|
Tolimidone
Tolimidone (CP-26154; MLR-1023) is a compound which was discovered by scientists at Pfizer, was found to stimulate secretion of gastric mucosa, and was in development by Pfizer as a drug candidate to treat gastric ulcers but was abandoned. After the patent on the compound expired, scientists at the company Melior Discovery identified it as a potential drug candidate for diabetes through a phenotypic screen. The company proceeded to show that MLR-1023 is an allosteric activator of Lyn kinase with an EC50 of 63 nM. As of 2012 Melior was repurposing Repurposing is the process by which an object with one use value is transformed or redeployed as an object with an alternative use value. Description Repurposing is as old as human civilization, with many contemporary scholars investigating tha ... it for diabetes. In June 2016, the company reported positive results from their Phase 2a clinical study in diabetic subjects References {{H2-receptor antagonist Pyrimidines Ureas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pfizer
Pfizer Inc. ( ) is an American multinational pharmaceutical and biotechnology corporation headquartered on 42nd Street in Manhattan, New York City. The company was established in 1849 in New York by two German entrepreneurs, Charles Pfizer (1824–1906) and his cousin Charles F. Erhart (1821–1891). Pfizer develops and produces medicines and vaccines for immunology, oncology, cardiology, endocrinology, and neurology. The company has several blockbuster drugs or products that each generate more than billion in annual revenues. In 2020, 52% of the company's revenues came from the United States, 6% came from each of China and Japan, and 36% came from other countries. Pfizer was a component of the Dow Jones Industrial Average stock market index from 2004 to August 2020. The company ranks 64th on the Fortune 500 and 49th on the Forbes Global 2000. History 1849–1950: Early history Pfizer was founded in 1849 by Charles Pfizer and Charles F. Erhart, two cousins who had i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gastric Mucosa
The gastric mucosa is the mucous membrane layer of the stomach, which contains the glands and the gastric pits. In humans, it is about 1 mm thick, and its surface is smooth, soft, and velvety. It consists of simple columnar epithelium, lamina propria, and the muscularis mucosae. Description In its fresh state, it is of a pinkish tinge at the pyloric end and of a red or reddish-brown color over the rest of its surface. In infancy it is of a brighter hue, the vascular redness being more marked. It is thin at the cardiac extremity, but thicker toward the pylorus. During the contracted state of the organ it is thrown into numerous plaits or rugae, which, for the most part, have a longitudinal direction, and are most marked toward the pyloric end of the stomach, and along the greater curvature. These folds are entirely obliterated when the organ becomes distended. When examined with a lens, the inner surface of the mucous membrane presents a peculiar honeycomb appearance fro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
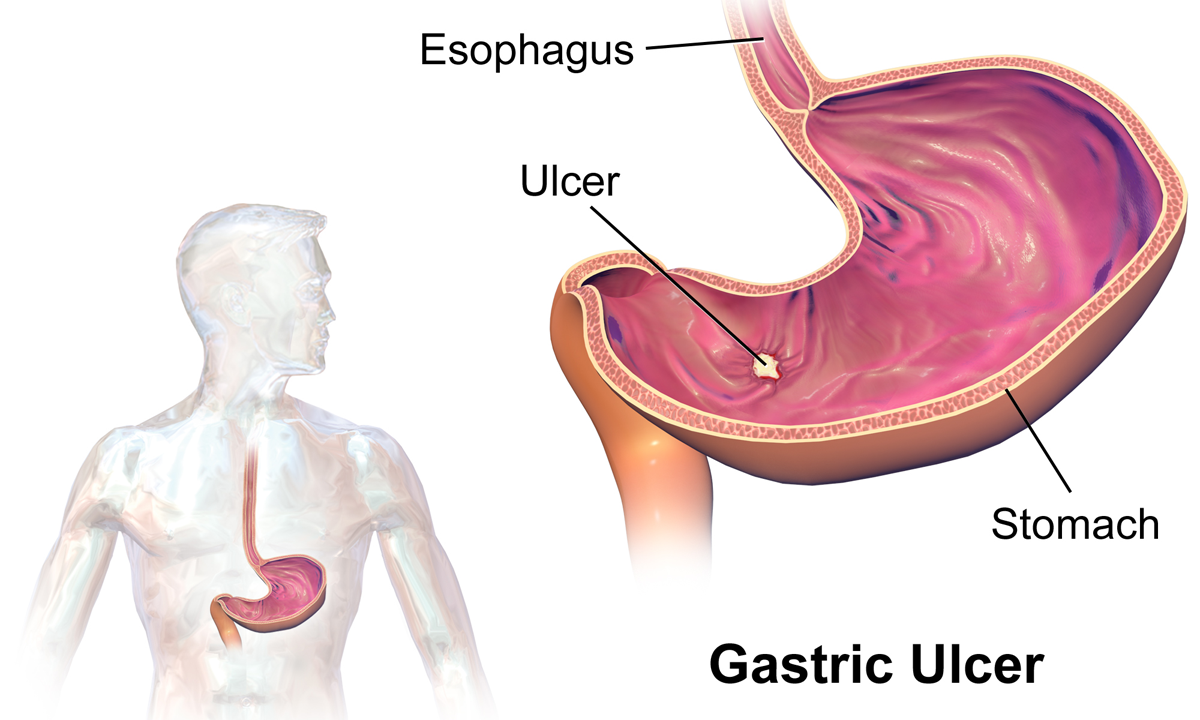
Gastric Ulcers
Peptic ulcer disease (PUD) is a break in the inner lining of the stomach, the first part of the small intestine, or sometimes the lower esophagus. An ulcer in the stomach is called a gastric ulcer, while one in the first part of the intestines is a duodenal ulcer. The most common symptoms of a duodenal ulcer are waking at night with upper abdominal pain and upper abdominal pain that improves with eating. With a gastric ulcer, the pain may worsen with eating. The pain is often described as a burning or dull ache. Other symptoms include belching, vomiting, weight loss, or poor appetite. About a third of older people have no symptoms. Complications may include bleeding, perforation, and blockage of the stomach. Bleeding occurs in as many as 15% of cases. Common causes include the bacteria ''Helicobacter pylori'' and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). Other, less common causes include tobacco smoking, stress as a result of other serious health conditions, Behçet's d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Melior Discovery
Melior Discovery, Inc. is a private biopharmaceutical company based in Exton, Pennsylvania, USA. The company specializes in drug repositioning and has established a proprietary phenotypic screening platform that it uses for this purpose. Melior also offers certain contract research organization (CRO) services comprising animal models representing different disease conditions. The Company has issued press releases disclosing partnerships with Pfizer, Merck & Co., Johnson & Johnson, and AstraZeneca, all citing the use of the company’s drug repositioning technology. Melior Discovery has also used its technology to discover its own drug candidates. In March 2009, the Food and Drug Administration The United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA or US FDA) is a List of United States federal agencies, federal agency of the United States Department of Health and Human Services, Department of Health and Human Services. The FDA is respon ... (FDA) approved the company’s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phenotypic Screen
In genetics, the phenotype () is the set of observable characteristics or traits of an organism. The term covers the organism's morphology or physical form and structure, its developmental processes, its biochemical and physiological properties, its behavior, and the products of behavior. An organism's phenotype results from two basic factors: the expression of an organism's genetic code, or its genotype, and the influence of environmental factors. Both factors may interact, further affecting phenotype. When two or more clearly different phenotypes exist in the same population of a species, the species is called polymorphic. A well-documented example of polymorphism is Labrador Retriever coloring; while the coat color depends on many genes, it is clearly seen in the environment as yellow, black, and brown. Richard Dawkins in 1978 and then again in his 1982 book ''The Extended Phenotype'' suggested that one can regard bird nests and other built structures such as caddi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Drug Repurposing
Drug repositioning (also called drug repurposing) involves the investigation of existing drugs for new therapeutic purposes. Repurposing achievements A number of successes have been achieved, the foremost including sildenafil (Viagra) for erectile dysfunction and pulmonary hypertension and thalidomide for leprosy and multiple myeloma. Clinical trials have been performed on posaconazole and ravuconazole for Chagas disease. Other antifungal agents clotrimazole and ketoconazole have been investigated for anti- trypanosome therapy. Successful repositioning of antimicrobials has led to the discovery of broad-spectrum therapeutics, which are effective against multiple infection types. In psychiatry, repurposed drugs are emerging as feasible options to treat severe mental disorders. Strategy Drug repositioning is a "universal strategy" for neglected diseases due to 1) reduced number of required clinical trial steps could reduce the time and costs for the medicine to reach ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bronchodilators
A bronchodilator or broncholytic (although the latter occasionally includes secretory inhibition as well) is a substance that dilates the bronchi and bronchioles, decreasing resistance in the respiratory airway and increasing airflow to the lungs. Bronchodilators may be originating naturally within the body, or they may be medications administered for the treatment of breathing difficulties, usually in the form of inhalers. They are most useful in obstructive lung diseases, of which asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease are the most common conditions. Although this remains somewhat controversial, they might be useful in bronchiolitis and bronchiectasis. They are often prescribed but of unproven significance in restrictive lung diseases. Bronchodilators are either short-acting or long-acting. Short-acting medications provide quick or "rescue" relief from acute bronchoconstriction. Long-acting bronchodilators help to control and prevent symptoms. The three types of presc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pyrimidines
Pyrimidine (; ) is an aromatic, heterocyclic, organic compound similar to pyridine (). One of the three diazines (six-membered heterocyclics with two nitrogen atoms in the ring), it has nitrogen atoms at positions 1 and 3 in the ring. The other diazines are pyrazine (nitrogen atoms at the 1 and 4 positions) and pyridazine (nitrogen atoms at the 1 and 2 positions). In nucleic acids, three types of nucleobases are pyrimidine derivatives: cytosine (C), thymine (T), and uracil (U). Occurrence and history The pyrimidine ring system has wide occurrence in nature as substituted and ring fused compounds and derivatives, including the nucleotides cytosine, thymine and uracil, thiamine (vitamin B1) and alloxan. It is also found in many synthetic compounds such as barbiturates and the HIV drug, zidovudine. Although pyrimidine derivatives such as alloxan were known in the early 19th century, a laboratory synthesis of a pyrimidine was not carried out until 1879, when Grimaux reported the p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ureas
220 px, B vitamin, is a urea. In chemistry, ureas are a class of organic compounds with the formula (R2N)2CO where R = H, alkyl, aryl, etc. Thus, in addition to describing the specific chemical compound urea ((H2N)2CO), urea is the name of a functional group that is found in many compounds and materials of both practical and theoretical interest. Generally ureas are colorless crystalline solids, which, owing to the presence of fewer hydrogen bonds, exhibit melting points lower than that of urea itself. Synthesis Ureas can be prepared many methods, but rarely by direct carbonation, which is the route to urea itself. Instead, methods can be classified according those that assemble the urea functionality and those that start with preformed urea. Assembly of N-substituted urea functionality Phosgenation entails the reaction of amines with phosgene, proceeding via the isocyanate (or carbamoyl chloride) as an intermediate: :COCl2 + R2NH → R2NC(O)Cl + HCl :COCl2 + RNH2 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lactams
A lactam is a cyclic amide, formally derived from an amino alkanoic acid. The term is a portmanteau of the words ''lactone'' + ''amide''. Nomenclature Greek prefixes in alphabetical order indicate ring size: * α-Lactam (3-atom rings) * β-Lactam (4-atom rings) * γ-Lactam (5-atom rings) * δ-Lactam (6-atom rings) * ε-Lactam (7-atom rings) This ring-size nomenclature stems from the fact that a hydrolyzed α-Lactam leads to an α-amino acid and a β-Lactam to a β-amino acid, ''etc''. Synthesis General synthetic methods exist for the organic synthesis of lactams. Beckmann rearrangement Lactams form by the acid-catalyzed rearrangement of oximes in the Beckmann rearrangement. Schmidt reaction Lactams form from cyclic ketones and hydrazoic acid in the Schmidt reaction. Cyclization of amino acids Lactams can be formed from cyclisation of amino acids via the coupling between an amine and a carboxylic acid within the same molecule. Lactamization is most efficient in this wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |