|
Tissue Factor Pathway Inhibitor
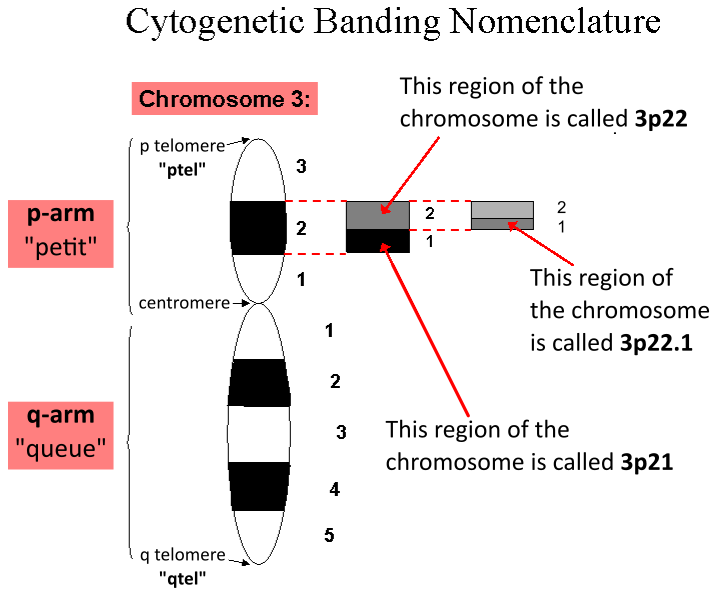
Tissue factor pathway inhibitor (or TFPI) is a single-chain polypeptide which can reversibly inhibit Factor Xa (Xa). While Xa is inhibited, the Xa-TFPI complex can subsequently also inhibit the FVIIa-tissue factor complex. TFPI contributes significantly to the inhibition of Xa in vivo, despite being present at concentrations of only 2.5 nM. Genetics The gene for TFPI is located on chromosome 2q31-q32.1, and has nine exons which span 70 kb. A similar gene, termed ''TFPI2'', has been identified on chromosome 7, at locus 7q21.3; in addition to TFPI activity, its product also has retinal pigment epithelial cell growth-promoting properties. Protein structure TFPI has a relative molecular mass of 34,000 to 40,000 depending on the degree of proteolysis of the C-terminal region. TFPI consists of a highly negatively charged amino-terminus, three tandemly linked Kunitz domains, and a highly positively charged carboxy-terminus. With its Kunitz domains, TFPI exhibits significant h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Factor Xa
Factor X, also known by the eponym Stuart–Prower factor, is an enzyme () of the coagulation cascade. It is a serine endopeptidase (protease group S1, PA clan). Factor X is synthesized in the liver and requires vitamin K for its synthesis. Factor X is activated, by hydrolysis, into factor Xa by both factor IX (with its cofactor, factor VIII in a complex known as ''intrinsic tenase'') and factor VII with its cofactor, tissue factor (a complex known as ''extrinsic tenase''). It is therefore the first member of the ''final common pathway'' or ''thrombin pathway''. It acts by cleaving prothrombin in two places (an arg- thr and then an arg-ile bond), which yields the active thrombin. This process is optimized when factor Xa is complexed with activated co-factor V in the prothrombinase complex. Factor Xa is inactivated by protein Z-dependent protease inhibitor (ZPI), a serine protease inhibitor (serpin). The affinity of this protein for factor Xa is increased 1000-fold by the pres ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Factor VII
Coagulation factor VII (, formerly known as proconvertin) is one of the proteins that causes blood to clot in the coagulation cascade, and in humans is coded for by the gene ''F7''. It is an enzyme of the serine protease class. Once bound to tissue factor released from damaged tissues, it is converted to factor VIIa (or ''blood-coagulation factor VIIa'', ''activated blood coagulation factor VII''), which in turn activates factor IX and factor X. Using genetic recombination a recombinant factor VIIa (eptacog alfa) (trade names include NovoSeven) has been approved by the FDA for the control of bleeding in hemophilia. It is sometimes used unlicensed in severe uncontrollable bleeding, although there have been safety concerns. A biosimilar form of recombinant activated factor VII (AryoSeven) is also available, but does not play any considerable role in the market. In April 2020, the US FDA approved a new rFVIIa product, eptacog beta (SEVENFACT), the first bypassing agent (BPA) appro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tissue Factor
Tissue factor, also called platelet tissue factor, factor III, or CD142, is a protein encoded by the ''F3'' gene, present in subendothelial tissue and leukocytes. Its role in the clotting process is the initiation of thrombin formation from the zymogen prothrombin. Thromboplastin defines the cascade that leads to the activation of factor X—the tissue factor pathway. In doing so, it has replaced the previously named extrinsic pathway in order to eliminate ambiguity. Function The F3 gene encodes coagulation factor III, which is a cell surface glycoprotein. This factor enables cells to initiate the blood coagulation cascades, and it functions as the high-affinity receptor for the coagulation factor VII. The resulting complex provides a catalytic event that is responsible for initiation of the coagulation protease cascades by specific limited proteolysis. Unlike the other cofactors of these protease cascades, which circulate as nonfunctional precursors, this factor is a potent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
TFPI2
Tissue factor pathway inhibitor 2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''TFPI2'' gene In biology, the word gene (from , ; "...Wilhelm Johannsen coined the word gene to describe the Mendelian units of heredity..." meaning ''generation'' or ''birth'' or ''gender'') can have several different meanings. The Mendelian gene is a ba .... References Further reading * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * {{PDB Gallery, geneid=7980 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chromosome 7
Chromosome 7 is one of the 23 pairs of chromosomes in humans, who normally have two copies of this chromosome. Chromosome 7 spans about 159 million base pairs (the building material of DNA) and represents between 5 and 5.5 percent of the total DNA in cells. Genes Number of genes The following are some of the gene count estimates of human chromosome 7. Because researchers use different approaches to genome annotation their predictions of the number of genes on each chromosome varies (for technical details, see gene prediction). Among various projects, the collaborative consensus coding sequence project ( CCDS) takes an extremely conservative strategy. So CCDS's gene number prediction represents a lower bound on the total number of human protein-coding genes. Gene list The following is a partial list of genes on human chromosome 7. For complete list, see the link in the infobox on the right. Diseases and disorders The following diseases are some of those related to genes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Locus (genetics)
In genetics, a locus (plural loci) is a specific, fixed position on a chromosome where a particular gene or genetic marker is located. Each chromosome carries many genes, with each gene occupying a different position or locus; in humans, the total number of protein-coding genes in a complete haploid set of 23 chromosomes is estimated at 19,000–20,000. Genes may possess multiple variants known as alleles, and an allele may also be said to reside at a particular locus. Diploid and polyploid cells whose chromosomes have the same allele at a given locus are called homozygous with respect to that locus, while those that have different alleles at a given locus are called heterozygous. The ordered list of loci known for a particular genome is called a gene map. Gene mapping is the process of determining the specific locus or loci responsible for producing a particular phenotype or biological trait. Association mapping, also known as "linkage disequilibrium mapping", is a method of ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Retinal Pigment Epithelial
The pigmented layer of retina or retinal pigment epithelium (RPE) is the pigmented cell layer just outside the neurosensory retina that nourishes retinal visual cells, and is firmly attached to the underlying choroid and overlying retinal visual cells. History The RPE was known in the 18th and 19th centuries as the pigmentum nigrum, referring to the observation that the RPE is dark (black in many animals, brown in humans); and as the tapetum nigrum, referring to the observation that in animals with a tapetum lucidum, in the region of the tapetum lucidum the RPE is not pigmented. Anatomy The RPE is composed of a single layer of hexagonal cells that are densely packed with pigment granules. When viewed from the outer surface, these cells are smooth and hexagonal in shape. When seen in section, each cell consists of an outer non-pigmented part containing a large oval nucleus and an inner pigmented portion which extends as a series of straight thread-like processes between the rods, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kunitz Domain
Kunitz domains are the active domains of proteins that inhibit the function of protein degrading enzymes or, more specifically, domains of Kunitz-type are protease inhibitors. They are relatively small with a length of about 50 to 60 amino acids and a molecular weight of 6 kDa. Examples of Kunitz-type protease inhibitors are aprotinin (bovine pancreatic trypsin inhibitor, BPTI), Alzheimer's amyloid precursor protein (APP), and tissue factor pathway inhibitor (TFPI). Kunitz STI protease inhibitor, the trypsin inhibitor initially studied by Moses Kunitz, was extracted from soybeans. Standalone Kunitz domains are used as a framework for the development of new pharmaceutical drugs. Structure The structure is a disulfide rich alpha+beta fold. Bovine pancreatic trypsin inhibitor is an extensively studied model structure. Certain family members are similar to the tick anticoagulant peptide (TAP, ). This is a highly selective inhibitor of factor Xa in the blood coagulation pathways. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inter-alpha-trypsin Inhibitor
Inter-alpha-trypsin inhibitors (IαI) are plasma proteins consisting of three of four heavy chains selected from the group ITIH1, ITIH2, ITIH3, ITIH4 and one light chain selected from the group Alpha-1-microglobulin/bikunin precursor, AMBP or SPINT2. They function as protease inhibitors. IαI form complexes with hyaluronan (HA), generating a serum-derived hyaluronan-associated protein (SHAP)-HA complex. The SHAP-HA complex is found in very high concentration in rheumatoid arthritic synovial fluid suggesting it has a role in the inflammatory response. References External links * Protease inhibitors Human proteins Arthritis {{protein-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Basic Pancreatic Trypsin Inhibitor
The drug aprotinin (Trasylol, previously Bayer and now Nordic Group pharmaceuticals), is a small protein bovine pancreatic trypsin inhibitor (BPTI), or basic trypsin inhibitor of bovine pancreas, which is an antifibrinolytic molecule that inhibits trypsin and related proteolytic enzymes. Under the trade name Trasylol, aprotinin was used as a medication administered by injection to reduce bleeding during complex surgery, such as heart and liver surgery. Its main effect is the slowing down of fibrinolysis, the process that leads to the breakdown of blood clots. The aim in its use was to decrease the need for blood transfusions during surgery, as well as end-organ damage due to hypotension (low blood pressure) as a result of marked blood loss. The drug was temporarily withdrawn worldwide in 2007 after studies suggested that its use increased the risk of complications or death; this was confirmed by follow-up studies. Trasylol sales were suspended in May 2008, except for very restricted ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Factor X
Factor X, also known by the eponym Stuart–Prower factor, is an enzyme () of the coagulation cascade. It is a serine endopeptidase (protease group S1, PA clan). Factor X is synthesized in the liver and requires vitamin K for its synthesis. Factor X is activated, by hydrolysis, into factor Xa by both factor IX (with its cofactor, factor VIII in a complex known as ''intrinsic tenase'') and factor VII with its cofactor, tissue factor (a complex known as ''extrinsic tenase''). It is therefore the first member of the ''final common pathway'' or ''thrombin pathway''. It acts by cleaving prothrombin in two places (an arg- thr and then an arg-ile bond), which yields the active thrombin. This process is optimized when factor Xa is complexed with activated co-factor V in the prothrombinase complex. Factor Xa is inactivated by protein Z-dependent protease inhibitor (ZPI), a serine protease inhibitor (serpin). The affinity of this protein for factor Xa is increased 1000-fold by the pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |