|
Trasianka
Trasianka ( be, трасянка, ) refers to a mixed form of speech in which Belarusian and Russian elements and structures alternate arbitrarily.Hentschel, Gerd Belarusian and Russian in the Mixed Speech of Belarus. In Besters-Dilger, J. et al. (eds.): “Congruence in Contact-Induced Language Change: Language Families, Typological Resemblance, and Perceived Similarity.” Berlin, Boston: De Gruyter, 2014, 93-121. There is a similar phenomenon in Ukraine, a Ukrainian–Russian language mixture, called surzhyk. Etymology In Belarusian the word literally means low quality hay, when indigent farmers mix (shake: , ) fresh grass/straw with the yesteryear's dried hay. The word acquired the second meaning ("language mixture of low quality") relatively recently, in the second half of the 1980s, when a series of publications in the literary newspaper criticized developments in the use of the Belarusian language under Soviet rule.Zaprudski, Siarhiej Zur öffentlichen Diskussion ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Belarusian Language
Belarusian ( be, беларуская мова, biełaruskaja mova, link=no, ) is an East Slavic language. It is the native language of many Belarusians and one of the two official state languages in Belarus. Additionally, it is spoken in some parts of Russia, Lithuania, Latvia, Poland, and Ukraine by Belarusian minorities in those countries. Before Belarus gained independence in 1991, the language was only known in English as ''Byelorussian'' or ''Belorussian'', the compound term retaining the English-language name for the Russian language in its second part, or alternatively as ''White Russian''. Following independence, it became known as ''Belarusan'' and since 1995 as ''Belarusian'' in English. As one of the East Slavic languages, Belarusian shares many grammatical and lexical features with other members of the group. To some extent, Russian, Rusyn, Ukrainian, and Belarusian retain a degree of mutual intelligibility. Its predecessor stage is known in Western academia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Russian Language
Russian (russian: русский язык, russkij jazyk, link=no, ) is an East Slavic languages, East Slavic language mainly spoken in Russia. It is the First language, native language of the Russians, and belongs to the Indo-European languages, Indo-European language family. It is one of four living East Slavic languages, and is also a part of the larger Balto-Slavic languages. Besides Russia itself, Russian is an official language in Belarus, Kazakhstan, and Kyrgyzstan, and is used widely as a lingua franca throughout Ukraine, the Caucasus, Central Asia, and to some extent in the Baltic states. It was the De facto#National languages, ''de facto'' language of the former Soviet Union,1977 Soviet Constitution, Constitution and Fundamental Law of the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics, 1977: Section II, Chapter 6, Article 36 and continues to be used in public life with varying proficiency in all of the post-Soviet states. Russian has over 258 million total speakers worldwide. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Languages Of Belarus
The official languages of Belarus are Belarusian and Russian. The pre-Slavic language of the area, as well as its geographic name was Sudovian and Sudavia, a Baltic language. Sudovian is believed to have gone extinct around the 17th century. At present, Belarusian and Russian are considered the sole native languages of Belarus, as seen below. The language situation in Belarus is characterized by a co-existence of several linguistic codes. The three most widespread codes are Belarusian, Russian and the so-called Trasianka, a mixed speech in which Belarusian and Russian elements and structures alternate arbitrarily.Hentschel, G. (2014) Belarusian and Russian in the Mixed Speech of Belarus. In: Besters-Dilger, J. et al. (eds.): Congruence in Contact-Induced Language Change: Language Families, Typological Resemblance, and Perceived Similarity. Berlin/Boston, 93-121. History The earliest known documents from ethnic Belarusian territories date from the 12th century.McMillin, A. (19 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Narkamaŭka
Narkamaŭka ( be, наркамаўка, narkamaŭka, or be, наркомаўка, narkomaŭka, ) is a colloquial name for the reformed Belarusian orthography. Evolved from the Belarusian ''narkam'' (), abbreviated early Soviet name for the ministry, '' narodny kamisar'' (). Narkamaŭka is the simplified version of the Belarusian language's orthography, with some scholars claiming that it turned out the language to become closer to Russian during Soviet era in Belarus.''Yuliya Brel.'' (University of DelawareThe Failure of the Language Policy in Belarus.''New Visions for Public Affairs'', Volume 9, Spring 2017, pp. 59--74 The name was coined around the end of the 1980s or the beginning of the 1990s by the Belarusian linguist Vincuk Viačorka.'' Zaprudski, S. . Minsk, 1999. pp. 20–26. See also * Taraškievica * Trasianka Trasianka ( be, трасянка, ) refers to a mixed form of speech in which Belarusian and Russian elements and structures alternate arbitrarily.He ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
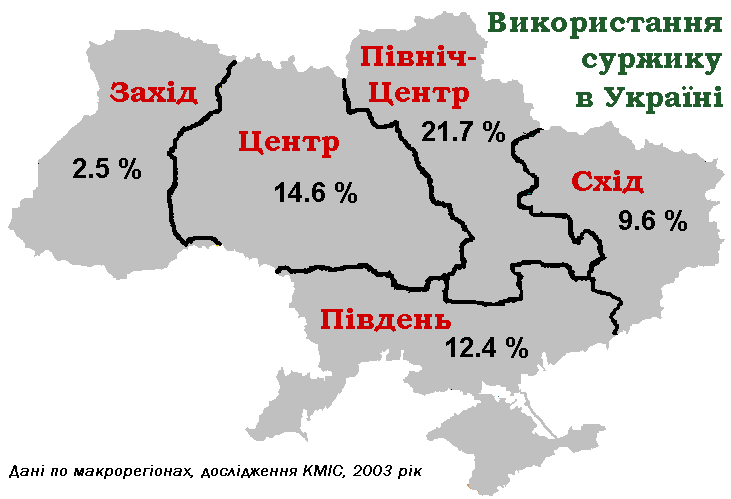
Surzhyk
Surzhyk (, ) refers to a range of mixed sociolects of Ukrainian and Russian languages used in certain regions of Ukraine and the neighboring regions of Russia and Moldova. There is no unifying set of characteristics; the term is, according to some authors, used for "norm-breaking, non-obedience to or non-awareness of the rules of the Ukrainian and Russian standard languages". Surzhyk is a Ukrainian word that could refer to any mixed language, not necessarily including Ukrainian or Russian. When used by non-Ukrainian speaking people of Ukraine, the word is most commonly used to refer to a mix of Ukrainian with another language, not necessarily Russian. When used in Russia the word almost always specifically refers to a Ukrainian-Russian language mix. It differs from both Ukrainian and spoken "Ukrainian Russian", although it is impossible to draw a clear line between them and surzhyk. The vocabulary mix of each of its constituent languages (Ukrainian and Russian) varies greatly ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Taraškievica
Taraškievica or Belarusian Classical Orthography (, be, тарашкевіца / клясычны правапіс) is a variant of orthography of the Belarusian language, based on the literary norm of the modern Belarusian language, the first normalization of which was made by Branislaŭ Taraškievič in 1918, and was in official use in Belarus until the Belarusian orthography reform of 1933. Since 1933, Taraškievica has been used informally in Belarus and by the Belarusian diaspora abroad. In a more common sense Taraškievica is sometimes considered to be a linguistic norm.Сяргей Шуп�Тарашкевіца ў Слоўніку Свабоды // Arche № 7 (12) — 2000 The name ''Taraškievica'' (Tarashkyevitsa) is intended to emphasize the similarity of the orthography to the work of Branislaŭ Taraškievič and may have appeared before World War II.Два стандарты беларускай літаратурнай мовы. — 2004 // Мова і со� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Surzhyk
Surzhyk (, ) refers to a range of mixed sociolects of Ukrainian and Russian languages used in certain regions of Ukraine and the neighboring regions of Russia and Moldova. There is no unifying set of characteristics; the term is, according to some authors, used for "norm-breaking, non-obedience to or non-awareness of the rules of the Ukrainian and Russian standard languages". Surzhyk is a Ukrainian word that could refer to any mixed language, not necessarily including Ukrainian or Russian. When used by non-Ukrainian speaking people of Ukraine, the word is most commonly used to refer to a mix of Ukrainian with another language, not necessarily Russian. When used in Russia the word almost always specifically refers to a Ukrainian-Russian language mix. It differs from both Ukrainian and spoken "Ukrainian Russian", although it is impossible to draw a clear line between them and surzhyk. The vocabulary mix of each of its constituent languages (Ukrainian and Russian) varies greatly ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Russification Of Belarus
The Russification of Belarus ( be, Расеізацыя Беларусі, Rasieizacyja Biełarusi; russian: Русификация Беларуси, translit=Rusyfikatsiya Byelarusi) is a policy of replacing the use of the Belarusian language and the presence of Belarusian culture and mentality in various spheres of public life in Belarus by the corresponding Russian analogs. Russification is one of the major reasons of insufficient adoption of the Belarusian language by Belarusians. In Belarus, Russification was carried out by the authorities of the Russian Empire and, later, by the authorities of the Soviet Union.''Yuliya Brel.'' (University of DelawareThe Failure of the Language Policy in Belarus.''New Visions for Public Affairs'', Volume 9, Spring 2017, pp. 59—74 Belarusian president Alexander Lukashenko has renewed the policy since coming to power in 1994,Vadzim Smok'Belarusian Identity: the Impact of Lukashenka’s Rule// ''Analytical Paper.'' Ostrogorski Centre, Belarus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Minsk
Minsk ( be, Мінск ; russian: Минск) is the capital and the largest city of Belarus, located on the Svislach and the now subterranean Niamiha rivers. As the capital, Minsk has a special administrative status in Belarus and is the administrative centre of Minsk Region ( voblast) and Minsk District (raion). As of January 2021, its population was 2 million, making Minsk the 11th most populous city in Europe. Minsk is one of the administrative capitals of the Commonwealth of Independent States (CIS) and the Eurasian Economic Union (EAEU). First documented in 1067, Minsk became the capital of the Principality of Minsk before being annexed by the Grand Duchy of Lithuania in 1242. It received town privileges in 1499. From 1569, it was the capital of the Minsk Voivodeship, an administrative division of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth. It was part of a region annexed by the Russian Empire in 1793, as a consequence of the Second Partition of Poland. From 1919 to 1991, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Romanization Of Belarusian
Romanization or Latinization of Belarusian is any system for transliterating written Belarusian from Cyrillic to the Latin alphabet. Standard systems for romanizing Belarusian Standard systems for romanizing Belarusian include: *BGN/PCGN romanization of Belarusian, 1979 ( United States Board on Geographic Names and Permanent Committee on Geographical Names for British Official Use), which is the US and Great Britain prevailing system for romanising of geographical information *British Standard 2979 : 1958 *Scientific transliteration, or the ''International Scholarly System'' for linguistics * ALA-LC romanization, 1997 (American Library Association and Library of Congress) *ISO 9:1995, which is also Belarusian state standard GOST 7.79–2000 for non-geographical information *''Instruction on transliteration of Belarusian geographical names with letters of Latin script'', which is Belarusian state standard for geographical information, adopted by State Committee on land resources ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Voiceless Retroflex Affricate
The voiceless retroflex sibilant affricate is a type of consonantal sound, used in some spoken languages. The symbol in the International Phonetic Alphabet that represents this sound is , sometimes simplified to or , and the equivalent X-SAMPA symbol is . The affricate occurs in a number of languages: * Asturian: Speakers of the western dialects of this language use it instead of the voiced palatal fricative, writing ḷḷ instead of ll. *Slavic languages: Polish, Belarusian, Old Czech, Serbo-Croatian; some speakers of Russian may use it instead of the voiceless alveolo-palatal affricate. *a number of Northwest Caucasian languages have retroflex affricates that contrast in secondary articulations like labialization. * Mandarin and other Sinitic languages. Features Features of the voiceless retroflex affricate: Occurrence See also *Index of phonetics articles A * Acoustic phonetics * Active articulator * Affricate * Airstream mechanism * Alexander John Ell ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Voiceless Alveolo-palatal Affricate
The voiceless alveolo-palatal sibilant affricate is a type of consonantal sound, used in some spoken languages. The symbols in the International Phonetic Alphabet that represent this sound are , , and , and the equivalent X-SAMPA symbols are t_s\ and c_s\, though transcribing the stop component with (c in X-SAMPA) is rare. The tie bar may be omitted, yielding or in the IPA and ts\ or cs\ in X-SAMPA. Neither nor are a completely narrow transcription of the stop component, which can be narrowly transcribed as ( retracted and palatalized ) or ( advanced ). The equivalent X-SAMPA symbols are t_-' or t_-_j and c_+, respectively. There is also a dedicated symbol , which is not a part of the IPA. Therefore, narrow transcriptions of the voiceless alveolo-palatal sibilant affricate include , and . This affricate used to have a dedicated symbol , which was one of the six dedicated symbols for affricates in the International Phonetic Alphabet. It occurs in languages such as Mandar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |