|
Tracheloraphis
''Tracheloraphis'' is a genus of ciliates in the family Trachelocercidae. Description Like other members of the family Trachelocercidae, ''Tracheloraphis'' are relatively large (often >1 mm in length) ciliates with an elongated, worm-like shape, evenly-ciliated cell body, and a distinct "head and neck" region. The cytostome ("mouth", or oral area) is at the apex of the anterior end and is surrounded by cilia (circumoral ciliature). They are distinguished from other genera in the family by having a ''glabrous stripe'', an unciliated area running longitudinally along one side of the body. ''Tracheloraphis'' lives in the marine interstitial habitat, living in the water between sediment grains like most karyorelictea Karyorelictea is a class of ciliates in the subphylum Postciliodesmatophora. Most species are members of the microbenthos community, that is, microscopic organisms found in the marine interstitial habitat, though one genus, ''Loxodes'', is foun ...n ciliat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tracheloraphis Phoenicopterus
''Tracheloraphis'' is a genus of ciliates in the family Trachelocercidae. Description Like other members of the family Trachelocercidae, ''Tracheloraphis'' are relatively large (often >1 mm in length) ciliates with an elongated, worm-like shape, evenly-ciliated cell body, and a distinct "head and neck" region. The cytostome ("mouth", or oral area) is at the apex of the anterior end and is surrounded by cilia (circumoral ciliature). They are distinguished from other genera in the family by having a ''glabrous stripe'', an unciliated area running longitudinally along one side of the body. ''Tracheloraphis'' lives in the marine interstitial habitat, living in the water between sediment grains like most karyorelictea Karyorelictea is a class of ciliates in the subphylum Postciliodesmatophora. Most species are members of the microbenthos community, that is, microscopic organisms found in the marine interstitial habitat, though one genus, ''Loxodes'', is foun ...n ciliat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trachelocercidae
Trachelocercidae is a family of ciliates in the class Karyorelictea Karyorelictea is a class of ciliates in the subphylum Postciliodesmatophora. Most species are members of the microbenthos community, that is, microscopic organisms found in the marine interstitial habitat, though one genus, ''Loxodes'', is foun .... Systematics Trachelocercidae is the largest family within the Karyorelictea with about 70 nominal species so far described. Description Trachelocercids usually have an elongated body, which may be divided into head, neck, trunk and tail regions, an apical oral cavity, and most have several macronuclei and micronuclei arranged in nuclear groups References Karyorelictea {{Ciliate-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eukaryota
Eukaryotes () are organisms whose Cell (biology), cells have a cell nucleus, nucleus. All animals, plants, fungi, and many unicellular organisms, are Eukaryotes. They belong to the group of organisms Eukaryota or Eukarya, which is one of the Three-domain system, three domains of life. Bacteria and Archaea (both prokaryotes) make up the other two domains. The eukaryotes are usually now regarded as having emerged in the Archaea or as a sister of the Asgard (archaea), Asgard archaea. This implies that there are only Two-domain system, two domains of life, Bacteria and Archaea, with eukaryotes incorporated among archaea. Eukaryotes represent a small minority of the number of organisms, but, due to their generally much larger size, their collective global biomass (ecology), biomass is estimated to be about equal to that of prokaryotes. Eukaryotes emerged approximately 2.3–1.8 billion years ago, during the Proterozoic eon, likely as Flagellated cell, flagellated phagotrophs. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Interstitial Habitat
An interstitial space or interstice is a space between structures or objects. In particular, interstitial may refer to: Biology * Interstitial cell tumor * Interstitial cell, any cell that lies between other cells * Interstitial collagenase, enzyme that breaks the peptide bonds in collagen * Interstitial cystitis * Interstitium, the contiguous fluid-filled space existing between the skin and body organs * Interstitial fluid, a solution that bathes and surrounds the cells of multicellular animals * Interstitial granulomatous dermatitis * Interstitial infusion * Interstitial keratitis * Interstitial lung disease * Interstitial nephritis * Interstitial pregnancy Other uses To describe the spaces within particulate matter such sands, gravels, cobbles, grain, etc. that lie between the discrete particles. * Interstitial art * Interstitial condensation, in construction * Interstitial site, in chemistry * Interstitial defect, in chemistry * Interstitial television show, in televisio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ferdinand Cohn
Ferdinand Julius Cohn (24 January 1828 – 25 June 1898) was a German biologist. He is one of the founders of modern bacteriology and microbiology. Ferdinand J. Cohn was born in the Jewish quarter of Breslau in the Kingdom of Prussia, Prussian Province of Silesia (which is now Wroclaw, Poland).Chung, King-ThomFerdinand Julius Cohn (1828-1898): Pioneer of Bacteriology Department of Microbiology and Molecular Cell Sciences, The University of Memphis. His father, Issak Cohn, was a successful merchant and manufacturer. At the age of 10 Ferdinand suffered hearing impairment (for an unknown reason). Starting at age 16 he studied botany under Heinrich Goppert at the University of Breslau. Due to Cohn's Jewish background he was prevented from taking the final degree examinations at Breslau. Biography.yourdictionary.com (2014-06 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Karyorelictea
Karyorelictea is a class of ciliates in the subphylum Postciliodesmatophora. Most species are members of the microbenthos community, that is, microscopic organisms found in the marine interstitial habitat, though one genus, ''Loxodes'', is found in freshwater. The majority of karyorelict taxa have not been cultivated in the laboratory, although clonal lines of ''Loxodes'' have been developed. Systematics According to Lynn (2008), the Karyorelictea class is divided into three orders: * Loxodida, containing the families Cryptopharyngidae and Loxodidae; * Protoheterotrichida, containing the families Aveliidae and Geleiidae; * Protostomatida, containing the families Kentrophoridae and Trachelocercidae. These three orders were defined morphologically, and have been confirmed with molecular phylogenetics. An additional family, Wilbertomorphidae, is of uncertain affiliation and has not been assigned to an order. Nuclear dimorphism All ciliates, including karyorelicteans, p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ciliate
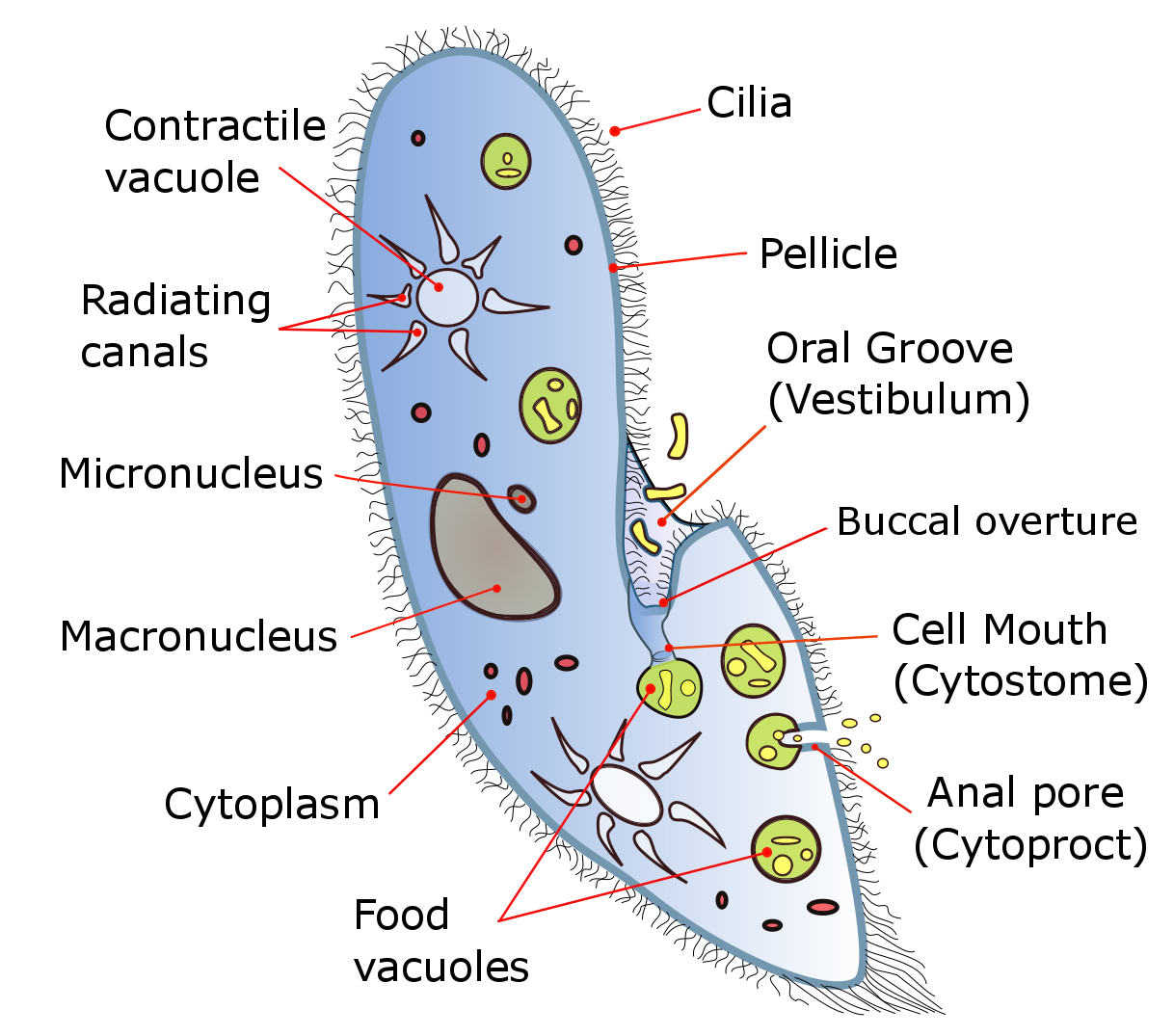
The ciliates are a group of alveolates characterized by the presence of hair-like organelles called cilia, which are identical in structure to flagellum, eukaryotic flagella, but are in general shorter and present in much larger numbers, with a different wikt:undulating, undulating pattern than flagella. Cilia occur in all members of the group (although the peculiar Suctoria only have them for part of their biological life cycle, life cycle) and are variously used in swimming, crawling, attachment, feeding, and sensation. Ciliates are an important group of protists, common almost anywhere there is water—in lakes, ponds, oceans, rivers, and soils. About 4,500 unique free-living species have been described, and the potential number of extant species is estimated at 27,000–40,000. Included in this number are many Ectosymbiosis, ectosymbiotic and endosymbiotic species, as well as some Obligate parasite, obligate and Facultative parasite, opportunistic parasites. Ciliate species r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cytostome
A cytostome (from ''cyto-'', cell and ''stome-'', mouth) or cell mouth is a part of a cell specialized for phagocytosis, usually in the form of a microtubule-supported funnel or groove. Food is directed into the cytostome, and sealed into vacuoles. Only certain groups of protozoa, such as the Ciliophora and Excavata, have cytostomes. An example is '' Balantidium coli'', a ciliate. In other protozoa, and in cells from multicellular organisms, phagocytosis takes place at any point on the cell or feeding takes place by absorption. Structure The cytostome forms an invagination on the cell surface and is typically directed towards the nucleus of the cell.Okuda, Kendi, et al. "The cytostome of Trypanosoma cruzi epimastigotes is associated with the flagellar complex." Experimental parasitology 92.4 (1999): 223-231. The cytostome is often labeled as the entire invagination, but in fact the cytostome only constitutes the opening of the invagination at the surface of the cell. The rest ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SAR Supergroup
The SAR supergroup, also just SAR or Harosa, is a clade that includes stramenopiles (heterokonts), alveolates, and Rhizaria. The name is an acronym derived from the first letters of each of these clades; it has been alternatively spelled "RAS". The term "Harosa" (at the subkingdom level) has also been used. The SAR supergroup is a node-based taxon. Note that as a formal taxon, "Sar" has only its first letter capitalized, while the earlier abbreviation, SAR, retains all uppercase letters. Both names refer to the same group of organisms, unless further taxonomic revisions deem otherwise. Members of the SAR supergroup were once included under the separate supergroups Chromalveolata (Chromista and Alveolata) and Rhizaria, until phylogenetic studies confirmed that stramenopiles and alveolates diverged with Rhizaria. This apparently excluded haptophytes and cryptomonads, leading Okamoto ''et al.'' (2009) to propose the clade Hacrobia to accommodate them. Phylogeny Based on a compi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jean Dragesco
Jean may refer to: People * Jean (female given name) * Jean (male given name) * Jean (surname) Fictional characters * Jean Grey, a Marvel Comics character * Jean Valjean, fictional character in novel ''Les Misérables'' and its adaptations * Jean Pierre Polnareff, a fictional character from ''JoJo's Bizarre Adventure'' Places * Jean, Nevada, USA; a town * Jean, Oregon, USA Entertainment * Jean (dog), a female collie in silent films * "Jean" (song) (1969), by Rod McKuen, also recorded by Oliver * ''Jean Seberg'' (musical), a 1983 musical by Marvin Hamlisch Other uses * JEAN (programming language) * USS ''Jean'' (ID-1308), American cargo ship c. 1918 * Sternwheeler Jean, a 1938 paddleboat of the Willamette River See also *Jehan * * Gene (other) * Jeanne (other) * Jehanne (other) * Jeans (other) * John (other) John is a common English name and surname: * John (given name) * John (surname) John may also refer to: New ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |