|
Tonsilitis
Tonsillitis is inflammation of the tonsils in the upper part of the throat. It can be acute or chronic. Acute tonsillitis typically has a rapid onset. Symptoms may include sore throat, fever, enlargement of the tonsils, trouble swallowing, and enlarged lymph nodes around the neck. Complications include peritonsillar abscess. Tonsillitis is most commonly caused by a viral infection and about 5% to 40% of cases are caused by a bacterial infection.Lang 2009p. 2083./ref> When caused by the bacterium group A streptococcus, it is classed as streptococcal tonsillitis also referred to as ''strep throat''. Rarely bacteria such as '' Neisseria gonorrhoeae'', '' Corynebacterium diphtheriae'', or ''Haemophilus influenzae'' may be the cause. Typically the infection is spread between people through the air. A scoring system, such as the Centor score, may help separate possible causes. Confirmation may be by a throat swab or rapid strep test. Treatment efforts involve improving symptoms an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Streptococcal Pharyngitis
Streptococcal pharyngitis, also known as streptococcal sore throat (strep throat), is pharyngitis (an infection of the pharynx, the back of the throat) caused by ''Streptococcus pyogenes'' a gram-positive, group A streptococcus. Common symptoms include fever, sore throat, red tonsils, and enlarged lymph nodes in the front of the neck. A headache and nausea or vomiting may also occur. Some develop a sandpaper-like rash which is known as scarlet fever. Symptoms typically begin one to three days after exposure and last seven to ten days. Strep throat is spread by respiratory droplets from an infected person, spread by talking, coughing or sneezing, or by touching something that has droplets on it and then touching the mouth, nose, or eyes. It may be spread directly through touching infected sores. It may also be spread by contact with skin infected with group A strep. The diagnosis is made based on the results of a rapid antigen detection test or throat culture. Some people may ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sore Throat
Sore throat, also known as throat pain, is pain or irritation of the throat. Usually, causes of sore throat include * viral infections * group A streptococcal infection (GAS) bacterial infection * pharyngitis (inflammation of the throat) * tonsillitis (inflammation of the tonsils), or dehydration, which leads to the throat drying up. The majority of sore throats are caused by a virus, for which antibiotics are not helpful. A strong association between antibiotic misuse and antibiotic resistance has been shown. Symptoms of sore throat include: * a scratchy sensation * pain during swallowing * discomfort while speaking * a burning sensation * swelling in the neck For sore throat caused by bacteria (GAS), treatment with antibiotics may help the person get better faster, reduce the risk that the bacterial infection spreads, prevent retropharyngeal abscesses and quinsy, and reduce the risk of other complications such as rheumatic fever and rheumatic heart disease. In most develop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Odynophagia
Odynophagia is pain when swallowing. The pain may be felt in the mouth or throat and can occur with or without difficulty swallowing. The pain may be described as an ache, burning sensation, or occasionally a stabbing pain that radiates to the back. Odynophagia often results in inadvertent weight loss. The term is from ''-'' 'pain' and ' 'to eat'. Causes Odynophagia may have environmental or behavioral causes, such as: * Very hot or cold food and drinks (termed cryodynophagia when associated with cold drinks, classically in the setting of cryoglobulinaemia). * Taking certain medications * Using drugs, tobacco, or alcohol * Trauma or injury to the mouth, throat, or tongue It can also be caused by certain medical conditions, such as: * Ulcers * Abscesses * Upper respiratory tract infections * Inflammation or infection of the mouth, tongue, or throat (esophagitis, pharyngitis, tonsillitis, epiglottitis) * Immune disorders * Oral or throat cancer See also * Phagophobia Phagophobia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
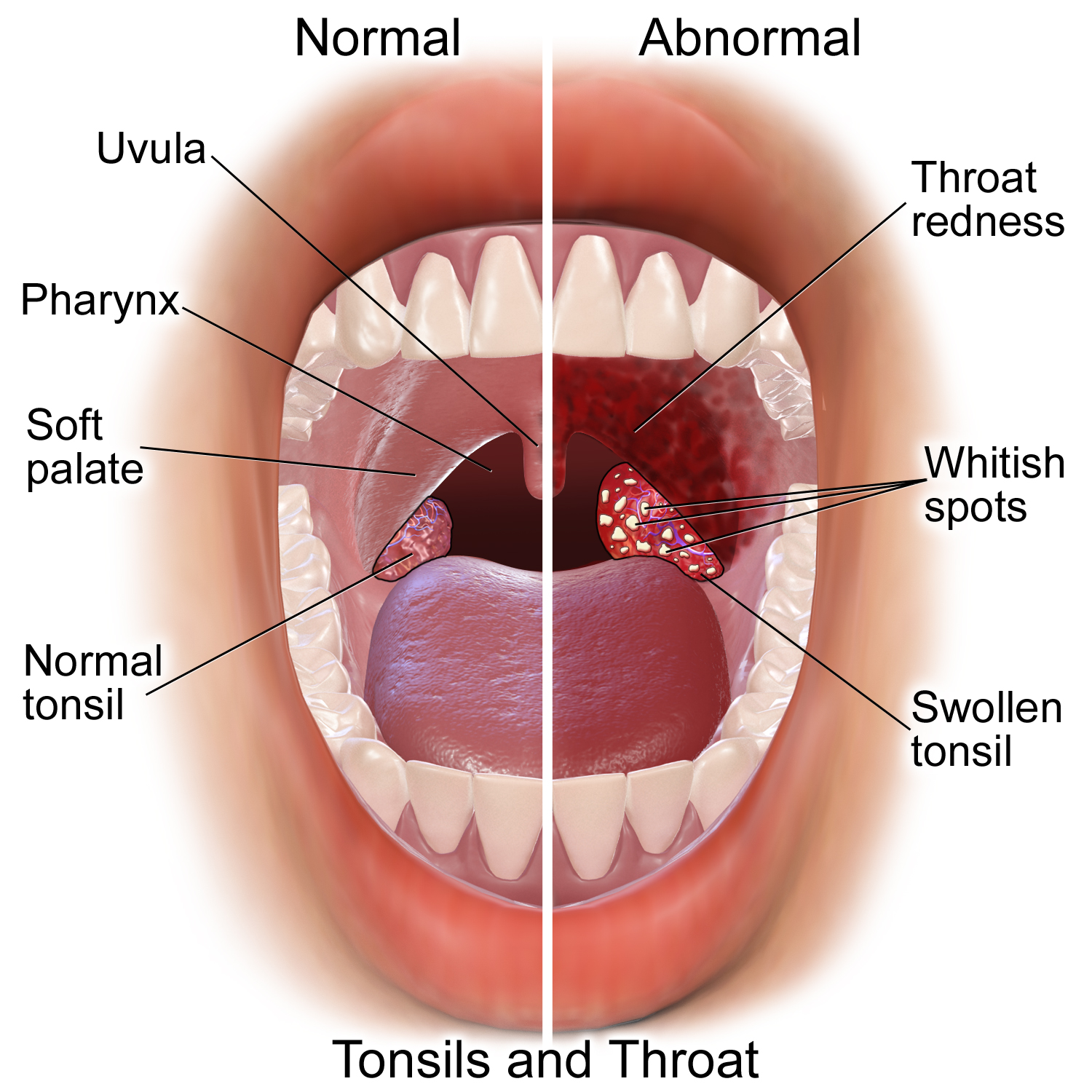
Blausen 0860 Tonsils&Throat Anatomy
Blausen Medical Communications, Inc. is the creator and owner of a library of two- and three-dimensional medical and scientific images and animations, a developer of information technology allowing access to that content, and a business focused on licensing and distributing the content. It was founded by Bruce Blausen in Houston, Texas, in 1991, and is privately held. Background Blausen Medical Communications, Inc. (BMC) is a privately held company founded by Bruce Blausen in Houston, Texas in 1991. BMC created and owns a library of medical and scientific images and animations, and has developed information technology tools allowing access to the library; as well, it licenses and otherwise works to distribute the content. As of this date, BMC's animation library comprised approximately 1,500 animations and over 27,000 two- and three-dimensional images designed for point-of-care patient education, which could be accessed by consumers or professional caregivers (primarily via ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tonsillectomy
Tonsillectomy is a list of surgical procedures, surgical procedure in which both palatine tonsils are fully removed from the back of the throat. The procedure is mainly performed for recurrent tonsillitis, throat infections and obstructive sleep apnea (OSA). For those with frequent throat infections, surgery results in 0.6 (95% confidence interval: 1.0 to 0.1) fewer sore throats in the following year, but there is no evidence of long term benefits. In children with OSA it results in improved quality of life. While generally safe, complications may include bleeding, vomiting, dehydration, trouble eating, and trouble talking. Sore throat, Throat pain typically lasts about one to two weeks after surgery. Bleeding occurs in about 1% within the first day and another 2% after that. Death occurs as a result in between 1 out of 2,360 and 1 in 56,000 procedures. Tonsillectomy does not appear to affect long term Immune system, immune function. Following the surgery ibuprofen and paracet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Macrolides
The Macrolides are a class of natural products that consist of a large macrocyclic lactone ring to which one or more deoxy sugars, usually cladinose and desosamine, may be attached. The lactone rings are usually 14-, 15-, or 16-membered. Macrolides belong to the polyketide class of natural products. Some macrolides have antibiotic or antifungal activity and are used as pharmaceutical drugs. Rapamycin is also a macrolide and was originally developed as an antifungal, but is now used as an immunosuppressant drug and is being investigated as a potential longevity therapeutic. Macrolides are bacteriostatic in that they suppress or inhibit bacterial growth rather than killing bacteria completely. Definition In general, any macrocyclic lactone having greater than 8-membered rings are candidates for this class. The macrocycle may contain amino nitrogen, amide nitrogen (but should be differentiated from cyclopeptides), an oxazole ring, or a thiazole ring. Benzene rings are exclu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cephalosporins
The cephalosporins (sg. ) are a class of β-lactam antibiotics originally derived from the fungus ''Acremonium'', which was previously known as ''Cephalosporium''. Together with cephamycins, they constitute a subgroup of β-lactam antibiotics called cephems. Cephalosporins were discovered in 1945, and first sold in 1964. Discovery The aerobic mold which yielded cephalosporin C was found in the sea near a sewage outfall in Su Siccu, by Cagliari harbour in Sardinia, by the Italian pharmacologist Giuseppe Brotzu in July 1945. Structure Cephalosporin contains a 6-membered dihydrothiazine ring. Substitutions at position 3 generally affect pharmacology; substitutions at position 7 affect antibacterial activity, but these cases are not always true. Medical uses Cephalosporins can be indicated for the prophylaxis and treatment of infections caused by bacteria susceptible to this particular form of antibiotic. First-generation cephalosporins are active predominantly against Gram- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Centor Score
The Centor criteria are a set of criteria which may be used to identify the likelihood of a bacterial infection in adult patients complaining of a sore throat. They were developed as a method to quickly diagnose the presence of Group A streptococcal infection or diagnosis of streptococcal pharyngitis in "adult patients who presented to an urban emergency room complaining of a sore throat." The Centor criteria are named after Robert M. Centor, an internist at the University of Alabama at Birmingham School of Medicine. Criteria The patients are judged on four criteria, with one point added for each positive criterion: * Absence of cough * Tonsillar exudates (ooze) * History of fever * Tender anterior cervical adenopathy The modified Centor criteria also incorporate the patient's age: * Age under 15 add 1 point * Age over 44 subtract 1 point Mnemonic using criteria name A mnemonic to remember Centor is: * C – Cough absent, or the incorrect but memorable "Can't Cough" * E – Exu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Haemophilus Influenzae
''Haemophilus influenzae'' (formerly called Pfeiffer's bacillus or ''Bacillus influenzae'') is a Gram-negative, non-motile, coccobacillary, facultatively anaerobic, capnophilic pathogenic bacterium of the family Pasteurellaceae. The bacteria are mesophilic and grow best at temperatures between 35 and 37℃. ''H. influenzae'' was first described in 1892 by Richard Pfeiffer during an influenza pandemic when he incorrectly described ''Haemophilus influenzae'' as the causative microbe, which is why the bacteria retain the name "influenza". ''H. influenzae'' is responsible for a wide range of localized and invasive infections, typically in infants and children, including pneumonia, meningitis, or bloodstream infections. Treatment consists of antibiotics, however ''H. influenzae'' is often resistant to the penicillin family but augmentin can be used in mild cases. The recommended form of prevention is a series of the Hib vaccine and boosters, which are most often given under the ag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Corynebacterium Diphtheriae
''Corynebacterium diphtheriae'' is the pathogenic bacterium that causes diphtheria. It is also known as the Klebs–Löffler bacillus, because it was discovered in 1884 by German bacteriologists Edwin Klebs (1834–1912) and Friedrich Löffler (1852–1915). The bacteria are usually harmless unless they are infected by a bacteriophage that carries a gene that gives rise to a toxin. This toxin causes the disease. Diphtheria is caused by the adhesion and infiltration of the bacteria into the mucosal layers of the body, primarily affecting the respiratory tract and the subsequent release of an endotoxin. The toxin has a localized effect on skin lesions, as well as a metastatic, proteolytic effects on other organ systems in severe infections. Originally a major cause of childhood mortality, diphtheria has been almost entirely eradicated due to the vigorous administration of the diphtheria vaccination in the 1910s. Diphtheria is no longer transmitted as frequently due to the d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neisseria Gonorrhoeae
''Neisseria gonorrhoeae'', also known as ''gonococcus'' (singular), or ''gonococci'' (plural), is a species of Gram-negative diplococci bacteria isolated by Albert Ludwig Sigesmund Neisser, Albert Neisser in 1879. It causes the sexually transmitted infection, sexually transmitted genitourinary infection gonorrhea as well as other forms of gonococcal disease including disseminated gonococcemia, septic arthritis, and gonococcal ophthalmia neonatorum. It is oxidase test, oxidase positive and aerobic, and it survives phagocyte, phagocytosis and grows inside neutrophils. Microbiological culture, Culturing it requires carbon dioxide supplementation and enriched agar (chocolate agar) with various antibiotics (Thayer–Martin agar, Thayer–Martin). It exhibits antigenic variation through genetic recombination of its pilus, pili and surface proteins that interact with the immune system. Sexual transmission is through vaginal, anal, or oral sex. Sexual transmission may be prevented throu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Group A Streptococcus
Lancefield grouping is a system of classification that classifies catalase-negative Gram-positive cocci based on the carbohydrate composition of bacterial antigens found on their cell walls. The system, created by Rebecca Lancefield, was historically used to organize the various members of the family Streptococcaceae, which includes the genera ''Lactococcus'' and ''Streptococcus'', but now is largely superfluous due to explosive growth in the number of streptococcal species identified since the 1970s. However, it has retained some clinical usefulness even after the taxonomic changes, and as of 2018, Lancefield designations are still often used to communicate medical microbiological test results. Enterococcus, formerly known as Group D Streptococcus, were classified as members of the genus Streptococcus until 1984 and were included in the original Lancefield grouping. Many - but not all - species of streptococcus are beta-hemolytic. Notably, Enterococci and ''Streptococcus bovis' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |