|
Timeline Of The Assyrian Empire
The timeline of ancient Assyria can be broken down into three main eras: the Old Assyrian period, Middle Assyrian Empire, and Neo-Assyrian Empire. Modern scholars typically also recognize an Early period preceding the Old Assyrian period and a post-imperial period succeeding the Neo-Assyrian period. Old Assyrian period, 2025–1364 BC Puzur-Ashur I (c. 2025 BC) is thought to have been the first independent ruler of Assur following the city's independence from the collapsing Third Dynasty of Ur, founding a royal dynasty which was to survive for eight generations (or 216 years) until Erishum II was overthrown by Shamshi-Adad I. Puzur-Ashur I's descendants left inscriptions mentioning him regarding the building of temples to gods such as Ashur, Adad and Ishtar in Assyria. The length of Puzur-Ashur I's reign is unknown. Hildegard Levy, writing in the Cambridge Ancient History, sees Puzur-Ashur I as part of a longer dynasty started by Sulili, suspected by other scholars to perhaps ha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Map Of Assyria
A map is a symbolic depiction emphasizing relationships between elements of some space, such as objects, regions, or themes. Many maps are static, fixed to paper or some other durable medium, while others are dynamic or interactive. Although most commonly used to depict geography, maps may represent any space, real or fictional, without regard to context or scale, such as in brain mapping, DNA mapping, or computer network topology mapping. The space being mapped may be two dimensional, such as the surface of the earth, three dimensional, such as the interior of the earth, or even more abstract spaces of any dimension, such as arise in modeling phenomena having many independent variables. Although the earliest maps known are of the heavens, geographic maps of territory have a very long tradition and exist from ancient times. The word "map" comes from the , wherein ''mappa'' meant 'napkin' or 'cloth' and ''mundi'' 'the world'. Thus, "map" became a shortened term referring to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Babylone 1
''Bābili(m)'' * sux, 𒆍𒀭𒊏𒆠 * arc, 𐡁𐡁𐡋 ''Bāḇel'' * syc, ܒܒܠ ''Bāḇel'' * grc-gre, Βαβυλών ''Babylṓn'' * he, בָּבֶל ''Bāvel'' * peo, 𐎲𐎠𐎲𐎡𐎽𐎢 ''Bābiru'' * elx, 𒀸𒁀𒉿𒇷 ''Babili'' *Kassite: ''Karanduniash'', ''Karduniash'' , image = Street in Babylon.jpg , image_size=250px , alt = A partial view of the ruins of Babylon , caption = A partial view of the ruins of Babylon , map_type = Near East#West Asia#Iraq , relief = yes , map_alt = Babylon lies in the center of Iraq , coordinates = , location = Hillah, Babil Governorate, Iraq , region = Mesopotamia , type = Settlement , part_of = Babylonia , length = , width = , area = , height = , builder = , material = , built = , abandoned = , epochs = , cultures = Sumerian, Akkadian, Amorite, Kassite, Assyrian, Chaldean, Achaemenid, Hellenistic, Parthian, Sasanian, Muslim , dependency_of = , occupants = , event = , excavations = , archaeologists = Hormuzd Rassam, Rober ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shekhna
Tell Leilan is an archaeological site situated near the Wadi Jarrah in the Khabur River basin in Al-Hasakah Governorate, northeastern Syria. The site has been occupied since the 5th millennium BC. During the late third millennium, the site was known as Shekhna. During that time it was under control of the Akkadian Empire and was used as an administrative center. Around 1800 BC, the site was renamed "Shubat-Enlil" by the king Shamshi-Adad I, and it became his residential capital. Shubat-Enlil was abandoned around 1700 BC. Geography The site is located close to some other flourishing cities of the time. Hamoukar is about 50 km away to the southeast. Tell Brak is about 50 km away to the southwest, and also in the Khabur River basin. Tell Mozan (Urkesh) is about 50 km to the west. Leilan, Brak and Urkesh were particularly prominent during the Akkadian period. History The city originated around 5000 BC as a small farming village and grew to be a large city BC, three ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Erishum II
ErishumI or Erišum II, the son and successor of Naram-Sin, was the king of the city-state Assur from 1828/1818 BC to 1809 BC. Like his predecessors, he bore the titles “Išši’ak Aššur” (Steward of Assur) and “ensí”. The length of Erishum II's reign is uncertain, however; based on various excavated "limmu" (eponym) lists, Naram-Sin's and Erishum II's reigns had a combined length of 64 years. The Amorites had in the centuries prior overrun the kingdoms of Lower Mesopotamia and the Levant between, but had hitherto been repelled by the Assyrian kings. However, Erishum II was to be the last king of the dynasty of Puzur-Ashur I (founded c. 2025 BC) as he was deposed and the throne of Assyria was usurped by Shamshi-Adad I during the expansion of the Amorite tribes from the Khabur River delta in the north-eastern Levant. Although regarded as an Amorite by later Assyrian tradition, Shamshi-Adad I's descent is suggested to be from the same line as the legendary native Assyria ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ekallatum
Ekallatum (Akkadian: 𒌷𒂍𒃲𒈨𒌍, URUE2.GAL.MEŠ, Ekallātum, "the Palaces") was an ancient Amorite city-state and kingdom in upper Mesopotamia. The exact location of it has not yet been identified, but it is thought to be located somewhere along the left bank of the Tigris, south of Assur. A tablet fragment was found at Tel Hazor which listed an expected trade path from Hazor to Mari and then on to Ekallatum. Ekallatum, whose name means "the palaces," became the capital of an Amorite dynasty related to Babylon, which was important in the 19th and 18th centuries BCE period. The history of upper Mesopotamia in this period is documented in the archives of Mari, Syria. History Its first known king was Ila-kabkabu, who seems to have entered into a conflict with Iagitlim of Mari. His son Shamshi-Adad I ascended to the throne around 1810 BCE, continuing the conflict and attempting to extend into the valley along the Khabur River. His expansion was halted by Iagitlim's son, Iakh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Naram-Sin Of Assyria
Naram-Sin, or Narām-Sîn or –Suen, inscribed in cuneiform on contemporary seal impressions as d''na-ra-am-''dEN.ZU, had been the "waklum" (ugula, Overseer) or "'' Išši’ak Aššur''" (énsi d''a-šùr'', Steward of Ashur) of the city-state Assur, listed as the 37th king of Assyria on the later Assyrian King Lists, where he is inscribed m''na-ram-''dEN.ZU,''SDAS List'', IM 60484, i 34.''Nassouhi List'', Istanbul A. 116 (Assur 8836), i 33.''Khorsabad List'', IM 60017 (excavation nos.: DS 828, DS 32-54), i 34. or a fragmentary list where he appears as -d30.''Assyrian Kinglist fragment'' VAT 9812 = KAV 14: ‘3 He was named for the illustrious Naram-Sin of Akkad and took the divine determinative in his name (just like Naram-Sin's grandfather: Sargon I, who may have been named after Sargon of Akkad.) Naram-Sin should not be confused with the Naram-Sin who had ruled Eshnunna for around twelve years (the successor and son, as identified on an inscription, of the long-reigning Ebiq- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Puzur-Ashur II
Puzur-Ashur II (also transcribed as Puzur-Aššur II) was king (Išši’ak Aššur, "Steward of Assur") during the Old Assyrian period 1880 to 1873 BC. Puzur-Ashur II had been both the son and successor of Sargon I. Due to Sargon I's long reign, Puzur-Ashur II came to the throne at a late age since one of his sons, named Ili-bani, was a witness in a contract (and so already a grown man) eleven years before Puzur-Ashur II became ruler. Puzur-Ashur II was succeeded by his son Naram-Sin. The following is a list of the nine annually-elected "limmu : Limmu was an Assyrian eponym. At the beginning of the reign of an Assyrian king, the limmu, an appointed royal official, would preside over the New Year festival at the capital. Each year a new limmu would be chosen. Although picked by lot, th ..." ("eponym") officials from the year of accession of Puzur-Ashur II, the "''waklum''" ("overseer"), in the limmu of Ashur-iddin (son of Shuli) to Puzur-Ashur II's death in the limmu of Inaya ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sargon I
Sargon I (also transcribed as Šarru-kīn I and Sharru-ken I) was the king (Išši’ak Aššur, "Steward of Assur") during the Old Assyrian period from 1920 BC to 1881 BC. On the Assyrian King List, Sargon appears as the son and successor of Ikunum, and the father and predecessor of Puzur-Ashur II. The name “Sargon” means “the king is legitimate” in the Akkadian language. Sargon I might have been named after Sargon of Akkad, perhaps reflecting the extent to which Sargon I identified with the prestigious Dynasty of Akkad. Sargon I is known for his work refortifying Assur. Very little is otherwise known about Sargon I. The following is a list of the 41 annually-elected limmu officials from the year of accession of Sargon I until the year of his death.Klaas R. Veenhof, ''The old Assyrian list of year eponyms from Karum Kanish and its chronological implications'' (Ankara, Turkish Historical Society, 2003) Dates are based on a date of 1833 BC for the solar eclipse A s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ikunum
Ikunum ( akk, , I-ku-nu-um) was a king of Assyria 1934–1921 BC and the son of Ilushuma. He built a temple for the god Ereshkigal, Ninkigal. He strengthened the fortifications of the city of Assur and maintained commercial colonies in Asia Minor. The following is a list of the sixteen annually-elected limmu officials from the year of accession of Ikunum until the year of his death.Cahit Günbattı, ''An Eponym List (KEL G) from Kültepe'' Altoriental. Forsch. 35 (2008) 1, 103-132. *1934 BC Buzi son of Adad-rabi *1933 BC Šuli son of Šalmah *1932 BC Iddin-Suen son of Šalmah *1931 BC Ikunum son of Šudaya *1930 BC Dan-Wer son of Ahu-ahi *1929 BC Šu-Anum from Nerabtim *1928 BC Il-massu son of Aššur-ṭab *1927 BC Šu-Hubur son of Šuli *1926 BC Idua son of Ṣulili *1925 BC Laqip son of Puzur-Laba *1924 BC Šu-Anum the hapirum *1923 BC Uku son of Bila *1922 BC Aššur-malik son of Panaka *1921 BC Dan-Aššur son of Puzur-Wer Notes References * Year of birth unknown ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
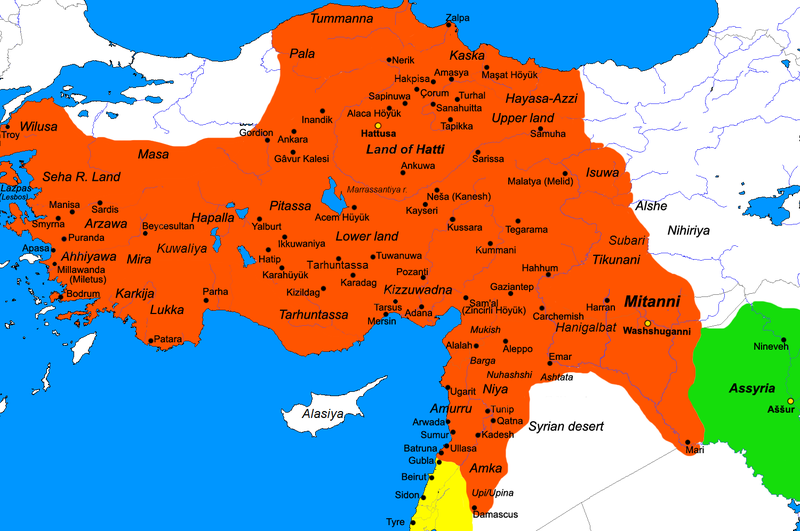
Hattusa
Hattusa (also Ḫattuša or Hattusas ; Hittite: URU''Ḫa-at-tu-ša'', Turkish: Hattuşaş , Hattic: Hattush) was the capital of the Hittite Empire in the late Bronze Age. Its ruins lie near modern Boğazkale, Turkey, within the great loop of the Kızılırmak River (Hittite: ''Marashantiya''; Greek: '' Halys''). Hattusa was added to the UNESCO World Heritage Site list in 1986. Surroundings The landscape surrounding the city included rich agricultural fields and hill lands for pasture as well as woods. Smaller woods are still found outside the city, but in ancient times, they were far more widespread. This meant the inhabitants had an excellent supply of timber when building their houses and other structures. The fields provided the people with a subsistence crop of wheat, barley and lentils. Flax was also harvested, but their primary source for clothing was sheep wool. They also hunted deer in the forest, but this was probably only a luxury reserved for the nobility. Dome ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Erishum I
Erishum I or Erišu(m) I (inscribed m''e-ri-šu'', or mAPIN''-ìš'' in later texts but always with an initial ''i'' in his own seal, inscriptions, and those of his immediate successors, “he has desired,”) 1974–1935 BC (middle chronology),Some historians quote ca. 1939–1900 BC (''after'' Amélie Kuhrt, The Ancient Near East, C. 3000-330 BC, Volume 1, Routledge, 1996, p. 82). son of Ilu-shuma, was the thirty-third ruler of Assyria to appear on the Assyrian King List. He reigned for forty years.Khorsabad kinglist. One of two copies of the Assyrian King ListSDAS Kinglist: m''E-ri-š''.html" ;"title="sup>m''E-ri-š''">sup>m''E-ri-š''''u'' DUMU mDINGIR''-šum-ma'', 'šá li-ma-ni''? ''-šu-ni'' 10+ 30 MU.MEŠ LUGAL''-ta'' DÙ''-uš''. which include him gives his reign length as only 30 years, but this contrasts with a complete list of his limmu, some 40, which are extant from tabletsKEL A (kt 92/k 193), aCDLI. recovered at Karum Kanesh. He had titled himself both as, " Ashu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |