|
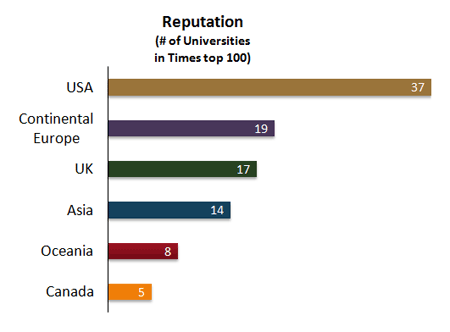
Times Higher Education World Reputation Rankings
The ''Times Higher Education World University Rankings'' (often referred to as the THE Rankings) is an annual publication of university rankings by the ''Times Higher Education'' (THE) magazine. The publisher had collaborated with Quacquarelli Symonds (QS) to publish the joint ''THE-QS World University Rankings'' from 2004 to 2009 before it turned to Thomson Reuters for a new ranking system from 2010 to 2013. In 2014, the magazine then signed a deal with Elsevier to provide it with the data used to compile the rankings. The publication now comprises global, subject, and reputation rankings, alongside three regional league tables for Asia, Latin America, and BRICS & emerging economies, which are generated using different weightings. The THE Rankings is often considered one of the most widely observed university rankings together with the ''Academic Ranking of World Universities'', the ''QS World University Rankings'', and others. It is praised for having a new, improved rankin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Higher Education
Higher education is tertiary education leading to award of an academic degree. Higher education, also called post-secondary education, third-level or tertiary education, is an optional final stage of formal learning that occurs after completion of secondary education. It represents levels 6, 7 and 8 of the 2011 version of the International Standard Classification of Education structure. Tertiary education at a non-degree level is sometimes referred to as further education or continuing education as distinct from higher education. The right of access to higher education The right of access to higher education is mentioned in a number of international human rights instruments. The UN International Covenant on Economic, Social and Cultural Rights of 1966 declares, in Article 13, that "higher education shall be made equally accessible to all, on the basis of capacity, by every appropriate means, and in particular by the progressive introduction of free education". In Eu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Globe And Mail
''The Globe and Mail'' is a Canadian newspaper printed in five cities in western and central Canada. With a weekly readership of approximately 2 million in 2015, it is Canada's most widely read newspaper on weekdays and Saturdays, although it falls slightly behind the ''Toronto Star'' in overall weekly circulation because the ''Star'' publishes a Sunday edition, whereas the ''Globe'' does not. ''The Globe and Mail'' is regarded by some as Canada's "newspaper of record". ''The Globe and Mail''s predecessors, '' The Globe'' and ''The Mail and Empire'' were both established in the 19th century. The former was established in 1844, while the latter was established in 1895 through a merger of '' The Toronto Mail'' and the ''Toronto Empire''. In 1936, ''The Globe'' and ''The Mail and Empire'' merged to form ''The Globe and Mail''. The newspaper was acquired by FP Publications in 1965, who later sold the paper to the Thomson Corporation in 1980. In 2001, the paper merged with broadc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
David Willetts
David Linsay Willetts, Baron Willetts, (born 9 March 1956) is a British politician and life peer. From 1992 to 2015, he was the Member of Parliament (MP) representing the constituency of Havant in Hampshire. He served as Minister of State for Universities and Science from 2010 until July 2014 and became a member of the House of Lords in 2015. He was appointed chair of the UK Space Agency's board in April 2022. He is also President of the Resolution Foundation – a living standards-focused think-tank. Education Willetts was educated at King Edward's School, Birmingham, and Christ Church, Oxford, where he studied Philosophy, politics and economics. Willetts graduated with a first-class degree. Policy researcher Having served as Nigel Lawson's private researcher, Willetts took charge of the Treasury monetary policy division at 26 before moving over to Margaret Thatcher's Policy Unit at 28. Aged 31, he subsequently took over the Centre for Policy Studies. Paul Foot wrote in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Universities UK
Universities UK (UUK) is an advocacy organisation for universities in the United Kingdom. It began life in the early 20th century through informal meetings of vice-chancellors of a number of universities and principals of university colleges and was previously known as the ''Committee of Vice-Chancellors and Principals of the Universities of the United Kingdom'' (CVCP). As of July 2022, UUK is led by President Steve West – Vice-Chancellor of the University of the West of England (UWE Bristol) – and Chief Executive Vivienne Stern. UUK is registered charity with an annual income of £13.7 million, which is largely raised from its member institutions. History In 1918 the first consultative meeting of all vice-chancellors was held. At that time, the committee consisted of just twenty-two universities and university colleges. In 1930, under the chairmanship of Sir Charles Grant Robertson, vice-chancellors secured a mandate from their respective universities that "it is desirabl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Steve Smith (academic)
Sir Steven Murray Smith, FAcSS, FRSA (born 4 February 1952) is an English international relations theorist and long serving university leader. He is the former Vice Chancellor of the University of Exeter and Professor of International Studies. Early life Smith was born on 4 February 1952 in Norwich, England. He attended the City of Norwich School, then a grammar school, on Eaton Road, Norwich. His parents were from working class backgrounds. At a parents' evening, his form master told his parents about their son that "people like you don't go to university". The school afterwards suggested finding a low-skilled job for him. Smith gained a Bachelor of Science (BSc) in Politics and International Studies in 1973, a Master of Science (MSc) degree in international studies in 1974 and a Doctor of Philosophy degree (PhD) in international relations in 1978, all from the University of Southampton. Academic career From 1976 to 1978, Smith lectured at Huddersfield Polytechnic. From 19 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Melbourne Institute
The Melbourne Institute of Applied Economic and Social Research (often simply referred to as "The Melbourne Institute") is an Australian economic research institute based in Melbourne, Victoria. The institute is a department of the Faculty of Business and Economics at the University of Melbourne. History The Melbourne Institute was formed in 1962 as the Institute of Applied Economic Research under the leadership of Professor Ronald Henderson. It was the first economic research institute in an Australian university. Henderson built up an organisation with about 40 staff by the early 1970s. It engaged in a wide range of research areas including macroeconomic forecasting, financial economics and social economics, and is best remembered for its work on poverty and the development of the Henderson Poverty Line. The name of the institute was later changed to Institute of Applied Economic and Social Research (IAESR). After the Henderson era, Duncan Ironmonger acted as director for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scopus
Scopus is Elsevier's abstract and citation database launched in 2004. Scopus covers nearly 36,377 titles (22,794 active titles and 13,583 inactive titles) from approximately 11,678 publishers, of which 34,346 are peer-reviewed journals in top-level subject fields: life sciences, social sciences, physical sciences and health sciences. It covers three types of sources: book series, journals, and trade journals. All journals covered in the Scopus database are reviewed for sufficiently high quality each year according to four types of numerical quality measure for each title; those are ''h''-Index, CiteScore, SJR ( SCImago Journal Rank) and SNIP (Source Normalized Impact per Paper). Searches in Scopus also incorporate searches of patent databases. Overview Comparing ease of use and coverage of Scopus and the Web of Science (WOS), a 2006 study concluded that "Scopus is easy to navigate, even for the novice user. ... The ability to search both forward and backward from a particu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Social Science
Social science is one of the branches of science, devoted to the study of societies and the relationships among individuals within those societies. The term was formerly used to refer to the field of sociology, the original "science of society", established in the 19th century. In addition to sociology, it now encompasses a wide array of academic disciplines, including anthropology, archaeology, economics, human geography, linguistics, management science, communication science and political science. Positivist social scientists use methods resembling those of the natural sciences as tools for understanding society, and so define science in its stricter modern sense. Interpretivist social scientists, by contrast, may use social critique or symbolic interpretation rather than constructing empirically falsifiable theories, and thus treat science in its broader sense. In modern academic practice, researchers are often eclectic, using multiple methodologies (for instan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Life Science
Life is a quality that distinguishes matter that has biological processes, such as signaling and self-sustaining processes, from that which does not, and is defined by the capacity for growth, reaction to stimuli, metabolism, energy transformation, and reproduction. Various forms of life exist, such as plants, animals, fungi, protists, archaea, and bacteria. Biology is the science that studies life. The gene is the unit of heredity, whereas the cell is the structural and functional unit of life. There are two kinds of cells, prokaryotic and eukaryotic, both of which consist of cytoplasm enclosed within a membrane and contain many biomolecules such as proteins and nucleic acids. Cells reproduce through a process of cell division, in which the parent cell divides into two or more daughter cells and passes its genes onto a new generation, sometimes producing genetic variation. Organisms, or the individual entities of life, are generally thought to be open s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Citation Index
A citation index is a kind of bibliographic index, an index of citations between publications, allowing the user to easily establish which later documents cite which earlier documents. A form of citation index is first found in 12th-century Hebrew religious literature. Legal citation indexes are found in the 18th century and were made popular by citators such as Shepard's Citations (1873). In 1961, Eugene Garfield's Institute for Scientific Information (ISI) introduced the first citation index for papers published in academic journals, first the '' Science Citation Index'' (SCI), and later the ''Social Sciences Citation Index'' (SSCI) and the '' Arts and Humanities Citation Index'' (AHCI). American Chemical Society converted its printed Chemical Abstract Service (established in 1907) into internet-accessible SciFinder in 2008. The first automated citation indexing was done by CiteSeer in 1997 and was patented. Other sources for such data include Google Scholar, Microsoft A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Academic Journal
An academic journal or scholarly journal is a periodical publication in which scholarship relating to a particular academic discipline is published. Academic journals serve as permanent and transparent forums for the presentation, scrutiny, and discussion of research. They nearly-universally require peer-review or other scrutiny from contemporaries competent and established in their respective fields. Content typically takes the form of articles presenting original research, review articles, or book reviews. The purpose of an academic journal, according to Henry Oldenburg (the first editor of '' Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society''), is to give researchers a venue to "impart their knowledge to one another, and contribute what they can to the Grand design of improving natural knowledge, and perfecting all Philosophical Arts, and Sciences." The term ''academic journal'' applies to scholarly publications in all fields; this article discusses the aspects common to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |