|
Token-based Replay
Token-based replay technique is a conformance checking algorithm that checks how well a process conforms with its model by replaying each trace on the model (in Petri net, Petri net notation ). Using the four counters ''produced tokens, consumed tokens, missing tokens, and remaining tokens,'' it records the situations where a transition is forced to fire and the remaining tokens after the replay ends. Based on the count at each counter, we can compute the ''fitness value'' between the trace and the model. The algorithm The token-replay technique uses four counters to keep track of a trace during the replaying: * : Produced tokens * : Consumed tokens * : Missing tokens (consumed while not there) * : Remaining tokens (produced but not consumed) Invariants: * At any time: p+m \ge c \ge m * At the end: r = p + m - c At the beginning, a token is produced for the source place (p = 1) and at the end, a token is consumed from the sink place (c' = c + 1). When the replay ends, th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Conformance Checking
Business process conformance checking (a.k.a. conformance checking for short) is a family of process mining techniques to compare a Process modeling, process model with an event log of the same process. It is used to check if the actual execution of a business process, as recorded in the event log, conforms to the model and vice versa. For instance, there may be a process model indicating that purchase orders of more than one million euros require two checks. Analysis of the event log will show whether this rule is followed or not. Another example is the checking of the so-called “Four-eyes principle, four-eyes” principle stating that particular activities should not be executed by one and the same person. By scanning the event log using a model specifying these requirements, one can discover potential cases of fraud. Hence, conformance checking may be used to detect, locate and explain deviations, and to measure the severity of these deviations. Overview Conformance checking ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
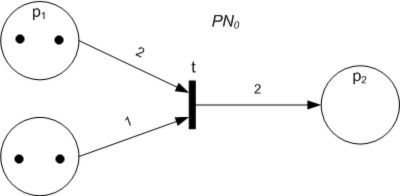
Petri Net
A Petri net, also known as a place/transition net (PT net), is one of several mathematical modeling languages for the description of distributed systems. It is a class of discrete event dynamic system. A Petri net is a directed bipartite graph that has two types of elements: places and transitions. Place elements are depicted as white circles and transition elements are depicted as rectangles. A place can contain any number of tokens, depicted as black circles. A transition is enabled if all places connected to it as inputs contain at least one token. Some sources state that Petri nets were invented in August 1939 by Carl Adam Petri — at the age of 13 — for the purpose of describing chemical processes. Like industry standards such as UML activity diagrams, Business Process Model and Notation, and event-driven process chains, Petri nets offer a graphical notation for stepwise processes that include choice, iteration, and concurrent execution. Unlike these standards, Pet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |