|
Tomislav I
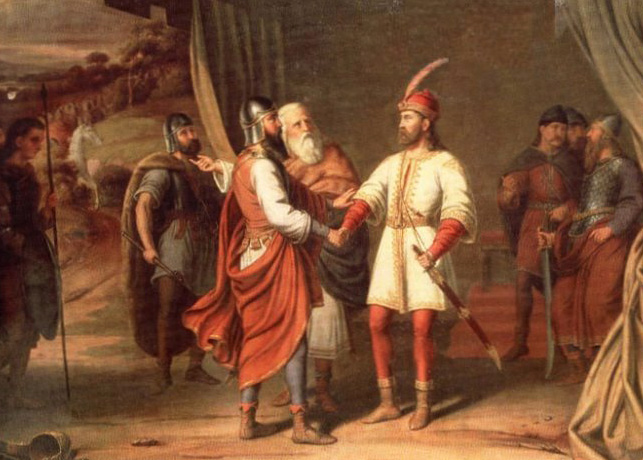
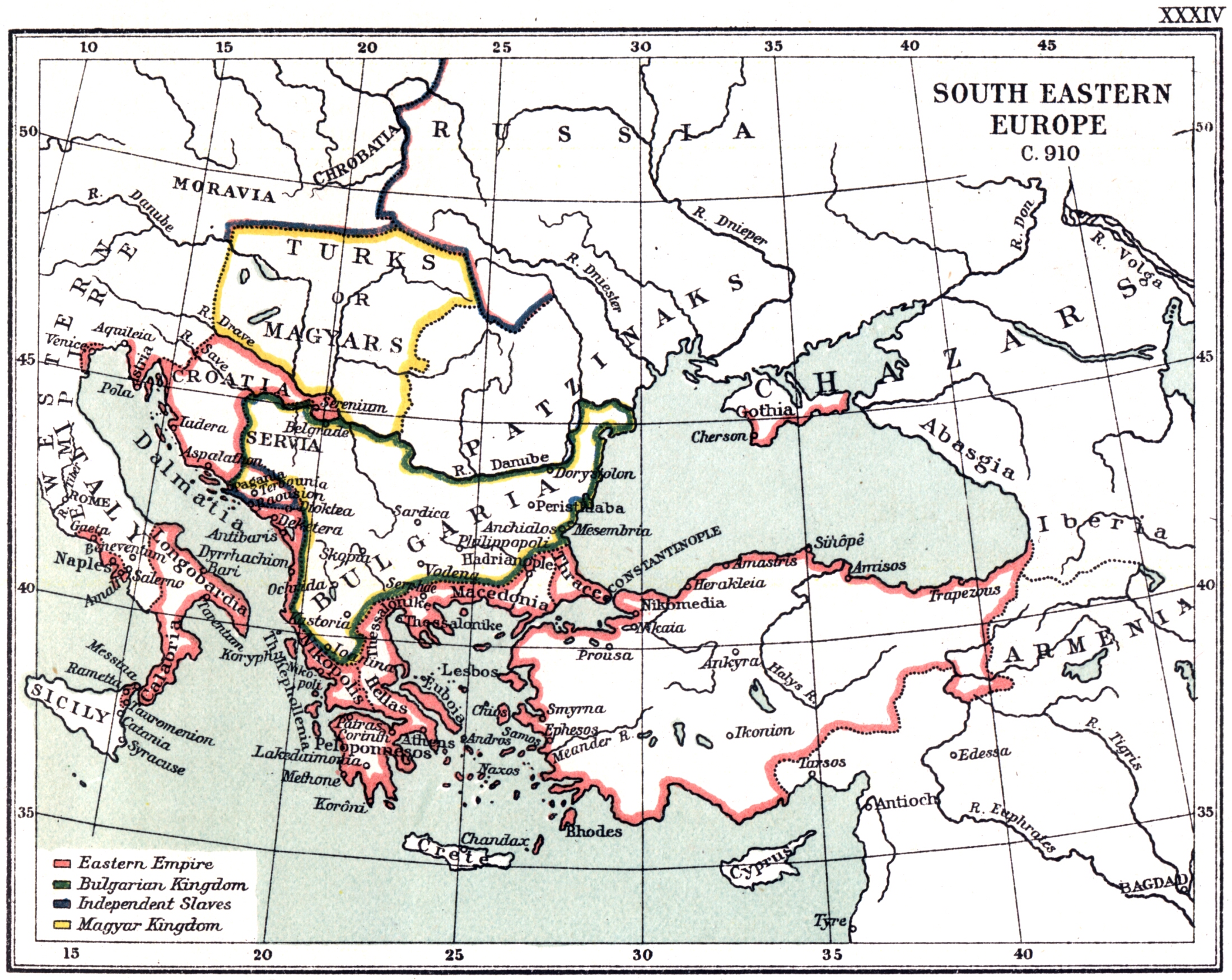
Tomislav (, la, Tamisclaus) was the first king of Croatia. He became Duke of Croatia and was crowned king in 925, reigning until 928. During Tomislav's rule, Croatia forged an alliance with the Byzantine Empire against Bulgaria. Croatia's struggles with the First Bulgarian Empire eventually led to war, which culminated in the decisive Battle of the Bosnian Highlands in 926. In the north, Croatia often clashed with the Principality of Hungary; the state retained its borders and, to some extent, expanded with the disintegrated Lower Pannonia. Tomislav attended the 925 Council of Split, convened by Pope John X, to discuss the use of Slavic languages in liturgy, and ecclesiastical jurisdiction over both Croatia and the Byzantine Theme of Dalmatia. Although the Pope sought to prohibit Slavic liturgy, the council did not agree. Jurisdiction over the region was given to the Archbishop of Split instead of Bishop Gregory of Nin. Since historical information on Tomislav is scar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
King Of Croatia
This is a complete list of rulers of Croatia under domestic ethnic and elected dynasties during the Croatian Kingdom (925–1918). This article follows the monarch's title number according to Hungarian succession for convenience. For example, the Hungarian monarch Béla IV is according to Croatian succession correctly titled Béla III. This is because Hungarians had a king named Béla prior to the incorporation of Croatia under the Hungarian Crown but the Croats did not. Early history The details of the arrival of the Croats in the Balkans are sparsely documented by reliable historical sources. Around 626 CE, Croats migrated from White Croatia (around present-day Galicia) at the invitation of the Byzantine Emperor Heraclius. According to a legend recorded in the 10th-century ''De Administrando Imperio'', the Croats came to their present region under the leadership of five brothers (called Kloukas, Lobelos, Kosentzis, Mouchlo, and Chrobatos) and of two sisters (called Touga and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gregory Of Nin
Gregory of Nin ( hr, Grgur Ninski ; la, Gregorius Ninnius) was a medieval bishop of Nin who strongly opposed the pope and official circles of the Church and introduced the Croatian language in the religious services after the Great Assembly in 926, according to traditional Croatian historiography. Until that time, services were held only in Latin (being under the jurisdiction of Roman influence before the Great Schism), not being understandable to a majority of the population. Not only was this important for Croatian language and culture, but it also made Christianity stronger within the Croatian kingdom.Dragutin Pavličević, Povijest Hrvatske, naklada Pavičić, Zagreb 2007. godine, Historical facts Gregory was the bishop of Nin and as such was under the strong protection of King Tomislav of Croatia. At the Synod in 925, held in Split, Gregory became subordinate to the Archbishop of Split. He rejected the offer of the Sisak Bishopric. After the conclusions of the first S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Béla III
Béla may refer to: * Béla (crater), an elongated lunar crater * Béla (given name), a common Hungarian male given name See also * Bela (other) * Belá (other) * Bělá (other) Bělá, derived from ''bílá'' (''white''), is the name of several places in the Czech Republic: *Bělá (Havlíčkův Brod District), a municipality and village in the Vysočina Region *Bělá (Mírová pod Kozákovem), a village, a part of the m ... {{DEFAULTSORT:Bela de:Béla pl:Béla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Andrea Dandolo
Andrea Dandolo (13067 September 1354) was elected the 54th doge of Venice in 1343, replacing Bartolomeo Gradenigo who died in late 1342. Early life Trained in historiography and law, Andrea Dandolo studied at the University of Padua, where he became a law professor until he was elected as doge. He was descended from an old Venetian noble family, the Dandolo, that played an important role in Venetian politics from the 12th to 15th centuries, and produced four Venetian doges, of whom he was the last, numerous admirals and several other prominent citizens. Dandolo's rise to prominence in Venetian public life was precocious. In 1331, at the age of only 25, he was named procurator of St. Mark's Basilica. Doge He became doge in 1343 at the age of 37. Dandolo was known as a benefactor of the arts. To St Mark's Basilica he added the Chapel of San Isidoro, oversaw changes to the Pala d'Oro and expanded and beautified the Baptistery. He reformed the Venetian legal code, formall ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Drava River
The Battle of Drava River was fought between the army of Tomislav of Croatia and the forces of Hungarian tribes led by Grand Prince Zoltán, the youngest son of Árpád, founder of the Árpád dynasty. According to the ''Chronicle of the Priest of Dioclea'' from the late 12th century, Tomislav of Croatia defeated the Hungarians in battle.Florin Curta, Southeastern Europe in the Middle Ages, 500-1250, Cambridge University Press, 2006, p. 193, Others question the reliability of this account, because there is no proof for this interpretation in other records. The exact place and time of the battle is not known, but very few remaining medieval sources suggest that the clash took place on the right bank of the Drava River in medieval Slavonia ( la, Sclavonia) or former Principality of Pannonian Croatia respectively, in 925. Slavonia should have been an integral part of the medieval Croatian state if the battle had happened, however according to the Byzantine ruler Constantine ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chronicle Of The Priest Of Duklja
The ''Chronicle of the Priest of Dioclea or Duklja'' ( sh, Ljetopis popa Dukljanina) is the usual name given to a purportedly medieval chronicle written in the late 13th century by an anonymous priest from Duklja. Its oldest preserved copy is in Latin from the 17th century, while it has been variously claimed by modern historians to have been compiled between the late 14th and early 16th centuries. Historians have yet to discount the work as based on inaccuracies and fiction. The postulates are there that Slavs lived in the Balkans from the 5th- to the 12th-century. It recounts the history of Dalmatia and nearby regions from the 5th to the mid-12th century. It contains some semi-mythological material on the early history of the Western South Slavs. The section "The Life of St. Jovan Vladimir", is believed to be a fictional account of earlier history. Authorship and date The work was purportedly compiled by an anonymous "priest of Duklja" (''presbyter Diocleas'', known in Serbo-C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Braslav, Duke Of Lower Pannonia
Braslav ( 882–896) was a prince who ruled the Slavs in Lower Pannonia, in a territory located mostly in modern-day Croatia, between 884 and 896 as a vassal of Arnulf of Carinthia. He participated in the Frankish–Moravian War (882–84) and the Frankish invasion of Moravia (891–92). He was last mentioned when he was entrusted Pannonia by Arnulf in order to secure the Frankish frontier against the Hungarians (896), who subsequently overran all of Pannonia and continued into Italy. Background In 882–84, a bloody war was fought between Arnulf of Carinthia and Svatopluk I of Moravia, during which Pannonia and the Danube suffered the most. Svatopluk is said to have "slaughtered" and "destroyed much with fire and sword". The two agreed on peace in 884. Life A Slavic prince and ardent Frankish loyalist, according to the ''Frankish Annals'', Braslav was the "Duke of Lower Pannonia" (). He ruled a province from the Drava to the Sava (modern-day Slavonia). He took part in the 88 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hungarian Conquest Of The Carpathian Basin
The Hungarian conquest of the Carpathian Basin, also known as the Hungarian conquest or the Hungarian land-taking (), was a series of historical events ending with the settlement of the Hungarians in Central Europe in the late 9th and early 10th century. Before the arrival of the Hungarians, three early medieval powers, the First Bulgarian Empire, East Francia, and Moravia, had fought each other for control of the Carpathian Basin. They occasionally hired Hungarian horsemen as soldiers. Therefore, the Hungarians who dwelt on the Pontic steppes east of the Carpathian Mountains were familiar with their future homeland when their conquest started. Archaeogenetic studies confirmed the Asian origin of the conquerors. The Hungarian conquest started in the context of a "late or 'small' migration of peoples". Contemporary sources attest that the Hungarians crossed the Carpathian Mountains following a joint attack by the Pechenegs and Bulgarians in 894 or 895. They first took control ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Split, Croatia
)'' , settlement_type = List of cities and towns in Croatia, City , anthem = ''Marjane, Marjane'' , image_skyline = , imagesize = 267px , image_caption = Top: Nighttime view of Split from Mosor; 2nd row: Cathedral of Saint Domnius; City center of Split; 3rd row: View of the city from Marjan, Split, Marjan Hill; Night in Poljička Street; Bottom: ''Riva'' waterfront , image_flag = Flag of the City of Split.svg , flag_size = 150px , flag_link = Flag of Split , image_seal = , seal_size = , image_shield = Coat of arms of Split.svg , shield_size = 90px , shield_link = Coat of arms of Split , image_map = , mapsize = , map_caption = Map of the Split city area. , image_map1 = , mapsize1 = , map_caption1 = ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thomas The Archdeacon
Thomas the Archdeacon ( la, Thomas Archidiaconus; it, Tommaso Arcidiacono; hr, Toma Arhiđakon; c. 1200 – 8 May 1268), also known as Thomas of Spalato ( la, Thomas Spalatensis, hu, Spalatói Tamás), was a Roman Catholic cleric, historian and chronicler from Split (Spalato). He is often referred to as one of the greatest sources in the historiography of Croatian lands. Life What is known about Thomas' life comes from his work, ''Historia Salonitana''. He speaks of his life in the third person and very briefly, in the style of medieval literature genres. Thomas was born in Split at the beginning of the 13th century. It is not known whether he was of noble or common birth, but he represented the elite Roman culture that had survived from before the Slav migration, and he had a negative view of Slavs, often mistakenly conflating them in his chronicle with the Goths.Fine (Jr), John V. A. (2006). ''When Ethnicity Did Not Matter in the Balkans: A Study of Identity in Pre-Nationali ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Historia Salonitana
''Historia Salonitanorum atque Spalatinorum pontificum'' or the History of the Bishops of Salona and Split ( hr, Povijest biskupa Salone i Splita), commonly known simply as the ''Historia Salonitana'', is a chronicle by Thomas the Archdeacon from the 13th century which contains significant information about the early history of the Croats. It was first published by Johannes Lucius. Gioanni, Stéphane (2009), ''The bishops of Salona (2nd-7th century) in the ''Historia Salonitana'' by Thomas the Archdeacon (13th century): history and hagiography'', in ''Écrire l’histoire des évêques et des papes'', Fr. Bougard and M. Sot (edd.), Brepols, pp. 243-263 rench text An extended version of this work, known as the ''Historia Salonitana maior'' was published in the 16th century, and critical editions of both have been republished by Nada Klaić (Belgrade: Naucno delo, 1967). The chronicle gives an account of the arrival of the Croats: :''From the Polish territories called Lingonia se ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trpimir I
Trpimir I (, la, Trepimerus/Trepimero) was a duke ( hr, knez) in Croatia from around 845 until his death in 864. He is considered the founder of the Trpimirović dynasty that ruled in Croatia, with interruptions, from around 845 until 1091. Although he was formally vassal of the Frankish Emperor Lothair I, Trpimir used Frankish-Byzantine conflicts to rule on his own. Reign Trpimir succeeded Croatia's Duke Mislav around 845, ascended the throne in Klis and expanded the early Roman stronghold into Klis Fortress, the capital of his domain. Trpimir battled successfully against his neighbours, the Byzantine coastal cities under the strategos of Zadar in 846. In 854 he repulsed an attack by an army of the Bulgarian Khan Boris I and concluded a peace treaty with him, exchanging gifts. The Bulgarians and Croatians coexisted peacefully after that time. On 4 March 852 Trpimir issued a charter in Biaći (''in loco Byaci dicitur'') in the Latin language, confirming Mislav's donation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)
.jpg)
