|
Tobiad
The Tobiads were a Jewish faction in Ammon at the beginning of the Hasmonean period. They were philhellene, supporters of Hellenistic Judaism, in the early years of the 2nd century BCE. What is known about the Tobiads is a combination of statements of Josephus (''Antiquities of the Jews'' xii. 160-236) and of 2 Maccabees . There are two accounts, both legendary, the hero of the one being Joseph, and of the other, Hyrcanus. Narrative During the reign of the Egyptian king Ptolemy and his wife Cleopatra, the high priest Onias, who was feeble-minded and extremely miserly, refused to pay the Jewish tribute of twenty talents which his father, Simon the Just, had always given from his own means. In his anger the king sent Athenion as a special envoy to Jerusalem, threatening to seize the land of the Jews and to hold it by force of arms if the money was not forthcoming. Although the high priest disregarded this threat, the people were greatly excited, whereupon Onias' nephew Joseph, a s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
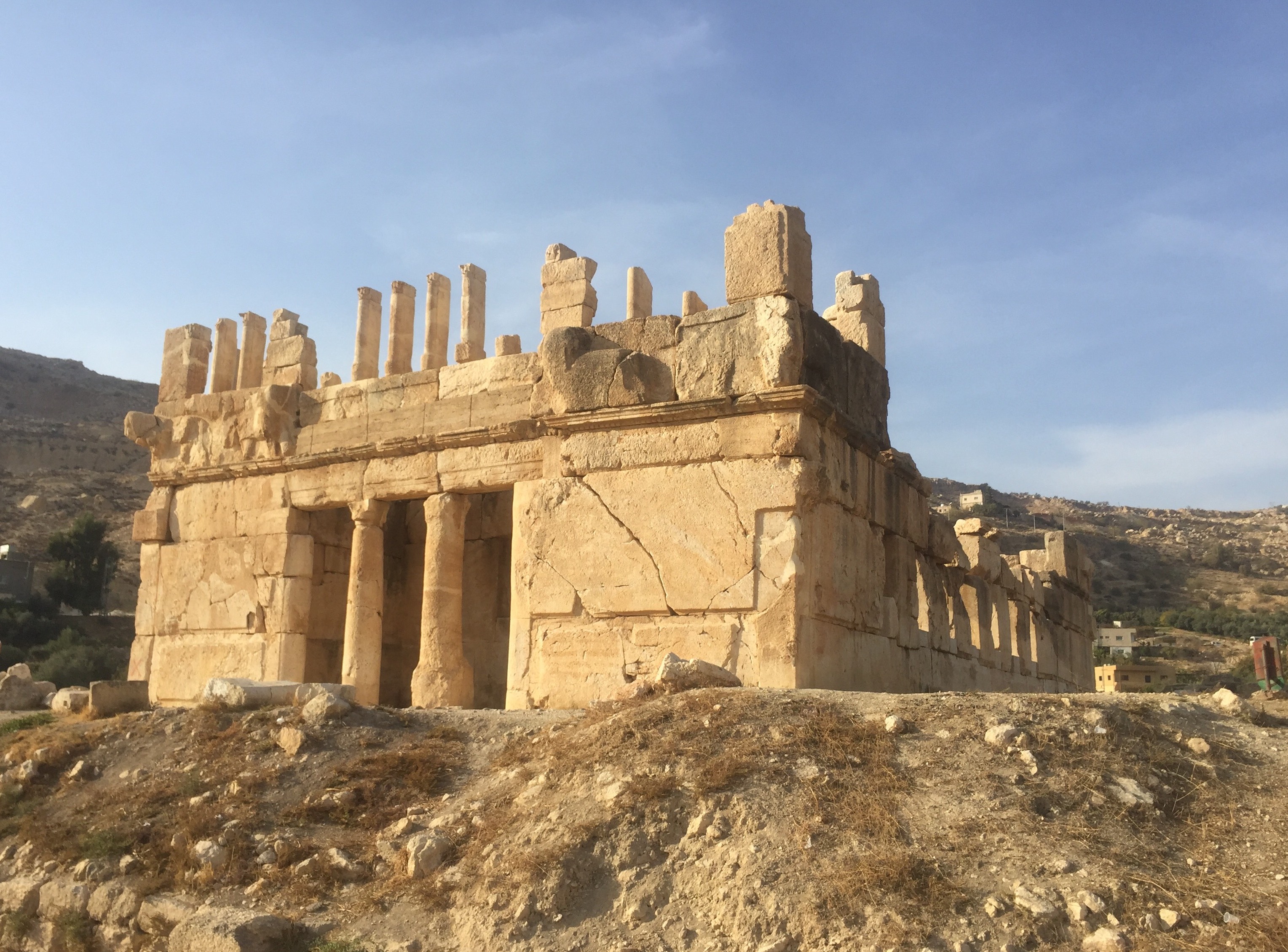
Qasr Al Abd
Qasr al-Abd ( ar, قصر العبد, , Castle of the Slave) is a large Hellenistic palace from the first quarter of the second century BCE. Most scholars agree it was built by the Tobiads, a notable Jewish family of the Second Temple period, although the descriptions doesn't mention that. Its ruins stand in modern-day Jordan in the valley of Wadi Seer, close to the village of Iraq Al-Amir, approximately 17 kilometers west of Amman. History Qasr al-Abd is believed to be Tyros, the palace of a Tobiad notable, Hyrcanus of Jerusalem, head of the powerful Tobiad family and governor of Ammon in the 2nd century BCE. The first known written description of the castle comes down to us from Josephus, a first-century Jewish-Roman historian: The association of the site with the Tobiads is based on a cave inscription found nearby. The Hebrew name 'Tuvya' or 'Toviyya' (Tobias) is engraved (טוביה, but in a more Aramaic script above the adjacent burial caves of Iraq al-Amir, which sha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Menelaus (High Priest)
Menelaus ( he, מנלאוס) was High Priest in Jerusalem from about 172 BC to about 161 BC. He was high priest at the beginning of the Maccabean revolt (167-160). He was the successor of Jason, the brother of Onias III. The sources are divided as to his origin. According to II Maccabees, he belonged to the Tribe of Benjamin and was the brother of the Simeon who had denounced Onias III to Seleucus IV Philopator, and revealed to the Syrians the existence of the treasure of the Temple; according to Flavius Josephus, Menelaus was the brother of Onias III and Jason, his two predecessors as High Priest, and also bore the name Onias. It is possible that Josephus confused Simeon, the brother of Menelaus, with Simeon, the father of Onias and Jason. Hellenizing tendencies Although during the three years of his pontificate Jason had given many proofs of his attachment to the Hellenistic party (by building a gymnasium in Jerusalem and by introducing many Greek customs) the Hellenists of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
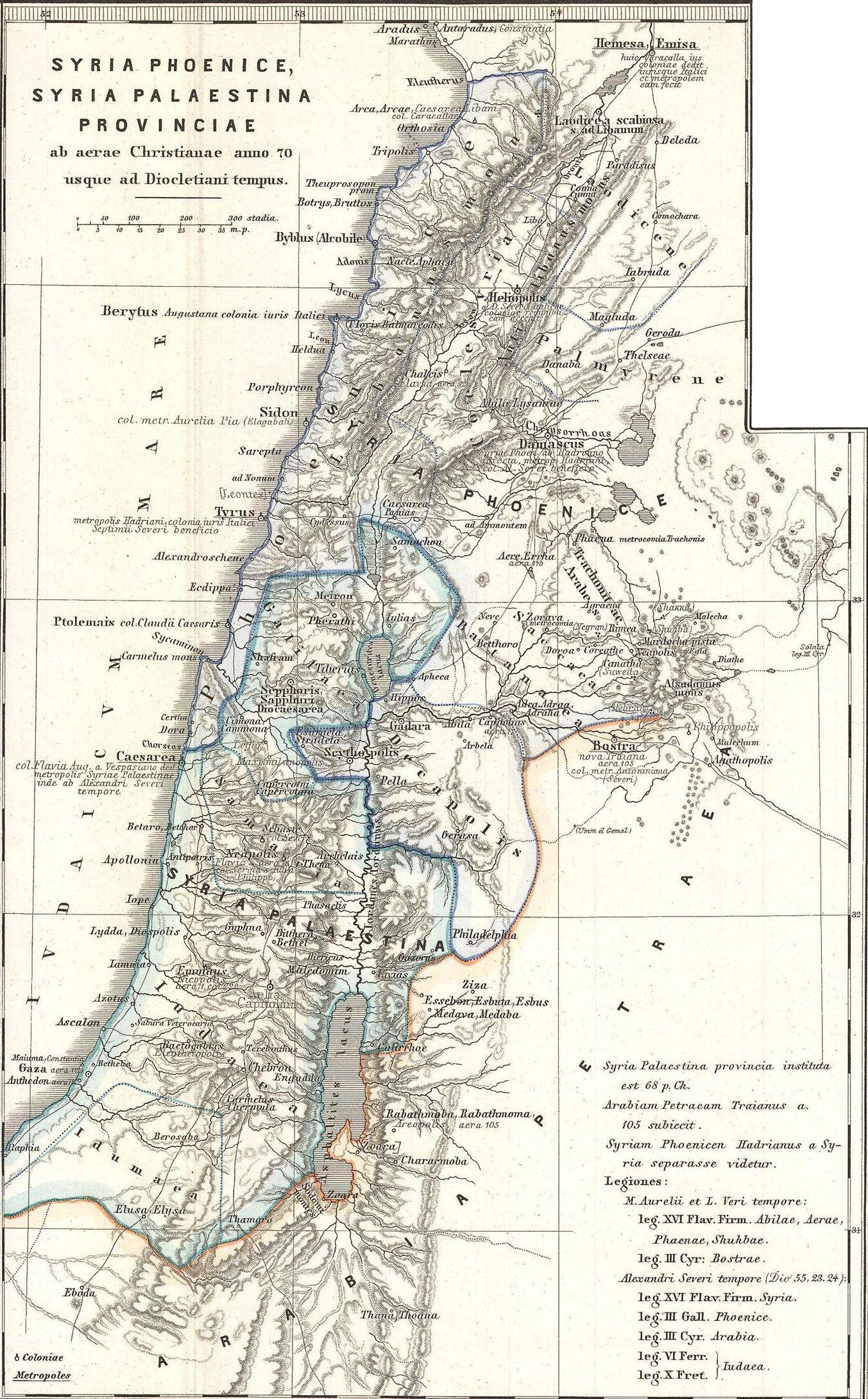
Ammon
Ammon (Ammonite: 𐤏𐤌𐤍 ''ʻAmān''; he, עַמּוֹן ''ʻAmmōn''; ar, عمّون, ʻAmmūn) was an ancient Semitic-speaking nation occupying the east of the Jordan River, between the torrent valleys of Arnon and Jabbok, in present-day Jordan. The chief city of the country was ''Rabbah'' or ''Rabbat Ammon'', site of the modern city of Amman, Jordan's capital. Milcom and Molech are named in the Hebrew Bible as the gods of Ammon. The people of this kingdom are called "Children of Ammon" or "Ammonites". History The Ammonites occupied the northern Central Trans-Jordanian Plateau from the latter part of the second millennium BCE to at least the second century CE. Ammon maintained its independence from the Neo-Assyrian Empire (10th to 7th centuries BCE) by paying tribute to the Assyrian kings at a time when that Empire raided or conquered nearby kingdoms. The Kurkh Monolith lists the Ammonite king Baasha ben Ruhubi's army as fighting alongside Ahab of Israel and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hasmonean Dynasty
The Hasmonean dynasty (; he, ''Ḥašmōnaʾīm'') was a ruling dynasty of Judea and surrounding regions during classical antiquity, from BCE to 37 BCE. Between and BCE the dynasty ruled Judea semi-autonomously in the Seleucid Empire, and from roughly 110 BCE, with the empire disintegrating, Judea gained further autonomy and expanded into the neighboring regions of Perea, Samaria, Idumea, Galilee, and Iturea. Some modern scholars regard the Hasmonean realm as an independent Israel. The Hasmonean rulers took the Greek title '' basileus'' ("king" or "emperor"). Forces of the Roman Republic conquered the Hasmonean kingdom in 63 BCE and made it into a client state; Herod the Great displaced the last reigning Hasmonean client-ruler in 37 BCE. Simon Thassi established the dynasty in 141 BCE, two decades after his brother Judas Maccabeus ( ''Yehudah HaMakabi'') had defeated the Seleucid army during the Maccabean Revolt of 167 to 141 BCE. According to 1 Maccabees, 2 Maccabee ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Skythopolis
Beit She'an ( he, בֵּית שְׁאָן '), also Beth-shean, formerly Beisan ( ar, بيسان ), is a town in the Northern District of Israel. The town lies at the Beit She'an Valley about 120 m (394 feet) below sea level. Beit She'an is believed to be one of the oldest cities in the region. It has played an important role in history due to its geographical location at the junction of the Jordan River Valley and the Jezreel Valley. The town's ancient tell contains remains beginning in the Chalcolithic period. It served as an Egyptian administrative center during the Late Bronze Age. During the Hellenistic period, the settlement was known as Scythopolis (Ancient Greek: ''Σκυθόπολις''). After the region came under Roman rule, Scythopolis gained imperial free status and was the leading city of the Decapolis. Later, under Byzantine rule, it served as the capital of Palaestina Secunda. Following the Arab conquest of the Levant, the city lost its prominence. The popula ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1 Maccabees
The First Book of Maccabees, also known as First Maccabees (written in shorthand as 1 Maccabees or 1 Macc.), is a book written in Hebrew by an anonymousRappaport, U., ''47. 1 Maccabees'' in Barton, J. and Muddiman, J. (2001)The Oxford Bible Commentary, p. 711 Jewish author after the restoration of an independent Jewish kingdom by the Hasmonean dynasty, around the late 2nd century BC. The original Hebrew is lost and the most important surviving version is the Greek translation contained in the Septuagint. The book is held as canonical scripture by the Catholic, Orthodox, and Oriental Orthodox churches (except for the Orthodox Tewahedo), but not by Protestant denominations nor any major branches of Judaism; it is not part of the Hebrew Bible. Some Protestants consider it to be an apocryphal book (see also Deuterocanonical books). 1 Maccabees is best known for its account of an early victory in the Maccabean Revolt against the Seleucid Empire: the recapture of Jerusalem in the year ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cœle-Syria
Coele-Syria (, also spelt Coele Syria, Coelesyria, Celesyria) alternatively Coelo-Syria or Coelosyria (; grc-gre, Κοίλη Συρία, ''Koílē Syría'', 'Hollow Syria'; lat, Cœlē Syria or ), was a region of Syria in classical antiquity. It probably derived from the Aramaic word for all of the region of Syria, but it was most often applied to the Beqaa Valley between the Lebanon and the Anti-Lebanon mountain ranges. The area is now part of the modern-day Syria and Lebanon. Name It is widely accepted that the term Coele is a transcription of Aramaic ''kul'', meaning "all, the entire", such that the term originally identified ''all'' of Syria.A History of the Jews and Judaism in the Second Temple Period, Volume 2, Lester L. Grab ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
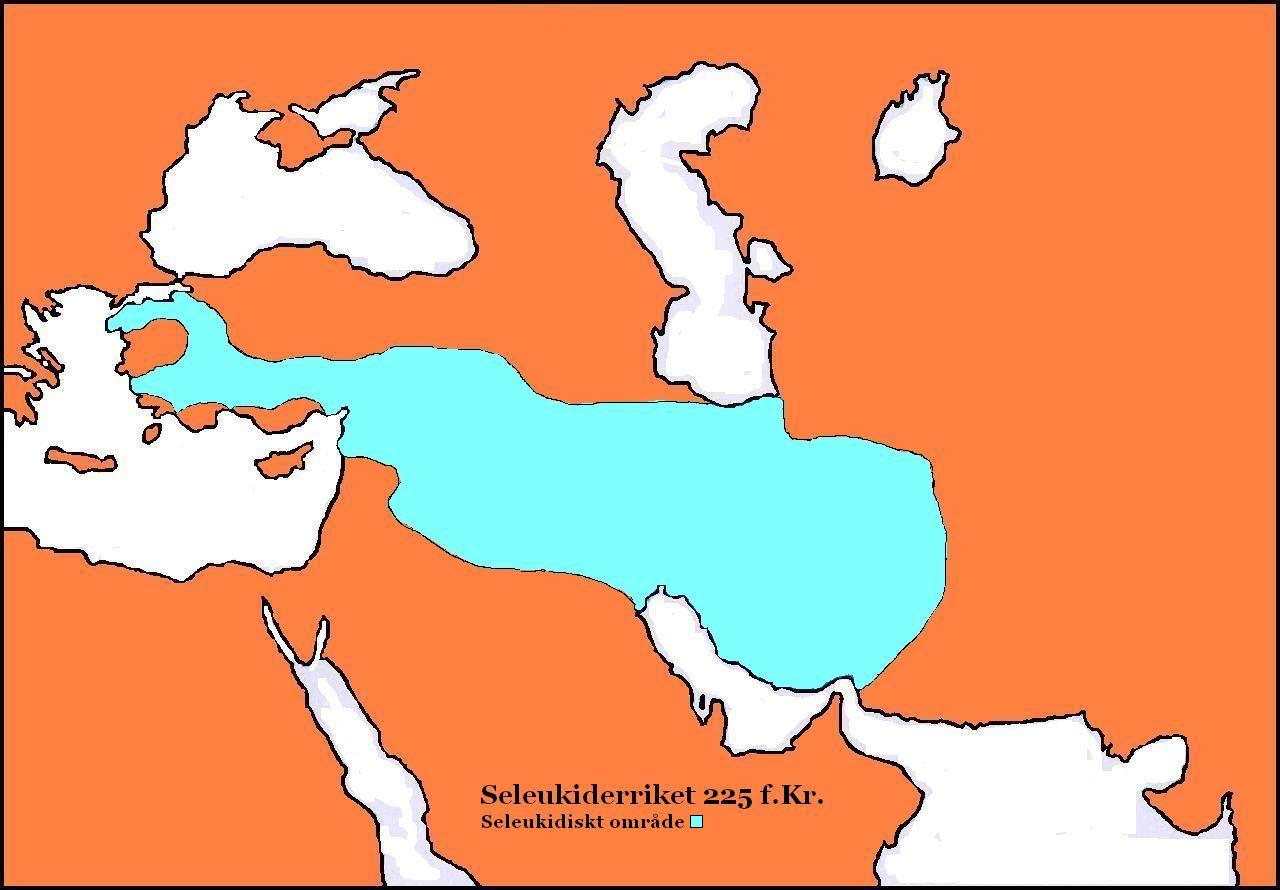
Antiochus III
Antiochus III the Great (; grc-gre, Ἀντίoχoς Μέγας ; c. 2413 July 187 BC) was a Greek Hellenistic king and the 6th ruler of the Seleucid Empire, reigning from 222 to 187 BC. He ruled over the region of Syria and large parts of the rest of western Asia towards the end of the 3rd century BC. Rising to the throne at the age of eighteen in 222 BC, his early campaigns against the Ptolemaic Kingdom were unsuccessful, but in the following years Antiochus gained several military victories and substantially expanded the empire's territory. His traditional designation, ''the Great'', reflects an epithet he assumed. He also assumed the title ''Basileus Megas'' (Greek for "Great King"), the traditional title of the Persian kings. A militarily active ruler, Antiochus restored much of the territory of the Seleucid Empire, before suffering a serious setback, towards the end of his reign, in his war against Rome. Declaring himself the "champion of Greek freedom against Roman dominat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cleopatra I Syra
Cleopatra I Syra (Greek: Κλεοπάτρα ἡ Σύρα; c. 204 – 176 BC) was a princess of the Seleucid Empire, Queen of Ptolemaic Egypt by marriage to Ptolemy V of Egypt, and regent of Egypt during the minority of their son, Ptolemy VI, from her husband’s death in 180 BC until her own death in 176 BC. Life Cleopatra I was the daughter of Antiochus III the Great, King of the Seleucid Empire, and Queen Laodice III. Queen In 197 BC, Antiochus III had captured a number of cities in Asia Minor previously under the control of the Ptolemaic Kingdom of Egypt. The Romans supported the Egyptian interests, when they negotiated with the Seleucid king in Lysimachia in 196 BC. In response, Antiochus III indicated his willingness to make peace with Ptolemy V and to have his daughter Cleopatra I marry Ptolemy V. They were betrothed in 195 BC and their marriage took place in 193 BC in Raphia. At that time Ptolemy V was about 16 years and Cleopatra I about 10 years old. Later on, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ptolemy III Euergetes
, predecessor = Ptolemy II , successor = Ptolemy IV , nebty = ''ḳn nḏtj-nṯrw jnb-mnḫ-n-tꜢmrj''''Qen nedjtinetjeru inebmenekhentamery''The brave one who has protected the gods, a potent wall for The Beloved Land , nebty_hiero = q*nw:n:D40-Aa27-nw:t-Z3-nTr-O36-mnx-n:N17:U7-r:O49*O5 , horus = ''ḥkn-nṯrw-rmṯ-ḥr.f''''Khekenetjeruremetj-heref''The one over whom gods and people have rejoiced Second Horus name:''ḥkn-nṯrw-rmṯ-ḥr.f m-šsp.f-nsyt-m-Ꜥ-jt.f''''Hekenetjeruremetj-heref emshesepefnesytemaitef''The one over whom gods and people have rejoiced when he has received the kingship from his father's hand , golden = ''wr-pḥtj jrj-Ꜣḫt nb-ḥꜢbw-sd-mi-ptḥ-tꜢ-ṯnn jty-mi-rꜤ''''Werpehty iryakhut nebkhabusedmiptah-tatenen itymire''Whose might is great, doing that which is beneficial,Lord of the years of Jubilee like Ptah Ta-Tjenen, a ruler like Ra , golden_hiero= wr:r-F9*F9:ir-Z3*Ax*x:nb-O23-Z3-p:t-H-C19-C18-mi-i-U33-i-i- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antiochus Epiphanes
Antiochus is a Greek male first name, which was a dynastic name for rulers of the Seleucid Empire and the Kingdom of Commagene. In Jewish historical memory, connected with the Maccabean Revolt and the holiday of Hanukkah, "Antiochus" refers specifically to Antiochus IV Epiphanes. Antiochus may refer to: The Seleucid Empire * Antiochus (father of Seleucus I Nicator) (born 4th-century BC), father of Seleucus I Nicator, founder of the Hellenistic Seleucid Empire * Antiochus I Soter (died 261 BC), king of the Seleucid Empire * Antiochus II Theos (286 BC–246 BC), king of the Seleucid Empire who reigned 261 BC–246 BC * Antiochus Hierax (died 226 BC), rebel brother of Seleucus II Callinicus * Antiochus III the Great (241–187 BC, king 222–187 BC), younger son of Seleucus II Callinicus, became the 6th ruler of the Seleucid Empire ** Antiochus (son of Antiochus III the Great), the first son of Antiochus III the Great * Antiochus IV Epiphanes (215 BC–164 BC), ruler of the Sele ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)


._Beisan_mound_LOC_matpc.17062.jpg)


%2C_Antioch_mint.jpg)