|
Totonacs
The Totonac are an indigenous people of Mexico who reside in the states of Veracruz, Puebla, and Hidalgo. They are one of the possible builders of the pre-Columbian city of El Tajín, and further maintained quarters in Teotihuacán (a city which they claim to have built). Until the mid-19th century they were the world's main producers of vanilla. Etymology The term "totonac" refers to the people living in Totonacapan. There is no agreement as to the origin of the term. Some authors have translated the term "totonac" as a Nahuatl word meaning "People of Hot Land". The translation for this word in the Totonac Language, according to sources, is "toto-nacu" meaning "three hearts" signifying their three cities or cultural centers: Cempoala, Tajin and Teayo. Evidence, however, is inconclusive. Geography and traditional lifestyle In the 15th century, the Aztecs labeled the region of the Totonac "Totonacapan"; which then extended roughly from Papantla in the north to Cempoala in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cempoala
Cempoala or Zempoala (Nahuatl Nahuatl (; ), Aztec, or Mexicano is a language or, by some definitions, a group of languages of the Uto-Aztecan language family. Varieties of Nahuatl are spoken by about Nahua peoples, most of whom live mainly in Central Mexico and have smaller ... ''Cēmpoalātl'' 'Place of Twenty Waters') is an important Mesoamerican archaeological site located in the Úrsulo Galván Municipality, in the state of Veracruz, Mexico. The site was inhabited mainly by Totonacs, Chinanteca (people), Chinantecas and Zapotec peoples, Zapotecs. It was one of the most important Totonac settlements during the postclassical Mesoamerican period and the capital of the kingdom of Totonacapan. It is located one kilometer from the shore of the Actopan River and six kilometres from the coast. Cempoala was the first urban settlement the Spaniards saw upon arrival on the American continent. According to some sources, the city was founded at least 1,500 years before the Spa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Totonacapan
Totonacapan refers to the historical extension where the Totonac people of Mexico dominated, as well as to a region in the modern states of Veracruz and Puebla. The historical territory was much larger than the currently named region, extending from the Cazones River in the north to the Papaloapan River in the south and then west from the Gulf of Mexico into what is now the Sierra Norte de Puebla region and into parts of Hidalgo. When the Spanish arrived, the Totonac ethnicity dominated this large region, although they themselves were dominated by the Aztec Empire. For this reason, they allied with Hernán Cortés against Tenochtitlán. However, over the colonial period, the Totonac population and territory shrank, especially after 1750 when mestizos began infiltrating Totonacapan, taking political and economic power. This continued into the 19th and 20th centuries, prompting the division of most of historical Totonacpan between the states of Puebla and Veracruz. Today, the term re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Veracruz
Veracruz (), formally Veracruz de Ignacio de la Llave (), officially the Free and Sovereign State of Veracruz de Ignacio de la Llave ( es, Estado Libre y Soberano de Veracruz de Ignacio de la Llave), is one of the 31 states which, along with Mexico City, comprise the 32 Federal Entities of Mexico. It is located in eastern Mexico and is bordered by seven states, which are Tamaulipas, San Luis Potosí, Hidalgo, Puebla, Oaxaca, Chiapas, and Tabasco. Veracruz is divided into 212 municipalities, and its capital city is Xalapa-Enríquez. Veracruz has a significant share of the coastline of the Gulf of Mexico on the east of the state. The state is noted for its mixed ethnic and indigenous populations. Its cuisine reflects the many cultural influences that have come through the state because of the importance of the port of Veracruz. In addition to the capital city, the state's largest cities include Veracruz, Coatzacoalcos, Córdoba, Minatitlán, Poza Rica, Boca Del Río and Or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Papantla
Papantla () is a city and municipality located in the north of the state of Veracruz, Mexico, in the Sierra Papanteca range and on the Gulf of Mexico. The city was founded in the 13th century by the Totonacs and has dominated the Totonacapan region of the state since then. This is the home of vanilla, which is native to this region, the Danza de los Voladores and the El Tajín archeological site, which was named a World Heritage Site. Papantla still has strong communities of Totonacs who maintain the culture and language. The city contains a number of large scale murals and sculptures done by native artist Teodoro Cano García, which honor the Totonac culture. The name Papantla is from Nahuatl and most often interpreted to mean "place of the papanes" (a species of crow). This meaning is reflected in the municipality's coat of arms. History The area in which Papantla is found has been dominated by a number of pre-Hispanic cultures. The first known is that of the Olmec, with the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
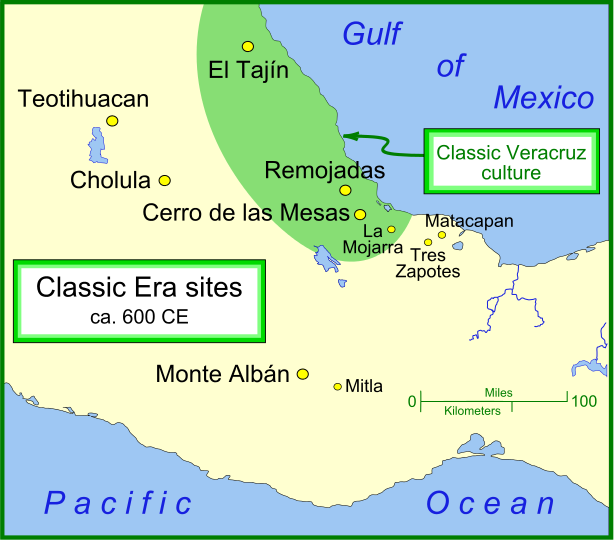
El Tajín
El Tajín is a pre-Columbian archeological site in southern Mexico and is one of the largest and most important cities of the Mesoamerican chronology, Classic era of Mesoamerica. A part of the Classic Veracruz culture, El Tajín flourished from 600 to 1200 CE and during this time numerous temples, palaces, Mesoamerican ballcourt, ballcourts, and pyramids were built. From the time the city fell, in 1230, to 1785, no European seems to have known of its existence, until a government inspector chanced upon the Pyramid of the Niches. El Tajín, named after the Totonac rain god, was named a World Heritage site in 1992, due to its cultural importance and its architecture. This architecture includes the use of decorative niches and cement in forms unknown in the rest of Mesoamerica. Its best-known monument is the Pyramid of the Niches, but other important monuments include the Arroyo Group, the North and South Ballcourts and the palaces of Tajín Chico. In total there have been 20 ball ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
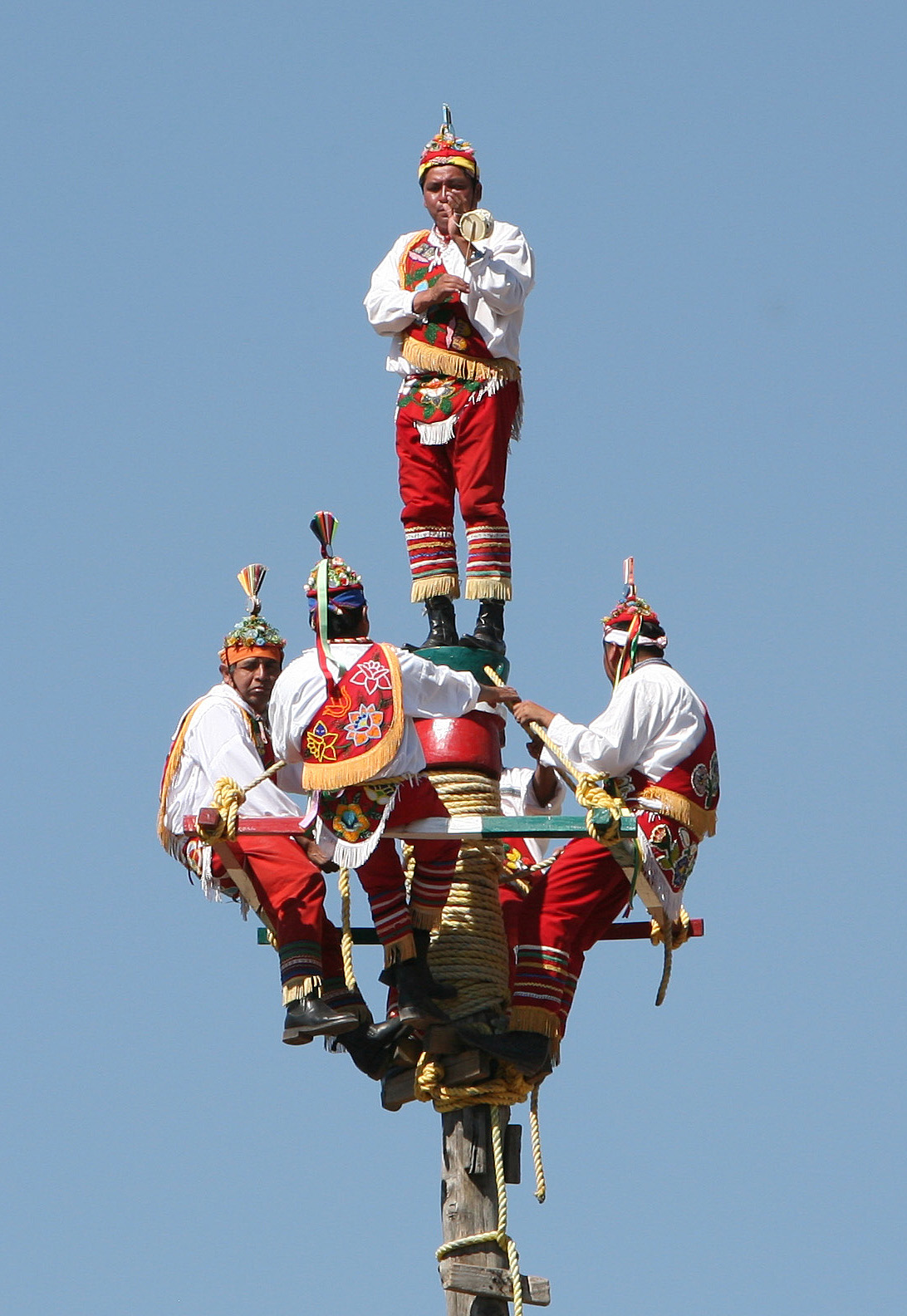
Danza De Los Voladores
The ''Danza de los Voladores'' (; "Dance of the Flyers"), or ''Palo Volador'' (; "flying pole"), is an ancient Mesoamerican ceremony/ritual still performed today, albeit in modified form, in isolated pockets in Mexico. It is believed to have originated with the Nahua, Huastec and Otomi peoples in central Mexico, and then spread throughout most of Mesoamerica. The ritual consists of dance and the climbing of a pole from which four of the five participants then launch themselves tied with ropes to descend to the ground. The fifth remains on top of the pole, dancing and playing a flute and drum. According to one myth, the ritual was created to ask the gods to end a severe drought. Although the ritual did not originate with the Totonac people, today it is strongly associated with them, especially those in and around Papantla in the Mexican state of Veracruz. The ceremony was named an Intangible cultural heritage by UNESCO in order to help the ritual survive and thrive in the mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vanilla
Vanilla is a spice derived from orchids of the genus ''Vanilla (genus), Vanilla'', primarily obtained from pods of the Mexican species, flat-leaved vanilla (''Vanilla planifolia, V. planifolia''). Pollination is required to make the plants produce the fruit from which the vanilla spice is obtained. In 1837, Belgian botanist Charles François Antoine Morren discovered this fact and pioneered a method of artificially pollinating the plant. The method proved financially unworkable and was not deployed commercially. In 1841, Edmond Albius, a 12-year-old enslaved child who lived on the French island of Réunion in the Indian Ocean, discovered that the plant could be hand-pollination, hand-pollinated. Hand-pollination allowed global cultivation of the plant. Noted French botanist and plant collector Jean Michel Claude Richard falsely claimed to have discovered the technique three or four years earlier. By the end of the 20th century, Albius was considered the true discoverer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cotton
Cotton is a soft, fluffy staple fiber that grows in a boll, or protective case, around the seeds of the cotton plants of the genus ''Gossypium'' in the mallow family Malvaceae. The fiber is almost pure cellulose, and can contain minor percentages of waxes, fats, pectins, and water. Under natural conditions, the cotton bolls will increase the dispersal of the seeds. The plant is a shrub native to tropical and subtropical regions around the world, including the Americas, Africa, Egypt and India. The greatest diversity of wild cotton species is found in Mexico, followed by Australia and Africa. Cotton was independently domesticated in the Old and New Worlds. The fiber is most often spun into yarn or thread and used to make a soft, breathable, and durable textile. The use of cotton for fabric is known to date to prehistoric times; fragments of cotton fabric dated to the fifth millennium BC have been found in the Indus Valley civilization, as well as fabric remnants dated back ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aztecs
The Aztecs () were a Mesoamerican culture that flourished in central Mexico in the post-classic period from 1300 to 1521. The Aztec people included different Indigenous peoples of Mexico, ethnic groups of central Mexico, particularly those groups who spoke the Nahuatl, Nahuatl language and who dominated large parts of Mesoamerica from the 14th to the 16th centuries. Aztec culture was organized into city-states (''altepetl''), some of which joined to form alliances, political confederations, or empires. The Aztec Empire was a confederation of three city-states established in 1427: Tenochtitlan, city-state of the Mexica or Tenochca; Texcoco (altepetl), Texcoco; and Tlacopan, previously part of the Tepanec empire, whose dominant power was Azcapotzalco (altepetl), Azcapotzalco. Although the term Aztecs is often narrowly restricted to the Mexica of Tenochtitlan, it is also broadly used to refer to Nahuas, Nahua polities or peoples of central Pre-Columbian Mexico, Mexico in the preh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
El Tajin Los Voladores Fcm
EL, El or el may refer to: Religion * El (deity), a Semitic word for "God" People * EL (rapper) (born 1983), stage name of Elorm Adablah, a Ghanaian rapper and sound engineer * El DeBarge, music artist * El Franco Lee (1949–2016), American politician * Ephrat Livni (born 1972), American street artist Arts, entertainment, and media Fictional entities * El, a character from the manga series ''Shugo Chara!'' by Peach-Pit * El, short for Eleven, a fictional character in the TV series ''Stranger Things'' * El, family name of Kal-El (Superman) and his father Jor-El in ''Superman'' *E.L. Faldt, character in the road comedy film ''Road Trip'' Literature * ''Él'', 1926 autobiographical novel by Mercedes Pinto * ''Él'' (visual novel), a 2000 Japanese adult visual novel Music * Él Records, an independent record label from the UK founded by Mike Alway * ''Él'' (Lucero album), a 1982 album by Lucero * "Él", Spanish song by Rubén Blades from ''Caminando'' (album) * "Él" (Luc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Comal (cookware)
A comal is a smooth, flat griddle typically used in Mexico, Central America, and parts of South America, to cook tortillas and arepas, toast spices and nuts, sear meat, and generally prepare food. Similar cookware is called a budare in South America. Some comals are concave and made of ''barro'' (clay). These are still made and used by the indigenous peoples of Mexico and Central America. Comals are similar to the American griddle or the Indian tawa, and are often used and named interchangeably with these. Comals for home use are generally made from heavy cast iron, and sized to fit over either one burner on the stovetop (round) or two burners front to back (elongated oval). In many indigenous and pre-Hispanic cultures, the comal is handed down from grandmother to mother to daughter, the idea being that a comal tempered over many years of usage will heat faster and cook cleaner. History The history of such cooking methods dates back to the pre-Columbian era, when powdered-homin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




.jpg)


