|
Title Safe
Safe area is a term used in television production to describe the areas of the television picture that can be seen on television display device, screens. Older televisions can display less of the space outside of the safe area than ones made more recently. Flat panel screens, plasma displays and liquid crystal display (LCD) screens generally can show most of the picture outside the safe areas. The use of safe areas in television production ensures that the most important parts of the picture are seen by the majority of viewers. The size of the title-safe area is typically specified in pixels or percent. The NTSC and PAL analog television standards do not specify official overscan amounts, and producers of television programming use their own guidelines. Some video editing software packages for non-linear editing systems (NLE) solutions have a setting which shows the safe areas while editing. Title-safe area The title-safe area or graphics-safe area is, in television broad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pal Safe Area
Phase Alternating Line (PAL) is a colour encoding system for analogue television. It was one of three major analogue colour television standards, the others being NTSC and SECAM. In most countries it was broadcast at 625 lines, 50 fields (25 frames) per second, and associated with CCIR analogue broadcast television systems CCIR System B, B, CCIR System D, D, CCIR System G, G, CCIR System H, H, CCIR System I, I or CCIR System K, K. The articles on analog broadcast television systems further describe frame rates, image resolution, and audio modulation. PAL video is composite video because Luma (video), luminance (luma, monochrome image) and chrominance (chroma, colour applied to the monochrome image) are transmitted together as one signal. A latter evolution of the standard, PALplus, added support for widescreen broadcasts with no loss of vertical Image resolution, resolution, while retaining compatibility with existing sets. Almost all of the countries using PAL are currentl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lower Third
In the television industry, a lower third is a graphic overlay placed in the title-safe lower area of the screen, though not necessarily the entire lower third of it, as the name suggests. In its simplest form, a lower third can just be text overlaying the video. Frequently this text is white with a drop shadow to make the words easier to read. A lower third can also contain graphical elements such as boxes, images or shading. Some lower thirds have animated backgrounds and text. Lower thirds can be created using basic home-video editing software or professional-level equipment. This equipment makes use of video's alpha channel to determine what parts of the graphic or text should be transparent, allowing the video in the background to show through. Terminology Lower thirds are also often known as "CG" (from character generator) or captions, and sometimes chyrons in North America, due to the popularity of Chyron Corporation's Chiron I character generator, an early digital s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Letterboxing (filming)
Letterboxing is the practice of transferring film shot in a widescreen aspect ratio to standard-width video formats while preserving the film's original aspect ratio. The resulting videographic image has mattes (black bars) above and below it; these mattes are part of each frame of the video signal. LBX and LTBX are identifying abbreviations for films and images thus formatted. Etymology The term refers to the shape of a letter box, a slot in a wall or door through which mail is delivered, being rectangular and wider than it is high. Early home video use The first use of letterbox in consumer video appeared with the RCA Capacitance Electronic Disc (CED) videodisc format. Initially, letterboxing was limited to several key sequences of a film such as opening and closing credits, but was later used for entire films. The first fully letterboxed CED release was '' Amarcord'' in 1984, and several others followed including '' The Long Goodbye'', ''Monty Python and the Holy Grail' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aspect Ratio (image)
The aspect ratio of an image is the ratio of its width to its height, and is expressed with two numbers separated by a colon, such as ''16:9'', sixteen-to-nine. For the ''x'':''y'' aspect ratio, the image is ''x'' units wide and ''y'' units high. Common aspect ratios are 1.85:1 and 2.39:1 in cinematography, 4:3 and 16:9 in television photography, and 3:2 in still photography. Some common examples The common film aspect ratios used in cinemas are 1.85:1 and 2.39:1.The 2.39:1 ratio is commonly labeled 2.40:1, e.g., in the American Society of Cinematographers' ''American Cinematographer Manual'' (Many widescreen films before the 1970 SMPTE revision used 2.35:1). Two common videographic aspect ratios are 4:3 (1.:1), the universal video format of the 20th century, and 16:9 (1.:1), universal for high-definition television and European digital television. Other cinema and video aspect ratios exist, but are used infrequently. In still camera photography, the most common aspect ra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nominal Analogue Blanking
Nominal analogue blanking is the outermost part of the overscan of a standard definition digital television image. It consists of a gap of black (or nearly black) pixels at the left and right sides, which correspond to the end and start of the horizontal blanking interval: the front porch at the right side (the end of a line, before the sync pulse), and the back porch at the left side (the start of a line, after the sync pulse and before drawing the next line). Digital television ordinarily contains 720 pixels per line, but only 702 (PAL) to 704 (NTSC) of them contain picture content. The location is variable, since analogue equipment may shift the picture sideways in an unexpected amount or direction. The exact width is determined by taking the definition of the time required for an active line in PAL or NTSC, and multiplying it by the pixel clock of 13.5 MHz of Digital SDTV. PAL is exactly 52μs, so it will equate to exactly 702 pixels. Notably, screen shapes and aspe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MPEG-4
MPEG-4 is a group of international standards for the compression of digital audio and visual data, multimedia systems, and file storage formats. It was originally introduced in late 1998 as a group of audio and video coding formats and related technology agreed upon by the ISO/IEC Moving Picture Experts Group (MPEG) ( ISO/IEC JTC 1/SC29/WG11) under the formal standard ISO/IEC 14496 – ''Coding of audio-visual objects''. Uses of MPEG-4 include compression of audiovisual data for Internet video and CD distribution, voice (telephone, videophone) and broadcast television applications. The MPEG-4 standard was developed by a group led by Touradj Ebrahimi (later the JPEG president) and Fernando Pereira. Background MPEG-4 absorbs many of the features of MPEG-1 and MPEG-2 and other related standards, adding new features such as (extended) VRML support for 3D rendering, object-oriented composite files (including audio, video and VRML objects), support for externally specified Digital ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blanking (video)
In analog video, blanking occurs between horizontal lines and between frames. In raster scan equipment, an image is built up by scanning an electron beam from left to right across a screen to produce a visible trace of one scan line, reducing the brightness of the beam to zero (horizontal blanking), moving it back as fast as possible to the left of the screen at a slightly lower position (the next scan line), restoring the brightness, and continuing until all the lines have been displayed and the beam is at the bottom right of the screen. Its intensity is then reduced to zero again (vertical blanking), and it is rapidly moved to the top left to start again, creating the next frame. In television Television, sometimes shortened to TV, is a telecommunication medium for transmitting moving images and sound. The term can refer to a television set, or the medium of television transmission. Television is a mass medium for advertisin ..., in particular, the vertical blanking ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DVD Player
A DVD player is a device that plays DVDs produced under both the DVD-Video and DVD-Audio technical standards, two different and incompatible standards. Some DVD players will also play audio CDs. DVD players are connected to a television to watch the DVD content, which could be a movie, a recorded TV show, or other content. History The first DVD player is claimed to have been created by the Japanese electronics vendor Toshiba in November 1996, and the first to be released to US customers is claimed to have been by Sony in April 1997. Some manufacturers originally announced that DVD players would be available as early as the middle of 1996. These predictions were too optimistic. Delivery was initially held up for "political" reasons of copy protection demanded by movie studios, but was later delayed by lack of movie titles. The first players appeared in Japan on November 1, 1996, followed by the United States on March 31, 1997, with distribution limited to only seven major ci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
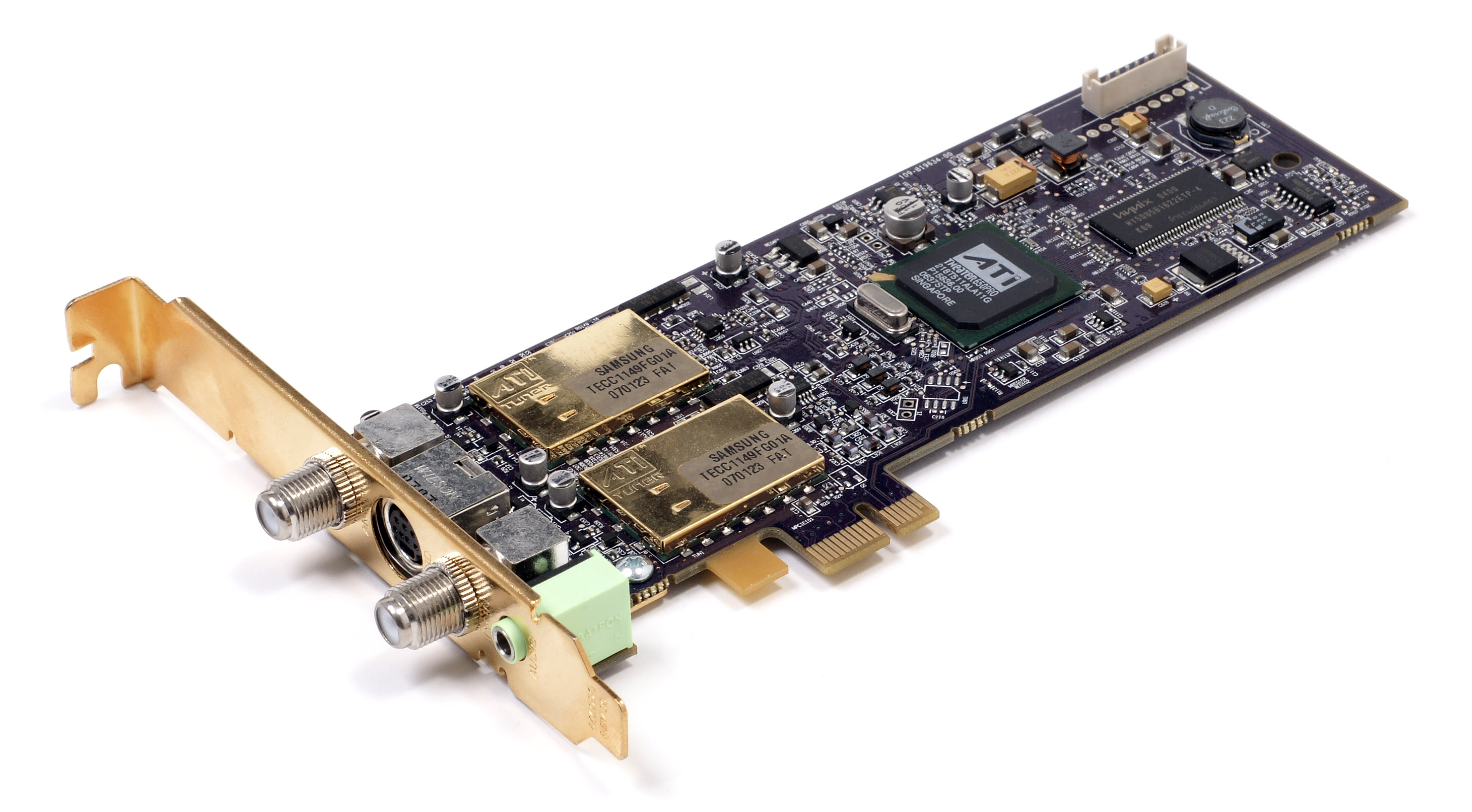
TV Tuner Card
A TV tuner card is a kind of television tuner that allows television signals to be received by a computer. Most TV tuners also function as video capture cards, allowing them to record television programs onto a hard disk much like the digital video recorder (DVR) does. The interfaces for TV tuner cards are most commonly either PCI bus expansion card or the newer PCI Express (PCIe) bus for many modern cards, but PCMCIA, ExpressCard, or USB devices also exist. In addition, some video cards double as TV tuners, notably the ATI All-In-Wonder series. The card contains a tuner and an analog-to-digital converter (collectively known as the analog front end) along with demodulation and interface logic. Some lower-end cards lack an onboard processor and, like a Winmodem, rely on the system's CPU for demodulation. Types There are many types of tuner cards. Analog tuners Analog television cards output a raw video stream, suitable for real-time viewing but ideally requiring some sort ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Television Studio
A television studio, also called a television production studio, is an installation room in which video productions take place, either for the production of live television and its recording onto video tape or other media such as SSDs, or for the acquisition of raw footage for post-production. The design of a studio is similar to, and derived from, movie studios, with a few amendments for the special requirements of television production. A professional television studio generally has several rooms, which are kept separate for noise and practicality reasons. These rooms are connected via 'talkback' or an intercom, and personnel will be divided among these workplaces. Studio floor The studio floor is the actual stage on which the actions that will be recorded and viewed take place. A typical studio floor has the following characteristics and installations: * decoration and/or sets * professional video camera (sometimes one, usually several), typically mounted on pedestals * mic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
News Ticker
A news ticker (sometimes called a "crawler", "crawl", "slide", "zipper", or "ticker tape") is a horizontal or vertical (depending on a language's writing system) text-based display either in the form of a graphic that typically resides in the lower third of the screen space on a television station or network (usually during news programming) or as a long, thin scoreboard-style display seen around the facades of some offices or public buildings dedicated to presenting headlines or minor pieces of news. It is an evolution of the ticker tape, a continuous paper print-out of stock quotes from a printing telegraph which was mainly used in stock exchanges before the advance of technology in the 1960s. News tickers have been used in Europe in countries such as United Kingdom, Germany and Ireland for some years; they are also used in several Asian countries and Australia. In the United States, tickers were long used on a special event basis by broadcast television stations to disseminate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
BBC News (TV Channel)
BBC News (also known as the BBC News Channel) is a British free-to-air public broadcast television news channel for BBC News. It was launched as BBC News 24 on 9 November 1997 at 5:30 pm as part of the BBC's foray into digital domestic television channels, becoming the first competitor to Sky News, which had been running since 1989.About BBC News 24 TV Home For a time, looped news, sport and weather bulletins were available to view via . On 22 February 2006, the channel was named ''News Channel of the Year'' at the Royal Television Society Television Journalism Awards for the first time in its history. The judges remarked that this was the year that t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




.jpg)