|
Tobishima (Yamagata)
, native_name_link = , image_caption = Aerial photograph of Tobishima in 1976 , image_size = , pushpin_map = Japan , pushpin_label = , pushpin_label_position = , pushpin_map_alt = , pushpin_relief = 1 , pushpin_map_caption = , nickname = , location = Sea of Japan , coordinates = , archipelago = , total_islands = , major_islands = , area_km2 = 2.75 , length_km = 2 , width_km = 1 , coastline_km = 10.2 , highest_mount = Takamoriyama , elevation_m = 68 , country = Japan , country_admin_divisions_title = Prefecture , country_admin_divisions = Yamagata , country_admin_divisions_title_1 = City , country_admin_divisions_1 = Sakata , population = 275 , population_as_of = 2005 , density_km2 =91 , ethnic_groups = Japanese , additional_info = , is an inhabited island located i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
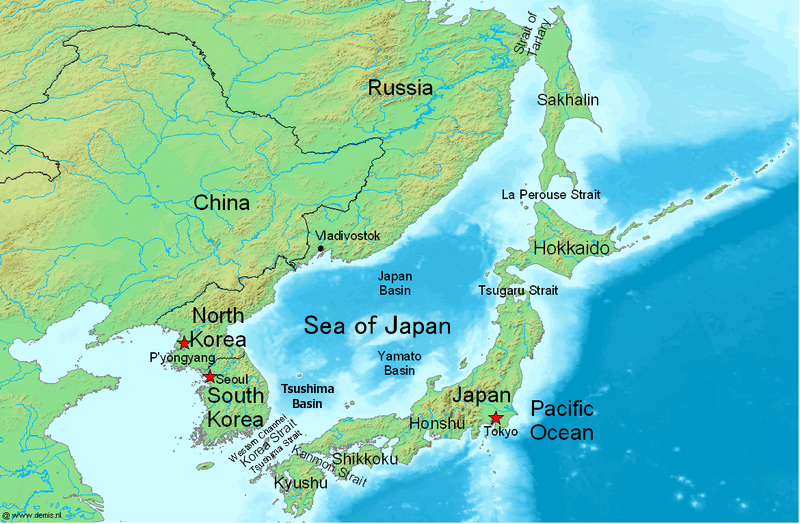
Sea Of Japan
The Sea of Japan is the marginal sea between the Japanese archipelago, Sakhalin, the Korean Peninsula, and the mainland of the Russian Far East. The Japanese archipelago separates the sea from the Pacific Ocean. Like the Mediterranean Sea, it has almost no tides due to its nearly complete enclosure from the Pacific Ocean. This isolation also affects faunal diversity and salinity, both of which are lower than in the open ocean. The sea has no large islands, bays or capes. Its water balance is mostly determined by the inflow and outflow through the straits connecting it to the neighboring seas and the Pacific Ocean. Few rivers discharge into the sea and their total contribution to the water exchange is within 1%. The seawater has an elevated concentration of dissolved oxygen that results in high biological productivity. Therefore, fishing is the dominant economic activity in the region. The intensity of shipments across the sea has been moderate owing to political issues, but it ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Islands Of The Sea Of Japan
An island (or isle) is an isolated piece of habitat that is surrounded by a dramatically different habitat, such as water. Very small islands such as emergent land features on atolls can be called islets, skerries, cays or keys. An island in a river or a lake island may be called an eyot or ait, and a small island off the coast may be called a holm. Sedimentary islands in the Ganges delta are called chars. A grouping of geographically or geologically related islands, such as the Philippines, is referred to as an archipelago. There are two main types of islands in the sea: continental and oceanic. There are also artificial islands, which are man-made. Etymology The word ''island'' derives from Middle English ''iland'', from Old English ''igland'' (from ''ig'' or ''ieg'', similarly meaning 'island' when used independently, and -land carrying its contemporary meaning; cf. Dutch ''eiland'' ("island"), German ''Eiland'' ("small island")). However, the spelling of the word ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Islands Of Yamagata Prefecture
An island (or isle) is an isolated piece of habitat that is surrounded by a dramatically different habitat, such as water. Very small islands such as emergent land features on atolls can be called islets, skerries, cays or keys. An island in a river or a lake island may be called an eyot or ait, and a small island off the coast may be called a holm. Sedimentary islands in the Ganges delta are called chars. A grouping of geographically or geologically related islands, such as the Philippines, is referred to as an archipelago. There are two main types of islands in the sea: continental and oceanic. There are also artificial islands, which are man-made. Etymology The word ''island'' derives from Middle English ''iland'', from Old English ''igland'' (from ''ig'' or ''ieg'', similarly meaning 'island' when used independently, and -land carrying its contemporary meaning; cf. Dutch language, Dutch ''eiland'' ("island"), German language, German ''Eiland'' ("small island")). ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
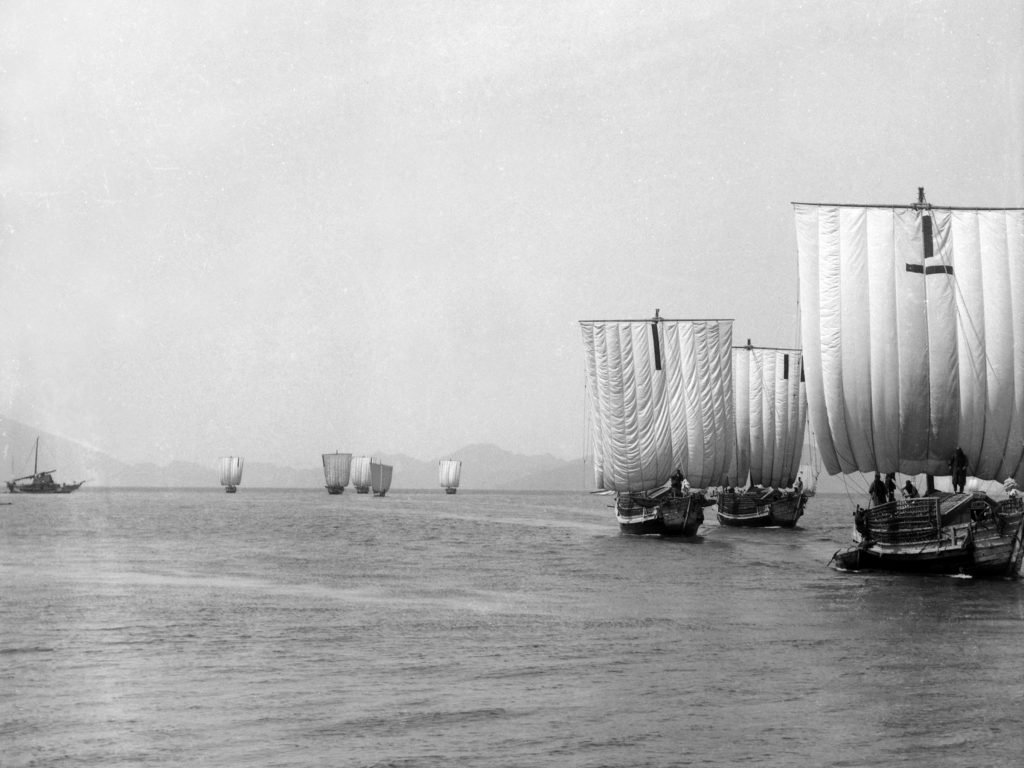
Kitamaebune
The was a shipping route (and also the ships involved) in Japan from the Edo period to the Meiji era. The route went from Osaka through the Seto Inland Sea and the Kanmon Straits to ports in Hokuriku on the Sea of Japan and later to Hokkaidō. Kaga Domain, which sold about 70,000 ''koku'' of rice every year in Osaka, succeeded in sending 100 ''koku'' by boat through this route in 1639. The Tokugawa shogunate also received rice from Dewa Province through merchant Kawamura Zuiken in 1672, but it is thought to be a response from these ships. Japanese ships at the time normally could make only one trip per year, but with the arrival of Western schooners in the Meiji era, ships were able to make up to four trips annually. The Meiji Restoration also brought the end of the feudal system and the introduction of the telegraph, removing gaps between regional markets and making it difficult for the shipping routes to make large profits. The national construction of railroads further led ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sakai Clan
The was a Japanese samurai clan that claimed descent from the Nitta branch of the Minamoto clan, who were in turn descendants of Emperor Seiwa. Serata (Nitta) Arichika, a samurai of the 14th century, was the common ancestor of both the Sakai clan and the Matsudaira clan, which the Sakai later served. In the Sengoku period, under Tokugawa Ieyasu (who was the head of what was formerly the main Matsudaira family line), the Sakai became chief retainers. In the Edo period, because of their longstanding service to the Tokugawa clan, the Sakai were classified as a '' fudai'' family, in contrast with the '' tozama'' ("outsider clans"). Clan branches and histories The ''fudai'' Sakai clan originated in 14th century Mikawa Province. They claim descent from Minamoto no Arichika. Arichika had two sons; one of them, Yasuchika, took the name of Matsudaira, while the other son, Chikauji, took the name of Sakai. Chikauji is the ancestor of the Sakai clan. Sakai Hirochika, Chikauji's son, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Edo Period
The or is the period between 1603 and 1867 in the history of Japan, when Japan was under the rule of the Tokugawa shogunate and the country's 300 regional '' daimyo''. Emerging from the chaos of the Sengoku period, the Edo period was characterized by economic growth, strict social order, isolationist foreign policies, a stable population, perpetual peace, and popular enjoyment of arts and culture. The period derives its name from Edo (now Tokyo), where on March 24, 1603, the shogunate was officially established by Tokugawa Ieyasu. The period came to an end with the Meiji Restoration and the Boshin War, which restored imperial rule to Japan. Consolidation of the shogunate The Edo period or Tokugawa period is the period between 1603 and 1867 in the history of Japan, when Japan was under the rule of the Tokugawa shogunate and the country's regional '' daimyo''. A revolution took place from the time of the Kamakura shogunate, which existed with the Tennō's court, to the Tok ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kiyohara Clan
The was a powerful clan of the far north of Japan during the Heian period, descended from Prince Toneri, son of Emperor Tenmu (631–686). Kiyohara no Fusanori (9th century) had two sons: the elder was the ancestor of the samurai branch family of Dewa Province; the younger of the ''kuge'' (court nobles) branch of the clan. The position of Governor of Dewa province was passed down within the family; the Kiyohara are particularly known for their involvement in the Zenkunen and Gosannen Wars of the 11th century. The erupted in 1051, when Minamoto no Yoriyoshi and his son Yoshiie arrived in the north, from Kyoto, as agents of the Imperial court. They were there to put an end to a conflict between the Governor of Mutsu Province (which bordered the Kiyohara's Dewa) and the '' Chinjufu-shōgun'' (Defender of the North), Abe no Yoritoki. The Kiyohara Governor of Dewa contributed warriors to the Minamoto effort, and aided in their victory over the Abe clan, which was achieved in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abe Clan
The was one of the oldest of the major Japanese clans (''uji''); and the clan retained its prominence during the Sengoku period and the Edo period.Meyer, Eva-Maria"Gouverneure von Kyôto in der Edo-Zeit." Universität Tübingen (in German). The clan's origin is said to be one of the original clans of the Yamato people; they truly gained prominence during the Heian period (794-1185), and experienced a resurgence in the 18th century. Although Abe is also a very common Japanese surname in modern times, not everyone with this name is descended from this clan. Origins and history According to the '' Nihon Shoki'', the Abe were descended from Prince Ōhiko, son of Emperor Kōgen. Asakawa, Kan'ichi. (1903). ''The Early Institutional Life of Japan,'' p.140. They originated in Iga province (today Mie prefecture); Though the clan name was originally written as 阿倍, it changed to 安倍 around the 8th century. Though this origin is not positive, it is likely. The northern region which ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heian Period
The is the last division of classical Japanese history, running from 794 to 1185. It followed the Nara period, beginning when the 50th emperor, Emperor Kanmu, moved the capital of Japan to Heian-kyō (modern Kyoto). means "peace" in Japanese. It is a period in Japanese history when the Chinese influences were in decline and the national culture matured. The Heian period is also considered the peak of the Japanese imperial court and noted for its art, especially poetry and literature. Two types of Japanese script emerged, including katakana, a phonetic script which was abbreviated into hiragana, a cursive alphabet with a unique writing method distinctive to Japan. This gave rise to Japan's famous vernacular literature, with many of its texts written by court women who were not as educated in Chinese compared to their male counterparts. Although the Imperial House of Japan had power on the surface, the real power was in the hands of the Fujiwara clan, a powerful aristocratic f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jōmon Period
The is the time in Japanese history, traditionally dated between 6,000–300 BCE, during which Japan was inhabited by a diverse hunter-gatherer and early agriculturalist population united through a common Jōmon culture, which reached a considerable degree of sedentism and cultural complexity. The name "cord-marked" was first applied by the American zoologist and orientalist Edward S. Morse, who discovered sherds of pottery in 1877 and subsequently translated it into Japanese as ''Jōmon''.Mason, 14 The pottery style characteristic of the first phases of Jōmon culture was decorated by impressing cords into the surface of wet clay and is generally accepted to be among the oldest in the world. The Jōmon period was rich in tools and jewelry made from bone, stone, shell and antler; pottery figurines and vessels; and lacquerware.Imamura, K. (1996) ''Prehistoric Japan: New Perspectives on Insular East Asia''. Honolulu: University of Hawaii Press It is often compared to pre-C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |