|
Toxoplasma
''Toxoplasma gondii'' () is an obligate intracellular parasitic protozoan (specifically an apicomplexan) that causes toxoplasmosis. Found worldwide, ''T. gondii'' is capable of infecting virtually all warm-blooded animals, but felids, such as domestic cats, are the only known definitive hosts in which the parasite may undergo sexual reproduction. ''T. gondii'' has been shown to alter the behavior of infected rodents in ways that increase the rodents' chances of being preyed upon by felids. Support for this "manipulation hypothesis" stems from studies showing that ''T. gondii''-infected rats have a decreased aversion to cat urine. Because cats are the only hosts within which ''T. gondii'' can sexually reproduce to complete and begin its lifecycle, such behavioral manipulations are thought to be evolutionary adaptations that increase the parasite's reproductive success. Rats that do not avoid cat habitations will more likely become cat prey. ''Toxoplasma gondii'' infection i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
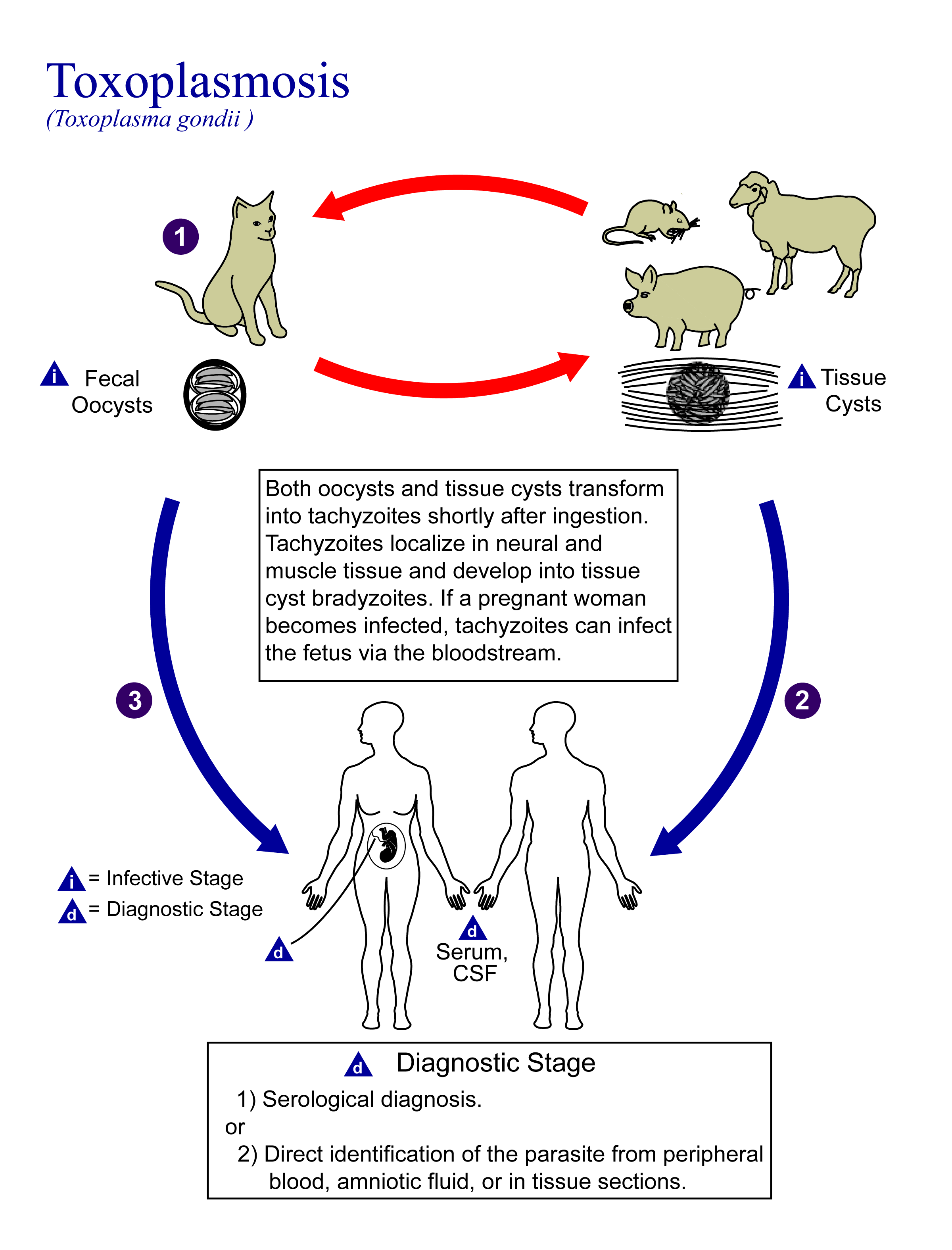
Toxoplasmosis
Toxoplasmosis is a parasitic disease caused by ''Toxoplasma gondii'', an apicomplexan. Infections with toxoplasmosis are associated with a variety of neuropsychiatric and behavioral conditions. Occasionally, people may have a few weeks or months of mild, flu-like illness such as muscle aches and tender lymph nodes. In a small number of people, eye problems may develop. In those with a weak immune system, severe symptoms such as seizures and poor coordination may occur. If a person becomes infected during pregnancy, a condition known as congenital toxoplasmosis may affect the child. Toxoplasmosis is usually spread by eating poorly cooked food that contains cysts, exposure to infected cat feces, and from an infected woman to their baby during pregnancy. Rarely, the disease may be spread by blood transfusion. It is not otherwise spread between people. The parasite is known to reproduce sexually only in the cat family. However, it can infect most types of warm-blooded animals, in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Latent Toxoplasmosis
Toxoplasmosis is a parasitic disease caused by ''Toxoplasma gondii'', an apicomplexan. Infections with toxoplasmosis are associated with a variety of neuropsychiatric and behavioral conditions. Occasionally, people may have a few weeks or months of mild, flu-like illness such as muscle aches and tender lymph nodes. In a small number of people, eye problems may develop. In those with a weak immune system, severe symptoms such as seizures and poor coordination may occur. If a person becomes infected during pregnancy, a condition known as congenital toxoplasmosis may affect the child. Toxoplasmosis is usually spread by eating poorly cooked food that contains cysts, exposure to infected cat feces, and from an infected woman to their baby during pregnancy. Rarely, the disease may be spread by blood transfusion. It is not otherwise spread between people. The parasite is known to reproduce sexually only in the cat family. However, it can infect most types of warm-blooded animals, incl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Toxoplasma Gondii
''Toxoplasma gondii'' () is an obligate intracellular parasitic protozoan (specifically an apicomplexan) that causes toxoplasmosis. Found worldwide, ''T. gondii'' is capable of infecting virtually all warm-blooded animals, but felids, such as domestic cats, are the only known definitive hosts in which the parasite may undergo sexual reproduction. ''T. gondii'' has been shown to alter the behavior of infected rodents in ways that increase the rodents' chances of being preyed upon by felids. Support for this "manipulation hypothesis" stems from studies showing that ''T. gondii''-infected rats have a decreased aversion to cat urine. Because cats are the only hosts within which ''T. gondii'' can sexually reproduce to complete and begin its lifecycle, such behavioral manipulations are thought to be evolutionary adaptations that increase the parasite's reproductive success. Rats that do not avoid cat habitations will more likely become cat prey. ''Toxoplasma gondii'' infection i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Behavior-altering Parasites And Parasitoids
Behavior-altering parasites are parasites with two or more hosts, capable of causing changes in the behavior of one of their hosts to enhance their transmission, sometimes directly affecting the hosts' decision-making and behavior control mechanisms. They do this by making the intermediate host, where they may reproduce asexually, more likely to be eaten by a predator at a higher trophic level which becomes the definitive host where the parasite reproduces sexually; the mechanism is therefore sometimes called parasite increased trophic facilitation or parasite increased trophic transmission. Examples can be found in bacteria, protozoa, viruses, and animals. Parasites may also alter the host behaviour to increase protection of the parasites or their offspring; the term bodyguard manipulation is used for such mechanisms. Among the behavioral changes caused by parasites is carelessness, making their hosts easier prey.Moore, J. (2002). Parasites and the behavior of animals. Oxford: Oxf ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tachyzoite
Apicomplexans, a group of intracellular parasites, have life cycle stages that allow them to survive the wide variety of environments they are exposed to during their complex life cycle. Each stage in the life cycle of an apicomplexan organism is typified by a ''cellular variety'' with a distinct morphology and biochemistry. Not all apicomplexa develop all the following cellular varieties and division methods. This presentation is intended as an outline of a hypothetical generalised apicomplexan organism. Methods of asexual replication Apicomplexans (sporozoans) replicate via ways of multiple fission (also known as schizogony). These ways include , and , although the latter is sometimes referred to as schizogony, despite its general meaning. Merogony is an asexually reproductive process of apicomplexa. After infecting a host cell, a trophozoite ( see glossary below) increases in size while repeatedly replicating its nucleus and other organelles. During this process, the or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apicomplexa
The Apicomplexa (also called Apicomplexia) are a large phylum of parasitic alveolates. Most of them possess a unique form of organelle that comprises a type of non-photosynthetic plastid called an apicoplast, and an apical complex structure. The organelle is an adaptation that the apicomplexan applies in penetration of a host cell. The Apicomplexa are unicellular and spore-forming. All species are obligate endoparasites of animals, except '' Nephromyces'', a symbiont in marine animals, originally classified as a chytrid fungus. Motile structures such as flagella or pseudopods are present only in certain gamete stages. The Apicomplexa are a diverse group that includes organisms such as the coccidia, gregarines, piroplasms, haemogregarines, and plasmodia. Diseases caused by Apicomplexa include: * Babesiosis (''Babesia'') * Malaria (''Plasmodium'') * Cryptosporidiosis (''Cryptosporidium parvum'') * Cyclosporiasis (''Cyclospora cayetanensis'') * Cystoisosporiasis (''Cystoisosp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Louis Manceaux
Louis Herbert Manceaux (1865–1934) was a French physician, parasitologist, and co-discover of ''Toxoplasma gondii'' with Charles Nicolle in 1908. Biography Manceaux's life is not well known, but he was physician-scientist recruited by Charles Nicolle to study at the Pasteur Institute of Tunis. He assisted Nicolle with capturing gundi in the Djerid Desert to study a parasite associated with a disease known as oriental sore in North Africa. The parasite observed in the tissue samples rodents was originally named Leishmania gondii in 1908. Upon further analysis, they concluded that the parasite was a newly discovered genus, so it was renamed to Toxoplasma gondii in 1909. After his discovery, Manceaux served as a French military doctor and was on active duty with medical corps during World War I. After retiring from the Army An army (from Old French ''armee'', itself derived from the Latin verb ''armāre'', meaning "to arm", and related to the Latin noun ''arma'', meaning ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protozoa
Protozoa (singular: protozoan or protozoon; alternative plural: protozoans) are a group of single-celled eukaryotes, either free-living or parasitic, that feed on organic matter such as other microorganisms or organic tissues and debris. Historically, protozoans were regarded as "one-celled animals", because they often possess animal-like behaviours, such as motility and predation, and lack a cell wall, as found in plants and many algae. When first introduced by Georg Goldfuss (originally spelled Goldfuß) in 1818, the taxon Protozoa was erected as a class within the Animalia, with the word 'protozoa' meaning "first animals". In later classification schemes it was elevated to a variety of higher ranks, including phylum, subkingdom and kingdom, and sometimes included within Protoctista or Protista. The approach of classifying Protozoa within the context of Animalia was widespread in the 19th and early 20th century, but not universal. By the 1970s, it became usual to require th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Latent Infection
An infection is the invasion of tissues by pathogens, their multiplication, and the reaction of host tissues to the infectious agent and the toxins they produce. An infectious disease, also known as a transmissible disease or communicable disease, is an illness resulting from an infection. Infections can be caused by a wide range of pathogens, most prominently bacteria and viruses. Hosts can fight infections using their immune system. Mammalian hosts react to infections with an innate response, often involving inflammation, followed by an adaptive response. Specific medications used to treat infections include antibiotics, antivirals, antifungals, antiprotozoals, and antihelminthics. Infectious diseases resulted in 9.2 million deaths in 2013 (about 17% of all deaths). The branch of medicine that focuses on infections is referred to as infectious disease. Types Infections are caused by infectious agents (pathogens) including: * Bacteria (e.g. '' Mycobacterium tuberculosis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Obligate Intracellular Parasite
Intracellular parasites are microparasites that are capable of growing and reproducing inside the cells of a host. Types of parasites There are two main types of intracellular parasites: Facultative and Obligate. Facultative intracellular parasites are capable of living and reproducing in or outside of host cells. Obligate intracellular parasites, on the other hand, need a host cell to live and reproduce. Many of these types of cells require specialized host types, and invasion of host cells occurs in different ways. Facultative Facultative intracellular parasites are capable of living and reproducing either inside or outside cells. Bacterial examples include: *''Bartonella henselae'' *''Francisella tularensis'' *''Listeria monocytogenes'' * ''Salmonella'' Typhi *''Brucella'' *''Legionella'' *''Mycobacterium'' *''Nocardia'' *''Neisseria'' *''Rhodococcus equi'' *''Yersinia'' *''Staphylococcus aureus'' Fungal examples include: *''Histoplasma capsulatum''. *''Cryptococcus neofor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Astrocytes
Astrocytes (from Ancient Greek , , "star" + , , "cavity", "cell"), also known collectively as astroglia, are characteristic star-shaped glial cells in the brain and spinal cord. They perform many functions, including biochemical control of endothelial cells that form the blood–brain barrier, provision of nutrients to the nervous tissue, maintenance of extracellular ion balance, regulation of cerebral blood flow, and a role in the repair and scarring process of the brain and spinal cord following infection and traumatic injuries. The proportion of astrocytes in the brain is not well defined; depending on the counting technique used, studies have found that the astrocyte proportion varies by region and ranges from 20% to 40% of all glia. Another study reports that astrocytes are the most numerous cell type in the brain. Astrocytes are the major source of cholesterol in the central nervous system. Apolipoprotein E transports cholesterol from astrocytes to neurons and other glial ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Schizophrenia
Schizophrenia is a mental disorder characterized by continuous or relapsing episodes of psychosis. Major symptoms include hallucinations (typically hearing voices), delusions, and disorganized thinking. Other symptoms include social withdrawal, decreased emotional expression, and apathy. Symptoms typically develop gradually, begin during young adulthood, and in many cases never become resolved. There is no objective diagnostic test; diagnosis is based on observed behavior, a history that includes the person's reported experiences, and reports of others familiar with the person. To be diagnosed with schizophrenia, symptoms and functional impairment need to be present for six months (DSM-5) or one month (ICD-11). Many people with schizophrenia have other mental disorders, especially substance use disorders, depressive disorders, anxiety disorders, and obsessive–compulsive disorder. About 0.3% to 0.7% of people are diagnosed with schizophrenia during their lifetime. In 2 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |