|
Toe Walking
Toe walking refers to a condition where a person walks on their toes without putting much or any weight on the heel or any other part of the foot. This term also includes the inability to connect one's foot fully to the ground while in the standing phase of the walking cycle. Toe walking in toddlers is common. Children who toe walk as toddlers commonly adopt a heel-toe walking pattern as they grow older. If a child continues to walk on their toes past the age of three, or can't get their heels to the ground at all, they should be evaluated by a health professional who is experienced in assessing children's walking. Toe walking can be caused by a number of health conditions. When there is no medical reason for toe walking and no underlying condition can be identified, health professionals will commonly refer to it as "idiopathic" toe walking. This is not a formal or recognized diagnosis; rather, it is simply a term indicating that there is no identifiable reason or causal factor f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pediatrics
Pediatrics ( also spelled ''paediatrics'' or ''pædiatrics'') is the branch of medicine that involves the medical care of infants, children, adolescents, and young adults. In the United Kingdom, paediatrics covers many of their youth until the age of 18. The American Academy of Pediatrics recommends people seek pediatric care through the age of 21, but some pediatric subspecialists continue to care for adults up to 25. Worldwide age limits of pediatrics have been trending upward year after year. A medical doctor who specializes in this area is known as a pediatrician, or paediatrician. The word ''pediatrics'' and its cognates mean "healer of children," derived from the two Greek words: (''pais'' "child") and (''iatros'' "doctor, healer"). Pediatricians work in clinics, research centers, universities, general hospitals and children's hospitals, including those who practice pediatric subspecialties (e.g. neonatology requires resources available in a NICU). History The ear ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
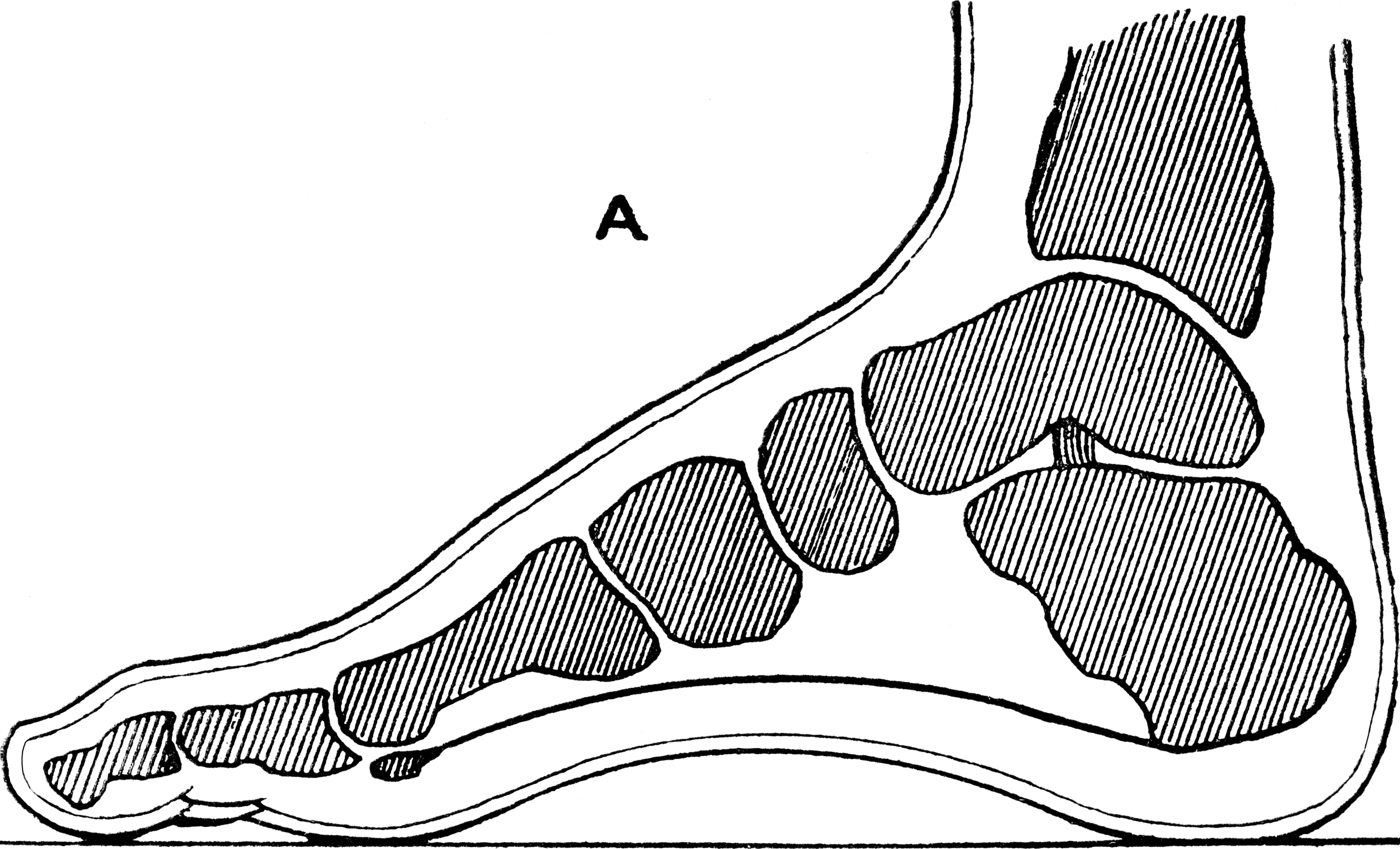
Heel
The heel is the prominence at the posterior end of the foot. It is based on the projection of one bone, the calcaneus or heel bone, behind the articulation of the bones of the lower Human leg, leg. Structure To distribute the compressive forces exerted on the heel during gait, and especially the stance phase when the heel contacts the ground, the sole (foot), sole of the foot is covered by a layer of subcutaneous connective tissue up to 2 cm thick (under the heel). This tissue has a system of pressure chambers that both acts as a shock absorber and stabilises the sole. Each of these chambers contains fibrofatty tissue covered by a layer of tough connective tissue made of collagen fibers. These septum, septa ("walls") are firmly attached both to the plantar aponeurosis above and the sole's Dermis, skin below. The sole of the foot is one of the most highly vascularized regions of the body surface, and the dense system of blood vessels further stabilize the septa. The Ach ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Achilles Tendon
The Achilles tendon or heel cord, also known as the calcaneal tendon, is a tendon at the back of the lower leg, and is the thickest in the human body. It serves to attach the plantaris, gastrocnemius (calf) and soleus muscles to the calcaneus (heel) bone. These muscles, acting via the tendon, cause plantar flexion of the foot at the ankle joint, and (except the soleus) flexion at the knee. Abnormalities of the Achilles tendon include inflammation ( Achilles tendinitis), degeneration, rupture, and becoming embedded with cholesterol deposits (xanthomas). The Achilles tendon was named in 1693 after the Greek hero Achilles. History The oldest-known written record of the tendon being named for Achilles is in 1693 by the Flemish/Dutch anatomist Philip Verheyen. In his widely used text he described the tendon's location and said that it was commonly called "the cord of Achilles." The tendon has been described as early as the time of Hippocrates, who described it as the "" (Latin f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cerebral Palsy
Cerebral palsy (CP) is a group of movement disorders that appear in early childhood. Signs and symptoms vary among people and over time, but include poor coordination, stiff muscles, weak muscles, and tremors. There may be problems with sensation, vision, hearing, and speaking. Often, babies with cerebral palsy do not roll over, sit, crawl or walk as early as other children of their age. Other symptoms include seizures and problems with thinking or reasoning, which each occur in about one-third of people with CP. While symptoms may get more noticeable over the first few years of life, underlying problems do not worsen over time. Cerebral palsy is caused by abnormal development or damage to the parts of the brain that control movement, balance, and posture. Most often, the problems occur during pregnancy, but they may also occur during childbirth or shortly after birth. Often, the cause is unknown. Risk factors include preterm birth, being a twin, certain infections during pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy
Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD) is a severe type of muscular dystrophy that primarily affects boys. Muscle weakness usually begins around the age of four, and worsens quickly. Muscle loss typically occurs first in the thighs and pelvis followed by the arms. This can result in trouble standing up. Most are unable to walk by the age of 12. Affected muscles may look larger due to increased fat content. Scoliosis is also common. Some may have intellectual disability. Females with a single copy of the defective gene may show mild symptoms. The disorder is X-linked recessive. About two thirds of cases are inherited from a person's mother, while one third of cases are due to a new mutation. It is caused by a mutation in the gene for the protein dystrophin. Dystrophin is important to maintain the muscle fiber's cell membrane. Genetic testing can often make the diagnosis at birth. Those affected also have a high level of creatine kinase in their blood. Although there is no know ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Foot Drop
Foot drop is a gait abnormality in which the dropping of the forefoot happens due to weakness, irritation or damage to the deep fibular nerve (deep peroneal), including the sciatic nerve, or paralysis of the muscles in the anterior portion of the lower leg. It is usually a symptom of a greater problem, not a disease in itself. Foot drop is characterized by inability or impaired ability to raise the toes or raise the foot from the ankle (dorsiflexion). Foot drop may be temporary or permanent, depending on the extent of muscle weakness or paralysis and it can occur in one or both feet. In walking, the raised leg is slightly bent at the knee to prevent the foot from dragging along the ground. Foot drop can be caused by nerve damage alone or by muscle or spinal cord trauma, abnormal anatomy, atoxins, or disease. Toxins include organophosphate compounds which have been used as pesticides and as chemical agents in warfare. The poison can lead to further damage to the body such as a n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Autism
The autism spectrum, often referred to as just autism or in the context of a professional diagnosis autism spectrum disorder (ASD) or autism spectrum condition (ASC), is a neurodevelopmental condition (or conditions) characterized by difficulties in social interaction, verbal and nonverbal communication, and the presence of repetitive behavior and restricted interests. Other common signs include unusual responses to sensory stimuli. Autism is generally understood as a ''spectrum disorder'', which means that it can manifest differently in each person: any given autistic individual is likely to show some, but not all, of the characteristics associated with it, and the person may exhibit them to varying degrees. Some autistic people remain nonspeaking over the course of their lifespan, while others have relatively unimpaired spoken language. There is large variation in the level of support people require, and the same person may present differently at varying times. Historically ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Annual Review Of Medicine
The ''Annual Review of Medicine'' is a peer-reviewed medical journal that publishes review articles about all aspects of medicine. It was established in 1950. Its longest-serving editors have been William P. Creger (1974–1993) and C. Thomas Caskey (2001–2019). The current editor is Mary E. Klotman. As of 2022, ''Journal Citation Reports'' gives the journal a 2021 impact factor of 16.048, ranking it seventh of 139 titles in the category "Medicine, Research & Experimental". History The first volume of the journal was published in 1950 by the nonprofit publishing company Annual Reviews. It noted that the more "active" areas of medicine would be covered in each volume, while other subdisciplines would be covered every two or three years. Its first editor was Windsor C. Cutting. In 1996, it was one of the first Annual Reviews journals to be published electronically. Editors of volumes Dates indicate publication years in which someone was credited as a lead editor or co-editor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bilateria
The Bilateria or bilaterians are animals with bilateral symmetry as an embryo, i.e. having a left and a right side that are mirror images of each other. This also means they have a head and a tail (anterior-posterior axis) as well as a belly and a back (ventral-dorsal axis). Nearly all are bilaterally symmetrical as adults as well; the most notable exception is the echinoderms, which achieve secondary pentaradial symmetry as adults, but are bilaterally symmetrical during embryonic development. Most animals are bilaterians, excluding sponges, ctenophores, placozoans and cnidarians. For the most part, bilateral embryos are triploblastic, having three germ layers: endoderm, mesoderm, and ectoderm. Except for a few phyla (i.e. flatworms and gnathostomulids), bilaterians have complete digestive tracts with a separate mouth and anus. Some bilaterians lack body cavities ( acoelomates, i.e. Platyhelminthes, Gastrotricha and Gnathostomulida), while others display primary body cavities (de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Watchful Waiting
Watchful waiting (also watch and wait or WAW) is an approach to a medical problem in which time is allowed to pass before medical intervention or therapy is used. During this time, repeated testing may be performed. Related terms include ''expectant management'', ''active surveillance'', and ''masterly inactivity''. The term ''masterly inactivity'' is also used in nonmedical contexts. A distinction can be drawn between ''watchful waiting'' and ''medical observation'', but some sources equate the terms. Usually, watchful waiting is an outpatient process and may have a duration of months or years. In contrast, medical observation is usually an inpatient process, often involving frequent or even continuous monitoring and may have a duration of hours or days. Medical uses Often watchful waiting is recommended in situations with a high likelihood of self-resolution if there is high uncertainty concerning the diagnosis, and the risks of intervention or therapy may outweigh the benefit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Botulinum Toxin
Botulinum toxin, or botulinum neurotoxin (BoNT), is a neurotoxic protein produced by the bacterium ''Clostridium botulinum'' and related species. It prevents the release of the neurotransmitter acetylcholine from axon endings at the neuromuscular junction, thus causing flaccid paralysis. The toxin causes the disease botulism. The toxin is also used commercially for medical and cosmetic purposes. The seven main types of botulinum toxin are named types A to G (A, B, C1, C2, D, E, F and G). New types are occasionally found. Types A and B are capable of causing disease in humans, and are also used commercially and medically. Types C–G are less common; types E and F can cause disease in humans, while the other types cause disease in other animals. Botulinum toxins are among the most potent toxins known. Intoxication can occur naturally as a result of either wound or intestinal infection or by ingesting formed toxin in food. The estimated human lethal dose of type A toxin is 1.3 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anaesthesia
Anesthesia is a state of controlled, temporary loss of sensation or awareness that is induced for medical or veterinary purposes. It may include some or all of analgesia (relief from or prevention of pain), paralysis (muscle relaxation), amnesia (loss of memory), and unconsciousness. An individual under the effects of anesthetic drugs is referred to as being anesthetized. Anesthesia enables the painless performance of procedures that would otherwise cause severe or intolerable pain in a non-anesthetized individual, or would otherwise be technically unfeasible. Three broad categories of anesthesia exist: * General anesthesia suppresses central nervous system activity and results in unconsciousness and total lack of sensation, using either injected or inhaled drugs. * Sedation suppresses the central nervous system to a lesser degree, inhibiting both anxiety and creation of long-term memories without resulting in unconsciousness. * Regional and local anesthesia, which blocks ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |





.jpg)
