|
Tinnsjå
Tinnsjå ( eng, Lake Tinn), also called ''Tinnsjø'' and ''Tinnsjøen'', is one of the largest lakes in Norway, and one of the deepest in Europe. It is located between the municipalities of Tinn and Notodden in Vestfold og Telemark county. At its source in the west, the Måna river flows out of Møsvatn and past Rjukan into Tinnsjå. From the north, the river Mår flows from the Mår, Gøystavatn, and Kalhovdfjorden lakes into Tinnsjå. Tinnsjå is part of the Skiensvassdrag, and drains via the Tinnelva river in the south, down to Heddalsvatn. In 1944, during the German occupation of Norway, the ferry SF ''Hydro'' was sunk in Tinnsjå by the Norwegian resistance. The Germans were using the ferry to transport a large quantity of heavy water to Germany, where it was to be used for nuclear weapon research. The heavy water had been produced at Vemork, a factory located in Rjukan. The wreck of the ferry was discovered in 1993. In 2004, it was investigated and filmed for an e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vestfold Og Telemark
Vestfold og Telemark (; ) is a county under disestablishment in Norway. The county is the southernmost one of Eastern Norway and consists of two distinct and separate traditional regions: the former counties of Telemark and (most of) Vestfold. The capital is located at the town of Skien, which is also the county's largest city. While Skien is the seat of the county municipality, the seat of the County Governor is Tønsberg. It borders the counties of Viken, Vestland, Rogaland and Agder. Telemark voted against the merger, on the basis that the regions have nothing in common and do not constitute a natural geographical, cultural, social or political entity. Regardless, the Storting voted on 7 January 2018 to merge the counties by force, and the merger took effect on 1 January 2020. Unlike Telemark or Vestfold, it does not form a traditional or cultural region, but is instead administrative. On 15 February 2022, the county council decided to vote for the future of Vestfold og Telem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heddalsvatn
Heddalsvatnet ( en, Lake Heddal) is a lake in the municipalities Notodden and Sauherad in Vestfold og Telemark, Norway. The main influx comes from the rivers Tinnelva and Heddøla. The lake covers an area of 11.9 km2 or 13.2 km2 according to NVE. The catchment basin covers a total area of 5380,5 km2. The southern part of the lake is called Bråfjorden and is separated from the northern part by Nautsundet strait crossed county road 360 bridge. The railway line to Notodden (the Bratsberg Line) runs along the eastern shore. The lake is part of the Skien watershed and is connected to the ocean by the Telemark Canal. Heddalsvatnet is only 16 meters above sea level and only two locks at Skien were needed to allow ships to sail on the lake. The canal opened in 1861 and made Notodden into Norway's largest fresh water port. In the late 1800s seafaring vessels were constructed at the shores of Heddalsvatnet. History After the ice age the ocean was about 150 meter higher in this are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Swim Bladder
The swim bladder, gas bladder, fish maw, or air bladder is an internal gas-filled Organ (anatomy), organ that contributes to the ability of many bony fish (but not cartilaginous fish) to control their buoyancy, and thus to stay at their current water depth without having to expend energy in swimming. Also, the Dorsum (biology), dorsal position of the swim bladder means the center of mass is below the centroid, center of volume, allowing it to act as a stabilizing agent. Additionally, the swim bladder functions as a resonator, resonating chamber, to produce or receive sound. The swim bladder is evolutionarily Homology (biology), homologous to the lungs. Charles Darwin remarked upon this in ''On the Origin of Species''.Darwin, Charles (1859''Origin of Species''Page 190, reprinted 1872 by D. Appleton. Darwin reasoned that the lung in air-breathing vertebrates had derived from a more primitive swim bladder. In the embryonic stages, some species, such as Ophioblennius atlanticus, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arctic Char
The Arctic char or Arctic charr (''Salvelinus alpinus'') is a cold-water fish in the family Salmonidae, native to alpine lakes and arctic and subarctic coastal waters. Its distribution is Circumpolar North. It spawns in freshwater and populations can be lacustrine, riverine, or anadromous, where they return from the ocean to their fresh water birth rivers to spawn. No other freshwater fish is found as far north; it is, for instance, the only fish species in Lake Hazen which extend up to on Ellesmere Island in the Canadian Arctic. It is one of the rarest fish species in Great Britain and Ireland, found mainly in deep, cold, glacial lakes, and is at risk there from acidification. In other parts of its range, such as the Nordic countries, it is much more common, and is fished extensively. In Siberia, it is known as ''golets'' () and it has been introduced in lakes where it sometimes threatens less hardy endemic species, such as the small-mouth char and the long-finned char ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Isotope Separation
Isotope separation is the process of concentrating specific isotopes of a chemical element by removing other isotopes. The use of the nuclides produced is varied. The largest variety is used in research (e.g. in chemistry where atoms of "marker" nuclide are used to figure out reaction mechanisms). By tonnage, separating natural uranium into enriched uranium and depleted uranium is the largest application. In the following text, mainly the uranium enrichment is considered. This process is crucial in the manufacture of uranium fuel for nuclear power plants, and is also required for the creation of uranium-based nuclear weapons. Plutonium-based weapons use plutonium produced in a nuclear reactor, which must be operated in such a way as to produce plutonium already of suitable isotopic mix or ''grade''. While different chemical elements can be purified through chemical reaction, chemical processes, isotopes of the same element have nearly identical chemical properties, which makes this ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
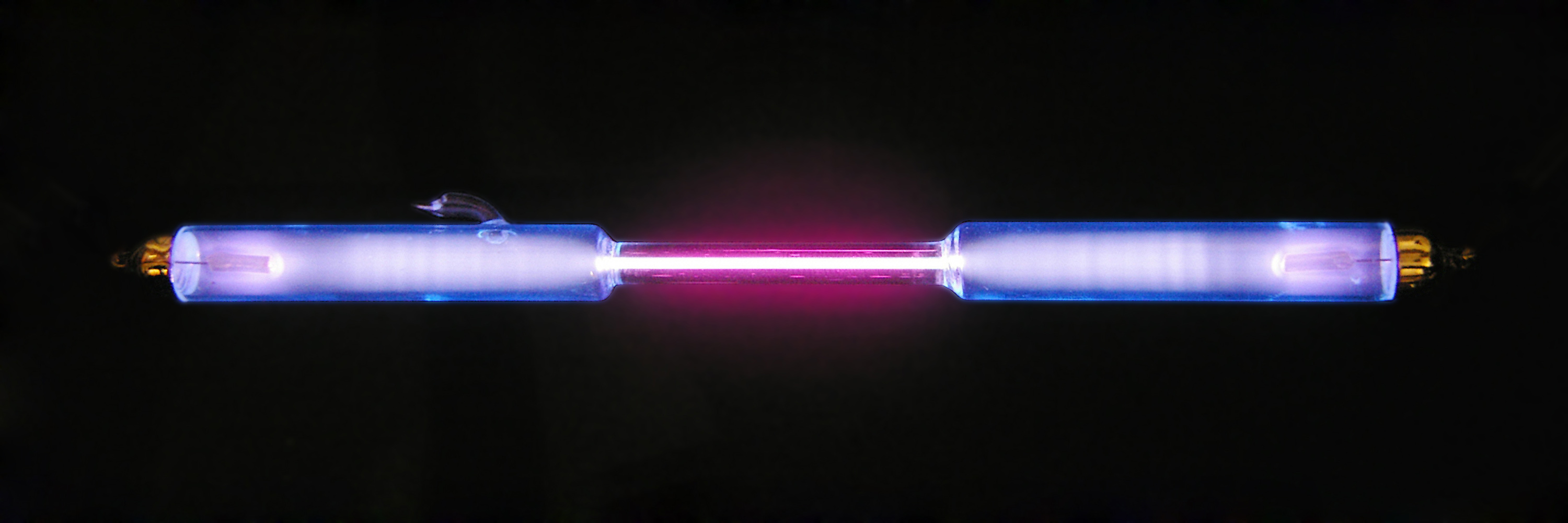
Deuterium
Deuterium (or hydrogen-2, symbol or deuterium, also known as heavy hydrogen) is one of two Stable isotope ratio, stable isotopes of hydrogen (the other being Hydrogen atom, protium, or hydrogen-1). The atomic nucleus, nucleus of a deuterium atom, called a deuteron, contains one proton and one neutron, whereas the far more common protium has no neutrons in the nucleus. Deuterium has a natural abundance in Earth's oceans of about one atom of deuterium among all atoms of hydrogen (see heavy water). Thus deuterium accounts for approximately 0.0156% by number (0.0312% by mass) of all the naturally occurring hydrogen in the oceans, while protium accounts for more than 99.98%. The abundance of deuterium changes slightly from one kind of natural water to another (see Vienna Standard Mean Ocean Water). (Tritium is yet another hydrogen isotope, with two neutrons, that is far more rare and is radioactive.) The name ''deuterium'' is derived from the Greek , meaning "second", to denot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nova (American TV Program)
''Nova'' (stylized as ''NOVΛ'') is an American popular science television program produced by WGBH in Boston, Massachusetts, since 1974. It is broadcast on PBS in the United States, and in more than 100 other countries. The program has won many major television awards. ''Nova'' often includes interviews with scientists doing research in the subject areas covered and occasionally includes footage of a particular discovery. Some episodes have focused on the history of science. Examples of topics covered include the following: Colditz Castle, the Drake equation, elementary particles, the 1980 eruption of Mount St. Helens, Fermat's Last Theorem, the AIDS epidemic, global warming, moissanite, Project Jennifer, storm chasing, Unterseeboot 869, Vinland, Tarim mummies, and the COVID-19 pandemic. The ''Nova'' programs have been praised for their pacing, writing, and editing. Websites that accompany the segments have also won awards. Episodes History ''Nova'' was first aired o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vemork
Vemork is a hydroelectric power plant outside Rjukan in Tinn, Norway. The plant was built by Norsk Hydro and opened in 1911, its main purpose being to fix nitrogen for the production of fertilizer. At opening, it was the world's largest power plant with a capacity of 108 MW. Vemork was later the site of the first plant in the world to mass-produce heavy water developing from the hydrogen production then used for the Haber process. During World War II, Vemork was the target of Norwegian heavy water sabotage operations. The heavy water plant was closed in 1971, and in 1988 the power station became the Norwegian Industrial Workers Museum. A new power plant was opened in 1971 and is located inside the mountain behind the old power plant. History In 1906, the then newly founded Norsk hydro-elektrisk Kvælstofaktieselskab started construction of what was to be the world's largest hydroelectric power plant. The 108-MW Vemork power station at the Rjukan waterfall was the world's lar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Norwegian Heavy Water Sabotage
The Norwegian heavy water sabotage ( nb, Tungtvannsaksjonen; nn, Tungtvassaksjonen) was a series of Allied-led efforts to halt German heavy water production via hydroelectric plants in Nazi Germany-occupied Norway during World War II, involving both Norwegian commandos and Allied bombing raids. During the war, the Allies sought to inhibit the German development of nuclear weapons with the removal of heavy water and the destruction of heavy-water production plants. The Norwegian heavy water sabotage was aimed at the 60 MW Vemork power station at the Rjukan waterfall in Telemark. The hydroelectric power plant at Vemork was built in 1934. It was the world's first site to mass-produce heavy water (as a byproduct of nitrogen fixing), with a capacity of 12 tonnes per year. Before the German invasion of Norway on 9 April 1940, the French Deuxième Bureau removed of heavy water from the Vemork plant in then-neutral Norway. The plant's managing director agreed to lend Fran ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SF Hydro
SF ''Hydro'' was a Norwegian steam powered railway ferry that operated in the first half of the 20th century on Lake Tinn in Telemark. It connected with the Rjukan Line and Tinnoset Line, at Mæl and Tinnoset, operating between 1914 and 1944. The combined track and ferry service was primarily used to transport raw materials and fertilizer from Norsk Hydro's factory at Rjukan to the port in Skien. It was the target of a Norwegian operation on 20 February 1944, when resistance fighters sank the ferry in the deepest part of Lake Tinn to prevent Nazi Germany from receiving heavy water. Usage The railway ferries operated a route connecting the Tinnoset Line and Rjukan Line. Transport included both railway cars, carrying primarily fertilizer, potassium nitrate and ammonia from Norsk Hydro, as well as passengers. ''Hydro'' was the second ship delivered for the service. The first ship, SF ''Rjukanfos'', was delivered in 1909 but proved too small for the service. ''Hydro'' was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



_(cropped).jpg)