|
Tosh, Himachal Pradesh
Tosh village is in Himachal Pradesh state of India. It is located at about in elevation on a mountain slope on the right bank of the Parvati River in the Parvati Valley, surrounded by mountains (''TOSH is the last village''). The main occupation of the people in Parvati valley is Tourism. Apple orchards are also a big source of income for the local people. Wooden houses in the village are excellent example of architecture of Mountain people. Tosh is less expensive than its neighbour town Kasol. The guest houses and the hotels are available both at the entrance and far end of the village. Alongside the village is a right-bank tributary of the Parvati River. The Parvati River begins at the Mantalai Glacier within the Parvati Valley. The peaks surrounding the glacier include Papasura, White Sail, Angduri, Pinnacle, and Devachan. Tosh village is reached by bus from Kullu to Barshaini via Kasol and Manikaran and then a one-hour hike. It is described as a "traditional village turned ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Village Of Tosh In Himachal Pradesh, India (photo By Jim Ankan Deka)
''The'' () is a grammatical article in English, denoting persons or things that are already or about to be mentioned, under discussion, implied or otherwise presumed familiar to listeners, readers, or speakers. It is the definite article in English. ''The'' is the most frequently used word in the English language; studies and analyses of texts have found it to account for seven percent of all printed English-language words. It is derived from gendered articles in Old English which combined in Middle English and now has a single form used with nouns of any gender. The word can be used with both singular and plural nouns, and with a noun that starts with any letter. This is different from many other languages, which have different forms of the definite article for different genders or numbers. Pronunciation In most dialects, "the" is pronounced as (with the voiced dental fricative followed by a schwa) when followed by a consonant sound, and as (homophone of the archaic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iris (plant)
''Iris'' is a flowering plant genus of 310 accepted species with showy flowers. As well as being the scientific name, ''iris'' is also widely used as a common name for all ''Iris'' species, as well as some belonging to other closely related genera. A common name for some species is 'flags', while the plants of the subgenus '' Scorpiris'' are widely known as 'junos', particularly in horticulture. It is a popular garden flower. The often-segregated, monotypic genera '' Belamcanda'' (blackberry lily, ''I. domestica''), '' Hermodactylus'' (snake's head iris, ''I. tuberosa''), and ''Pardanthopsis'' (vesper iris, '' I. dichotoma'') are currently included in ''Iris''. Three Iris varieties are used in the Iris flower data set outlined by Ronald Fisher in his 1936 paper ''The use of multiple measurements in taxonomic problems'' as an example of linear discriminant analysis. Description Irises are perennial plants, growing from creeping rhizomes (rhizomatous irises) or, in drier cl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brown Dipper
The brown dipper (''Cinclus pallasii''), also known as Pallas's dipper, Asian dipper or the Asiatic dipper, is an aquatic songbird found in the mountains of the east Palearctic. It is a thrush-like bird with a cocked tail. Its plumage is chocolate-brown with a slightly lighter coloured back and breast. At and , it is the largest of the dippers. This species, which is not often seen, is found at medium to low elevations where mountain streams flow. Taxonomy The brown dipper was described by the Dutch zoologist Coenraad Jacob Temminck in 1820 and given the binomial name ''Cinclus pallasii''. The type locality is Eastern Siberia. The specific epithet ''pallasii'' was chosen in honour of the Prussian naturalist Peter Simon Pallas (1741–1811). Of the five species now placed in the genus, a molecular genetic study has shown that the brown dipper is most closely related to the other Eurasian species, the white-throated dipper (''Cinclus cinclus''). There are three subspecies: * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Himalayan Griffon
The Himalayan vulture (''Gyps himalayensis'') or Himalayan griffon vulture is an Old World vulture native to the Himalayas and the adjoining Tibetan Plateau. It is one of the two largest Old World vultures and true Accipitridae, raptors. It is listed as Near Threatened on the IUCN Red List. It is not to be confused with the griffon vulture, which is a similar species. Description The Himalayan vulture has dark brown greater covert feathers, tail and wing quills, but a pale buff uniform upperside and paler tipped inner secondaries; its legs are covered with buffy feathers and vary in colour from greenish grey to pale brown. The underside and under-wing coverts are pale brown or buff, almost white in some individuals. The whitish down on the head of immatures changes to yellowish in adults who have a long and pale brown Ruff (bird), ruff with white streaks and long and spiky ruff feathers. The pale blue facial skin is lighter than the dark blue in ''Gyps fulvus'' with this spec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Himalayan Balsam
''Impatiens glandulifera'', Himalayan balsam, is a large annual plant native to the Himalayas. Via human introduction it is now present across much of the Northern Hemisphere and is considered an invasive species in many areas. Uprooting or cutting the plants is an effective means of control. In Europe, Himalayan balsam has been included since 2017 in the list of Invasive Alien Species of Union concern (the Union list). This implies that the species cannot be imported, cultivated, transported, commercialized, planted, or intentionally released into the environment in the whole of the European Union. Etymology The common names Himalayan balsam and kiss-me-on-the-mountain refer to the plant's native Himalayan mountains. Ornamental jewelweed refers to its cultivation as an ornamental plant. The specific epithet ''glandulifera'' is a compound word from ''glándula'' meaning 'small gland', and ''ferre'' meaning 'to bear'. Description It typically grows to high, with a soft gree ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
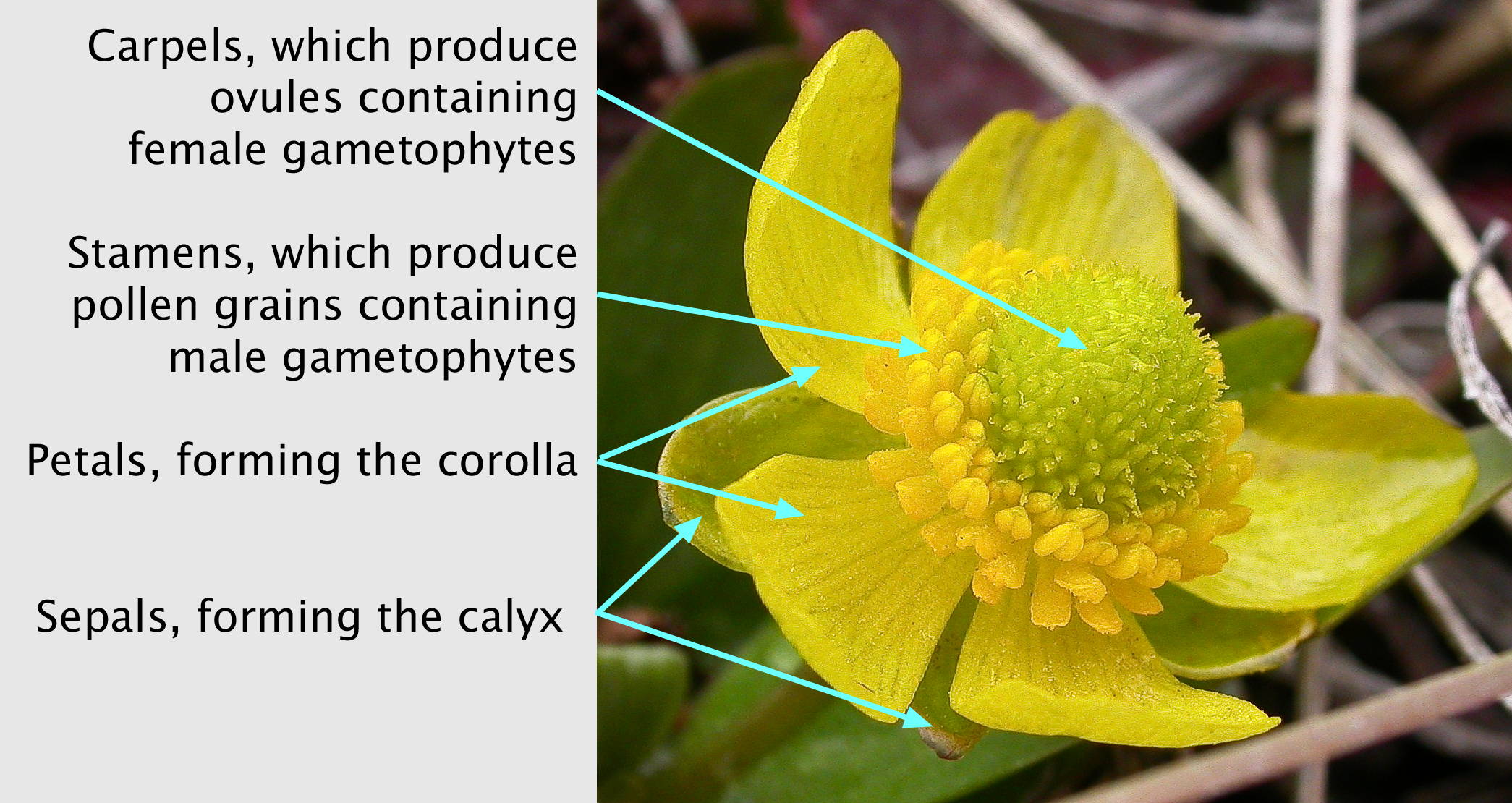
Buttercup
''Ranunculus'' is a large genus of about almost 1700 to more than 1800 species of flowering plants in the family Ranunculaceae. Members of the genus are known as buttercups, spearworts and water crowfoots. The genus is distributed in Europe, North America and South America. The familiar and widespread buttercup of gardens throughout Northern Europe (and introduced elsewhere) is the creeping buttercup ''Ranunculus repens'', which has extremely tough and tenacious roots. Two other species are also widespread, the bulbous buttercup ''Ranunculus bulbosus'' and the much taller meadow buttercup ''Ranunculus acris''. In ornamental gardens, all three are often regarded as weeds. Buttercups usually flower in the spring, but flowers may be found throughout the summer, especially where the plants are growing as opportunistic colonizers, as in the case of garden weeds. The water crowfoots (''Ranunculus'' subgenus ''Batrachium''), which grow in still or running water, are sometimes tre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Primula
''Primula'' () is a genus of herbaceous flowering plants in the family Primulaceae. They include the primrose ('' P. vulgaris''), a familiar wildflower of banks and verges. Other common species are '' P. auricula'' (auricula), '' P. veris'' (cowslip), and '' P. elatior'' (oxlip). These species and many others are valued for their ornamental flowers. They have been extensively cultivated and hybridised (in the case of the primrose, for many hundreds of years). ''Primula'' are native to the temperate Northern Hemisphere, south into tropical mountains in Ethiopia, Indonesia, and New Guinea, and in temperate southern South America. Almost half of the known species are from the Himalayas. ''Primula'' has over 500 species in traditional treatments, and more if certain related genera are included within its circumscription.''Primula''. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caltha Palustris
''Caltha palustris'', known as marsh-marigold and kingcup, is a small to medium size perennial herbaceous plant of the buttercup family, native to marshes, fens, ditches and wet woodland in temperate regions of the Northern Hemisphere. It flowers between April and August, dependent on altitude and latitude, but occasional flowers may occur at other times. Description ''Caltha palustris'' is a high, hairless, fleshy, perennial, herbaceous plant that dies down in autumn and overwinters with buds near the surface of the marshy soil. The plants have many, thick strongly branching roots. Its flowering stems are hollow, erect or more or less decumbent. The alternate true leaves are in a rosette, each of which consist of a leaf stem that is about four times as long as the kidney-shaped leaf blade, itself between long and wide, with a heart-shaped foot, a blunt tip, and a scalloped to toothed, sometime almost entire margin particularly towards the tip. In their youth the leaves ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Meconopsis Betonicifolia
''Meconopsis betonicifolia'' (syn. ''Meconopsis baileyi''), the Himalayan blue poppy, is a species of flowering plant in the family Papaveraceae. It was first formally named for western science in 1912 by the British officer Lt. Col. Frederick Marshman Bailey. ''Meconopsis betonicifolia'' is hardy in most of the United Kingdom and it has striking large blue flowers. This herbaceous perennial A perennial plant or simply perennial is a plant that lives more than two years. The term ('' per-'' + '' -ennial'', "through the years") is often used to differentiate a plant from shorter-lived annuals and biennials. The term is also wide ... is often short-lived. References External links * {{Taxonbar, from=Q3083496 betonicifolia Flora of China Flora of Arunachal Pradesh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Himachal Pradesh
Himachal Pradesh (; ; "Snow-laden Mountain Province") is a state in the northern part of India. Situated in the Western Himalayas, it is one of the thirteen mountain states and is characterized by an extreme landscape featuring several peaks and extensive river systems. Himachal Pradesh is the northernmost state of India and shares borders with the union territories of Jammu and Kashmir and Ladakh to the north, and the states of Punjab to the west, Haryana to the southwest, Uttarakhand to the southeast and a very narrow border with Uttar Pradesh to the south. The state also shares an international border to the east with the Tibet Autonomous Region in China. Himachal Pradesh is also known as , meaning 'Land of Gods' and which means 'Land of the Brave'. The predominantly mountainous region comprising the present-day Himachal Pradesh has been inhabited since pre-historic times, having witnessed multiple waves of human migrations from other areas. Through its history, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Manikaran
Manikaran is located in the Parvati Valley on river Parvati, northeast of Bhuntar in the Kullu District of Himachal Pradesh. It is at an altitude of 1760 m and is located 4 km ahead of Kasol and about 45 km from Kullu and about 35 km from Bhuntar. This small town attracts tourists visiting Manali and Kullu to its hot springs and pilgrim centres. An experimental geothermal energy plant has also been set up here. Religious centre Manikaran is a pilgrimage centre for Hindus and Sikhs. The Hindus believe that Manu recreated human life in Manikaran after the flood, making it a sacred area. It has many temples and a Gurudwara. There are temples of the Hindu deities Rama, Krishna, and Vishnu. The area is well known for its hot springs and its beautiful landscape. According to legend, when the Hindu God Shiva and his consort Parvati were walking in the valley, Parvati dropped one of her earrings. The jewel was seized by Shesha, the serpent deity, who then disappeared into the eart ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kasol
Kasol is a hamlet in the Kullu district of the Indian state of Himachal Pradesh. It is situated in Parvati Valley, on the banks of the Parvati River, Between Bhuntar and Manikaran, it is located from Bhuntar and from Kullu town, the district headquarters, 3.5 km from Manikaran. Kasol is the Himalayan hotspot for backpackers and acts as a base for nearby treks to Malana and Kheerganga. It is called ''Mini Israel of India'' due to a high percentage of Israeli tourists here. Climate Kasol has good weather for several months of the year and receives a fair amount of snowfall from late December to February. Köppen-Geiger climate classification system classifies its climate as humid subtropical A humid subtropical climate is a zone of climate characterized by hot and humid summers, and cool to mild winters. These climates normally lie on the southeast side of all continents (except Antarctica), generally between latitudes 25° and 40° ... (Cfa). Festivals Kasol Music F ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.png)