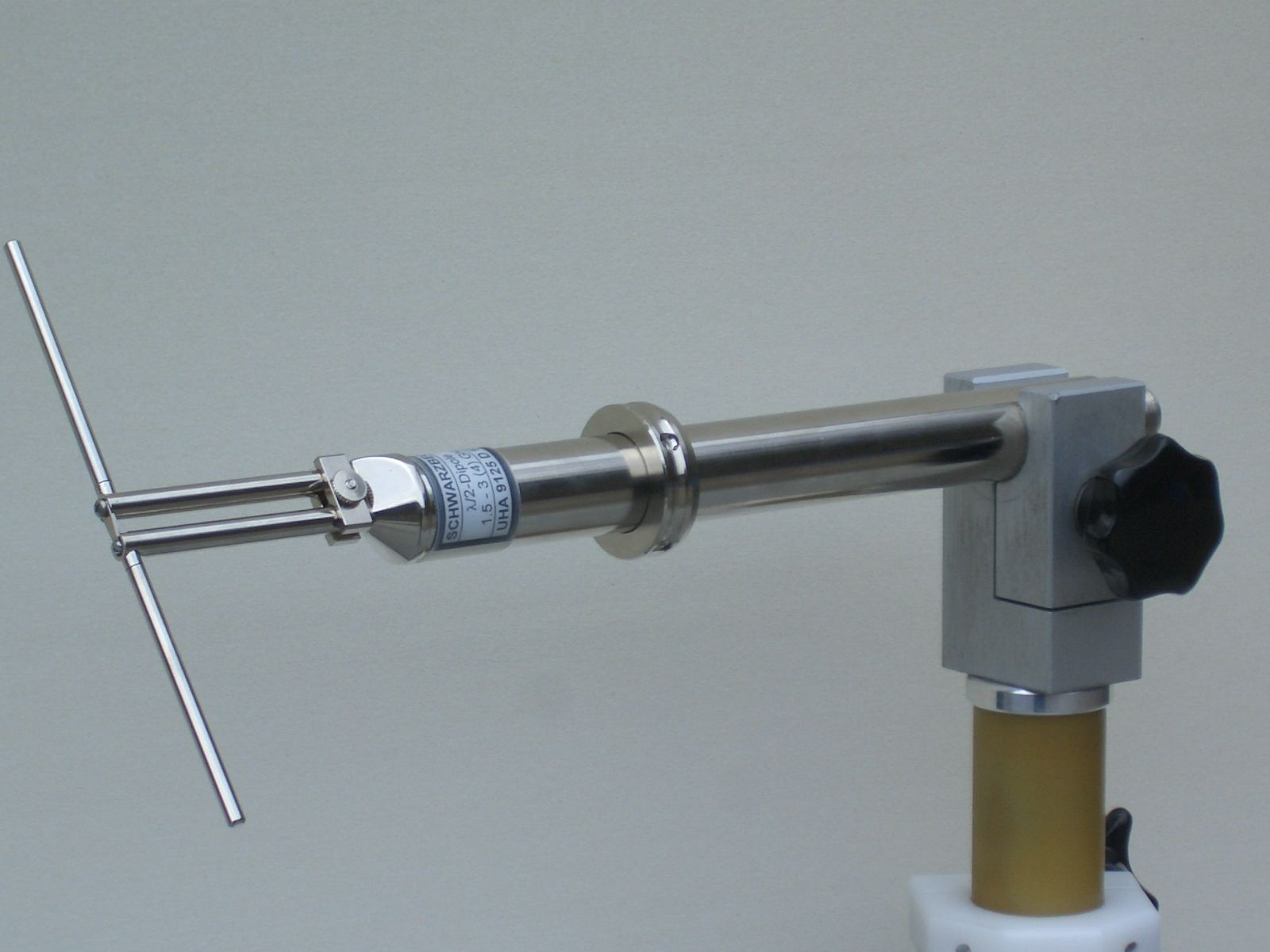
Dipole Antenna
In radio and telecommunications a dipole antenna or doublet is the simplest and most widely used class of antenna. The dipole is any one of a class of antennas producing a radiation pattern approximating that of an elementary electric dipole with a radiating structure supporting a line current so energized that the current has only one node at each end. A dipole antenna commonly consists of two identical conductive elements such as metal wires or rods. The driving current from the transmitter is applied, or for receiving antennas the output signal to the receiver is taken, between the two halves of the antenna. Each side of the feedline to the transmitter or receiver is connected to one of the conductors. This contrasts with a monopole antenna, which consists of a single rod or conductor with one side of the feedline connected to it, and the other side connected to some type of ground. A common example of a dipole is the "rabbit ears" television antenna found on broadcast telev ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Helical Antenna
A helical antenna is an antenna consisting of one or more conducting wires wound in the form of a helix. A helical antenna made of one helical wire, the most common type, is called ''monofilar'', while antennas with two or four wires in a helix are called ''bifilar'', or ''quadrifilar'', respectively. In most cases, directional helical antennas are mounted over a ground plane, while omnidirectional designs may not be. The feed line is connected between the bottom of the helix and the ground plane. Helical antennas can operate in one of two principal modes: normal or axial. In the ''normal mode'' or ''broadside'' helical antenna, the diameter and the pitch of the aerial are small compared with the wavelength. The antenna acts similarly to an electrically short dipole or monopole, equivalent to a wave vertical and the radiation pattern, similar to these antennas is omnidirectional, with maximum radiation at right angles to the helix axis. For monofilar designs the rad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leaky Wave Antenna
Leaky-wave antenna (LWA) belong to the more general class of traveling wave antenna, that use a traveling wave on a guiding structure as the main radiating mechanism. Traveling-wave antenna fall into two general categories, slow-wave antennas and fast-wave antennas, which are usually referred to as leaky-wave antennas. Introduction The traveling wave on a Leaky-Wave Antenna is a fast wave, with a phase velocity greater than the speed of light. This type of wave radiates continuously along its length, and hence the propagation wavenumber kz is complex, consisting of both a phase and an attenuation constant. Highly directive beams at an arbitrary specified angle can be achieved with this type of antenna, with a low sidelobe level. The phase constant β of the wave controls the beam angle (and this can be varied changing the frequency), while the attenuation constant α controls the beamwidth. The aperture distribution can also be easily tapered to control the sidelobe level or beam s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Helical Antenna
A helical antenna is an antenna consisting of one or more conducting wires wound in the form of a helix. A helical antenna made of one helical wire, the most common type, is called ''monofilar'', while antennas with two or four wires in a helix are called ''bifilar'', or ''quadrifilar'', respectively. In most cases, directional helical antennas are mounted over a ground plane, while omnidirectional designs may not be. The feed line is connected between the bottom of the helix and the ground plane. Helical antennas can operate in one of two principal modes: normal or axial. In the ''normal mode'' or ''broadside'' helical antenna, the diameter and the pitch of the aerial are small compared with the wavelength. The antenna acts similarly to an electrically short dipole or monopole, equivalent to a wave vertical and the radiation pattern, similar to these antennas is omnidirectional, with maximum radiation at right angles to the helix axis. For monofilar designs the rad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Telecommunication
Telecommunication is the transmission of information by various types of technologies over wire, radio, optical, or other electromagnetic systems. It has its origin in the desire of humans for communication over a distance greater than that feasible with the human voice, but with a similar scale of expediency; thus, slow systems (such as postal mail) are excluded from the field. The transmission media in telecommunication have evolved through numerous stages of technology, from beacons and other visual signals (such as smoke signals, semaphore telegraphs, signal flags, and optical heliographs), to electrical cable and electromagnetic radiation, including light. Such transmission paths are often divided into communication channels, which afford the advantages of multiplexing multiple concurrent communication sessions. ''Telecommunication'' is often used in its plural form. Other examples of pre-modern long-distance communication included audio messages, such as coded drumb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beverage Antenna
The Beverage antenna or "wave antenna" is a long-wire receiving antenna mainly used in the low frequency and medium frequency radio bands, invented by Harold H. Beverage in 1921. It is used by amateur radio, shortwave listening, and longwave radio DXers and military applications. A Beverage antenna consists of a horizontal wire from one-half to several wavelengths long (tens to hundreds of meters at HF to several kilometres for longwave) suspended above the ground, with the feedline to the receiver attached to one end, and the other end of the Beverage terminated through a resistor to ground., also archivehere/ref> The antenna has a unidirectional radiation pattern with the main lobe of the pattern at a shallow angle into the sky off the resistor-terminated end, making it ideal for reception of long distance skywave (skip) transmissions from stations over the horizon which reflect off the ionosphere. However the antenna must be built so the wire points in the direction ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bandwidth (signal Processing)
Bandwidth is the difference between the upper and lower frequencies in a continuous band of frequencies. It is typically measured in hertz, and depending on context, may specifically refer to ''passband bandwidth'' or ''baseband bandwidth''. Passband bandwidth is the difference between the upper and lower cutoff frequencies of, for example, a band-pass filter, a communication channel, or a signal spectrum. Baseband bandwidth applies to a low-pass filter or baseband signal; the bandwidth is equal to its upper cutoff frequency. Bandwidth in hertz is a central concept in many fields, including electronics, information theory, digital communications, radio communications, signal processing, and spectroscopy and is one of the determinants of the capacity of a given communication channel. A key characteristic of bandwidth is that any band of a given width can carry the same amount of information, regardless of where that band is located in the frequency spectrum. For example, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |






_(14569732060).jpg)