|
Toothette
Oral care swabs are disposable, single-use oral care sponges attached to a stick. They are used for oral care in the hospital and long-term care setting. Disposable oral care swabs may also be known by other various names, such as sponge swab, swabs for oral care, foam swab, mouth swab, oral swabstick, and the trademark name Toothette. Intended use The Toothette is meant to moisten and clear the oral cavity of food debris and thickened saliva associated with xerostomia (dry mouth). Most importantly, the oral care swab's intended use is as an adjunct to other oral care tools (toothbrush and interdental cleaners) in the hospital and long-term care setting. It is especially useful when caring for the oral health of Intubation, intubated and palliative care patients, and is recommended for individuals who are receiving radiation therapy, chemotherapy, Hematopoietic stem cell transplantation, bone marrow transplants, or are Immunosuppression, immunosuppressed. American Dental Associat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Toothette
Oral care swabs are disposable, single-use oral care sponges attached to a stick. They are used for oral care in the hospital and long-term care setting. Disposable oral care swabs may also be known by other various names, such as sponge swab, swabs for oral care, foam swab, mouth swab, oral swabstick, and the trademark name Toothette. Intended use The Toothette is meant to moisten and clear the oral cavity of food debris and thickened saliva associated with xerostomia (dry mouth). Most importantly, the oral care swab's intended use is as an adjunct to other oral care tools (toothbrush and interdental cleaners) in the hospital and long-term care setting. It is especially useful when caring for the oral health of intubated and palliative care patients, and is recommended for individuals who are receiving radiation therapy, chemotherapy, bone marrow transplants, or are immunosuppressed. The American Dental Association approved the Toothette Plus Oral Swab with Sodium Bicarbon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Toothette 2
Oral care swabs are disposable, single-use oral care sponges attached to a stick. They are used for oral care in the hospital and long-term care setting. Disposable oral care swabs may also be known by other various names, such as sponge swab, swabs for oral care, foam swab, mouth swab, oral swabstick, and the trademark name Toothette. Intended use The Toothette is meant to moisten and clear the oral cavity of food debris and thickened saliva associated with xerostomia (dry mouth). Most importantly, the oral care swab's intended use is as an adjunct to other oral care tools (toothbrush and interdental cleaners) in the hospital and long-term care setting. It is especially useful when caring for the oral health of intubated and palliative care patients, and is recommended for individuals who are receiving radiation therapy, chemotherapy, bone marrow transplants, or are immunosuppressed. The American Dental Association approved the Toothette Plus Oral Swab with Sodium Bicarbo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oral Hygiene
Oral hygiene is the practice of keeping one's mouth clean and free of disease and other problems (e.g. bad breath) by regular brushing of the teeth (dental hygiene) and cleaning between the teeth. It is important that oral hygiene be carried out on a regular basis to enable prevention of dental disease and bad breath. The most common types of dental disease are tooth decay (''cavities'', ''dental caries'') and gum diseases, including gingivitis, and periodontitis. General guidelines for adults suggest brushing at least twice a day with a fluoridated toothpaste: brushing last thing at night and at least on one other occasion. Cleaning between the teeth is called interdental cleaning and is as important as tooth brushing. This is because a toothbrush cannot reach between the teeth and therefore only removes about 50% of plaque from the surface of the teeth. There are many tools to clean between the teeth, including floss, tape and interdental brushes; it is up to each individual to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
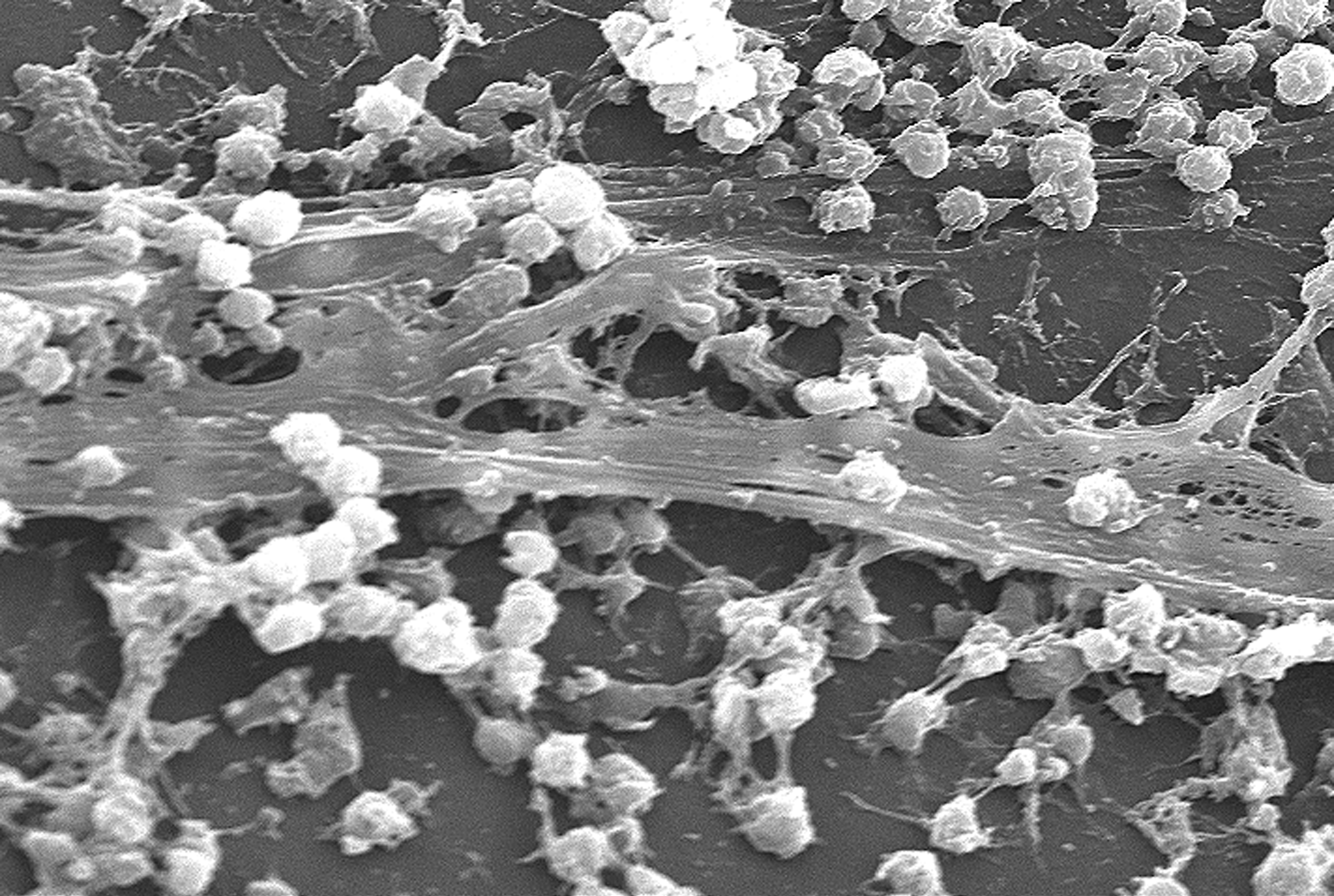
Biofilm
A biofilm comprises any syntrophic consortium of microorganisms in which cells stick to each other and often also to a surface. These adherent cells become embedded within a slimy extracellular matrix that is composed of extracellular polymeric substances (EPSs). The cells within the biofilm produce the EPS components, which are typically a polymeric conglomeration of extracellular polysaccharides, proteins, lipids and DNA. Because they have three-dimensional structure and represent a community lifestyle for microorganisms, they have been metaphorically described as "cities for microbes". Biofilms may form on living or non-living surfaces and can be prevalent in natural, industrial, and hospital settings. They may constitute a microbiome or be a portion of it. The microbial cells growing in a biofilm are physiologically distinct from planktonic cells of the same organism, which, by contrast, are single cells that may float or swim in a liquid medium. Biofilms can form ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Remineralisation Of Teeth
Tooth remineralization is the natural repair process for non-cavitated tooth decay, tooth lesions, in which calcium, phosphate and sometimes fluoride ions are deposition (chemistry), deposited into crystal voids in demineralised Tooth_enamel, enamel. Remineralization can contribute towards restoring strength and function within tooth structure. Demineralization is the removal of minerals (mainly calcium) from any of the hard tissues: Tooth enamel, enamel, dentine, and cementum.Li X, Wang J, Joiner A, Chang J. The remineralization of enamel: a review of the literature. Journal of dentistry. 2014 Jun 30;42:S12-20. It begins at the surface, and may progress into either cavitation (tooth decay) or erosion (tooth wear). Tooth decay demineralization is caused by acids from bacteria in the dental plaque biofilm whilst tooth wear is caused by acids from non-bacterial sources. These can be extrinsic in source, such as carbonated drinks, or intrinsic acids, usually from stomach acid coming ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pulmonary Aspiration
Pulmonary aspiration is the entry of material such as pharyngeal secretions, food or drink, or stomach contents from the oropharynx or gastrointestinal tract, into the larynx (voice box) and lower respiratory tract, the portions of the respiratory system from the trachea (windpipe) to the lungs. A person may inhale the material, or it may be delivered into the tracheobronchial tree during positive pressure ventilation. When pulmonary aspiration occurs during eating and drinking, the aspirated material is often colloquially referred to as "going down the wrong pipe". Consequences of pulmonary aspiration range from no injury at all, to chemical pneumonitis or pneumonia, to death within minutes from asphyxiation. These consequences depend on the volume, chemical composition, particle size, and presence of infectious agents in the aspirated material, and on the underlying health status of the person. In healthy people, aspiration of small quantities of material is common and rarel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Xerostomia
Xerostomia, also known as dry mouth, is dryness in the mouth, which may be associated with a change in the composition of saliva, or reduced salivary flow, or have no identifiable cause. This symptom is very common and is often seen as a side effect of many types of medication. It is more common in older people (mostly because this group tend to take several medications) and in persons who breathe through their mouths. Dehydration, radiotherapy involving the salivary glands, chemotherapy and several diseases can cause reduced salivation (hyposalivation), or a change in saliva consistency and hence a complaint of xerostomia. Sometimes there is no identifiable cause, and there may sometimes be a psychogenic reason for the complaint. Definition Xerostomia is the subjective sensation of dry mouth, which is often (but not always) associated with hypofunction of the salivary glands. The term is derived from the Greek words ξηρός (''xeros'') meaning "dry" and στόμα (''stoma' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saliva
Saliva (commonly referred to as spit) is an extracellular fluid produced and secreted by salivary glands in the mouth. In humans, saliva is around 99% water, plus electrolytes, mucus, white blood cells, epithelial cells (from which DNA can be extracted), enzymes (such as lipase and amylase), antimicrobial agents (such as secretory IgA, and lysozymes). The enzymes found in saliva are essential in beginning the process of digestion of dietary starches and fats. These enzymes also play a role in breaking down food particles entrapped within dental crevices, thus protecting teeth from bacterial decay. Saliva also performs a lubricating function, wetting food and permitting the initiation of swallowing, and protecting the oral mucosa from drying out. Various animal species have special uses for saliva that go beyond predigestion. Some swifts use their gummy saliva to build nests. ''Aerodramus'' nests form the basis of bird's nest soup. Cobras, vipers, and certain other membe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aspiration Pneumonia
Aspiration pneumonia is a type of lung infection that is due to a relatively large amount of material from the stomach or mouth entering the lungs. Signs and symptoms often include fever and cough of relatively rapid onset. Complications may include lung abscess, acute respiratory distress syndrome, empyema, and parapneumonic effusion. Some include chemical induced inflammation of the lungs as a subtype, which occurs from acidic but non-infectious stomach contents entering the lungs. Infection can be due to a variety of bacteria. Risk factors include decreased level of consciousness, problems with swallowing, alcoholism, tube feeding, and poor oral health. Diagnosis is typically based on the presenting history, symptoms, chest X-ray, and sputum culture. Differentiating from other types of pneumonia may be difficult. Treatment is typically with antibiotics such as clindamycin, meropenem, ampicillin/sulbactam, or moxifloxacin. For those with only chemical pneumonitis, antibio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cardiovascular Disease
Cardiovascular disease (CVD) is a class of diseases that involve the heart or blood vessels. CVD includes coronary artery diseases (CAD) such as angina and myocardial infarction (commonly known as a heart attack). Other CVDs include stroke, heart failure, hypertensive heart disease, rheumatic heart disease, cardiomyopathy, abnormal heart rhythms, congenital heart disease, valvular heart disease, carditis, aortic aneurysms, peripheral artery disease, thromboembolic disease, and venous thrombosis. The underlying mechanisms vary depending on the disease. It is estimated that dietary risk factors are associated with 53% of CVD deaths. Coronary artery disease, stroke, and peripheral artery disease involve atherosclerosis. This may be caused by high blood pressure, smoking, diabetes mellitus, lack of exercise, obesity, high blood cholesterol, poor diet, excessive alcohol consumption, and poor sleep, among other things. High blood pressure is estimated to account for approximat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diabetes Mellitus
Diabetes, also known as diabetes mellitus, is a group of metabolic disorders characterized by a high blood sugar level ( hyperglycemia) over a prolonged period of time. Symptoms often include frequent urination, increased thirst and increased appetite. If left untreated, diabetes can cause many health complications. Acute complications can include diabetic ketoacidosis, hyperosmolar hyperglycemic state, or death. Serious long-term complications include cardiovascular disease, stroke, chronic kidney disease, foot ulcers, damage to the nerves, damage to the eyes, and cognitive impairment. Diabetes is due to either the pancreas not producing enough insulin, or the cells of the body not responding properly to the insulin produced. Insulin is a hormone which is responsible for helping glucose from food get into cells to be used for energy. There are three main types of diabetes mellitus: * Type 1 diabetes results from failure of the pancreas to produce enough insulin due to lo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Systemic Disease
A systemic disease is one that affects a number of organs and tissues, or affects the body as a whole. Examples * Mastocytosis, including mast cell activation syndrome and eosinophilic esophagitis * Chronic fatigue syndrome * Systemic vasculitis e.g. SLE, PAN * Sarcoidosis – a disease that mainly affects the lungs, brain, joints and eyes, found most often in young African-American women. * Hypothyroidism – where the thyroid gland produces too little thyroid hormones. * Diabetes mellitus – an imbalance in blood glucose (sugar) levels. * Fibromyalgia * Adrenal insufficiency – where the adrenal glands don't produce enough steroid hormones * Coeliac disease – an autoimmune disease triggered by gluten consumption, which may involve several organs and cause a variety of symptoms, or be completely asymptomatic. * Ulcerative colitis – an inflammatory bowel disease * Crohn's disease – an inflammatory bowel disease * Hypertension (high blood pressure) * Metabolic syndrome ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |