|
Timeline Of Rocket And Missile Technology
This article gives a concise timeline of rocket and missile technology. 11th century-13th century * 11th century AD - The first documented record of what appears to be gunpowder and the fire arrow, an early form of rocketry, appears in the Chinese text ''Wujing Zongyao''. *In Europe, around 1250 both Roger Bacon and the Liber Ignium gave instructions for constructing devices that appear to be rockets. 17th century-19th century * 1633 - Lagâri Hasan Çelebi launched a 7-winged rocket using 50 okka (140 lbs) of gunpowder from Sarayburnu, the point below Topkapı Palace in Istanbul.Winter, Frank H. (1992). "Who First Flew in a Rocket?", Journal of the British Interplanetary Society 45 (July 1992), p. 275-80 * 1650 - ''Artis Magnae Artilleriae pars prima'' ("Great Art of Artillery, the First Part") is printed in Amsterdam, about a year before the death of its author, Kazimierz Siemienowicz. * 1664 - A "space rocket" is imagined as a future technology to be studied in Fra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
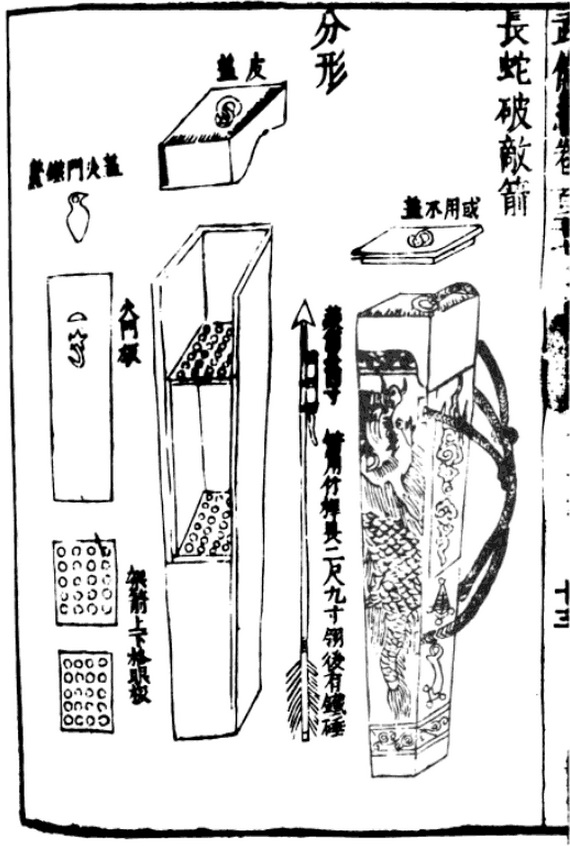
11th Century Long Serpent Fire Arrow Rocket Launcher
11 (eleven) is the natural number following 10 and preceding 12. It is the first repdigit. In English, it is the smallest positive integer whose name has three syllables. Name "Eleven" derives from the Old English ', which is first attested in Bede's late 9th-century ''Ecclesiastical History of the English People''. It has cognates in every Germanic language (for example, German ), whose Proto-Germanic ancestor has been reconstructed as , from the prefix (adjectival " one") and suffix , of uncertain meaning. It is sometimes compared with the Lithuanian ', though ' is used as the suffix for all numbers from 11 to 19 (analogously to "-teen"). The Old English form has closer cognates in Old Frisian, Saxon, and Norse, whose ancestor has been reconstructed as . This was formerly thought to be derived from Proto-Germanic (" ten"); it is now sometimes connected with or ("left; remaining"), with the implicit meaning that "one is left" after counting to ten.''Oxford English Di ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charles Le Brun
Charles Le Brun (baptised 24 February 1619 – 12 February 1690) was a French painter, physiognomist, art theorist, and a director of several art schools of his time. As court painter to Louis XIV, who declared him "the greatest French artist of all time", he was a dominant figure in 17th-century French art and much influenced by Nicolas Poussin. Biography Early life and training Born in Paris, Le Brun attracted the notice of Chancellor Séguier, who placed him at the age of eleven in the studio of Simon Vouet. He was also a pupil of François Perrier. At fifteen he received commissions from Cardinal Richelieu, in the execution of which he displayed an ability which obtained the generous commendations of Nicolas Poussin, in whose company Le Brun started for Rome in 1642. In Rome, he remained four years in the receipt of a pension due to the liberality of the chancellor. There he worked under Poussin, adapting the latter's theories of art. While in Rome, Le Brun studied an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spin-stabilisation
Spin stabilization is the method of stabilizing a satellite or launch vehicle by means of spin, i.e. rotation along the longitudinal axis. The concept originates from ballistics, where the spin is commonly obtain by means of rifling. For most satellite applications this approach has been superseded by three-axis stabilization. Despinning can be achieved by various techniques, including yo-yo de-spin. Use On rockets with a solid motor upper stage, spin stabilization is used to keep the motor from drifting off course as they don't have their own thrusters. Usually small rockets are used to spin up the spacecraft and rocket then fire the rocket and send the craft off. Some rockets, like the Jupiter-C, Delta II, Minotaur V and the satellite Aryabhata are spin-stabilised. The Pioneer 4 spacecraft, the second object sent on a lunar flyby in 1959, maintained its attitude using spin-stabilization. The Schiaparelli EDM lander was spun up to 2.5 RPM before being ejected from the E ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William Hale (British Inventor)
William Hale (21 October 1797 – 30 March 1870), was a British inventor and rocket pioneer. Biography Hale was born in Colchester, England in 1797. He was self-taught although his grandfather, the educator William Cole, is believed to have tutored him. By 1827 he had obtained his first patent; he also won a first class Gold Medal of the Royal Society of Arts in Paris for his paper on ship propulsion using an early form of jet propulsion. Hale was inducted into the International Space Hall of Fame in 2004. Rocketry In 1844, Hale patented a new form of rotary rocket that improved on the earlier Congreve rocket design. Hale removed the guidestick from the design, instead vectoring part of the thrust through canted exhaust holes to provide rotation of the rocket, which improved its stability in flight. These rockets could weigh up to 60 pounds (27 kg) and were noted for their glare and noise on ignition. Hale rockets were first used by the United States Army in t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Henry Trengrouse
Henry Trengrouse (18 March 1772 – 14 February 1854) was a British inventor who invented the "Rocket" lifesaving apparatus. On 24 December 1807 he witnessed the wreck of the frigate '' Anson'' in Mount's Bay, when over a hundred people died, and this disaster led him to devote his life and patrimony to the discovery of some means for saving lives at shipwrecks. He spent much labour in attempting to devise a lifeboat, but produced no satisfactory results, and turned his attention to the "Rocket" lifesaving apparatus, an early form of the Breeches buoy. In addition to this, Trengrouse was dismayed at the then common practice of burying victims of shipwrecks in common graves in unconsecrated ground near the site of the wreck, having seen the dead from the ''Anson'' buried in the dunes at Loe Bar. He persuaded his local MP, Davies Gilbert, to work for a change in the law, and from 1808 the practice was abolished. Early life Trengrouse was born in Helston, Cornwall, was the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rocket Equation
A rocket (from it, rocchetto, , bobbin/spool) is a vehicle that uses jet propulsion to accelerate without using the surrounding air. A rocket engine produces thrust by reaction to exhaust expelled at high speed. Rocket engines work entirely from propellant carried within the vehicle; therefore a rocket can fly in the vacuum of space. Rockets work more efficiently in a vacuum and incur a loss of thrust due to the opposing pressure of the atmosphere. Multistage rockets are capable of attaining escape velocity from Earth and therefore can achieve unlimited maximum altitude. Compared with airbreathing engines, rockets are lightweight and powerful and capable of generating large accelerations. To control their flight, rockets rely on momentum, airfoils, auxiliary reaction engines, gimballed thrust, momentum wheels, deflection of the exhaust stream, propellant flow, spin, or gravity. Rockets for military and recreational uses date back to at least 13th-century China. Signif ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William Moore (British Mathematician)
William Moore ( accessed 22 April 2006 ) was a British and early contributor to rocket theory. He worked at the Royal Military Academy, |
Claude Ruggieri
Claude Ruggieri (1777 – 30 August 1841) was a pyrotechnician in Paris, France, who developed and wrote about innovations in fireworks design. He and others in his family were renowned and patronized by royalty for their creation of great fireworks extravaganzas. They also opened a public pleasure garden where fireworks displays could be enjoyed by the people of Paris. The Ruggieris introduced a style of fireworks that was theatrical rather than being based on military gunnery. Following a disastrous fireworks accident on 30 May 1770, the Ruggieris fell from favor. Claude-Fortuné Ruggieri was primarily responsible for restoring the family to its position of prominence. He used the new science of chemistry to develop novel fireworks, in particular colored fireworks that distinguished the Ruggieris from their rivals. He discovered a way to reliably create a vivid "green fire" observed in Russian fireworks. In his writings, Claude Ruggieri discussed "aerial philosophy", the compos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Congreve Rocket
The Congreve rocket was a type of rocket artillery designed by British inventor Sir William Congreve in 1808. The design was based upon the rockets deployed by the Kingdom of Mysore against the East India Company during the Second, Third, and Fourth Anglo-Mysore Wars. Lieutenant general Thomas Desaguliers, colonel commandant of the Royal Artillery at Woolwich, was impressed by reports of their effectiveness, and undertook several unsuccessful experiments to produce his own rocket weapons. Several captured Mysorean rockets were sent to England following the annexation of the Mysorean kingdom into British India following the death of Tipu Sultan in the siege of Seringapatam. The project was continued chiefly with William Congreve, who set up a research and development programme at the Woolwich Arsenal's laboratory. After development work was complete the rockets were manufactured in quantity further north, near Waltham Abbey, Essex. He was told that "the British at Se ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mysorean Rockets
Mysorean rockets were an Indian military weapon, the iron-cased rockets were successfully deployed for military use. The Mysorean army, under Hyder Ali and his son Tipu Sultan, used the rockets effectively against the British East India Company during the 1780s and 1790s. Their conflicts with the company exposed the British to this technology further, which was then used to advance European rocketry with the development of the Congreve rocket in 1805. Technology and deployment There was a regular rocket corps in the Mysore Army, beginning with about 1,200 men in Hyder Ali's time. During the Second Anglo-Mysore War, Colonel William Baillie's ammunition stores are thought to have been detonated by a stray rocket at the Battle of Pollilur in 1780, which contributed to British defeat in the battle. At Pollilur rockets restricted East India Company vanguard movement, skimming along the surface, lacerating troops, and in one specific instance, shattered an Ensign’s leg. With r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mysore
Mysore (), officially Mysuru (), is a city in the southern part of the state of Karnataka, India. Mysore city is geographically located between 12° 18′ 26″ north latitude and 76° 38′ 59″ east longitude. It is located at an altitude of above mean sea level. Mysore is situated at the foothills of Chamundi Hills about towards the southwest of Bangalore and spread across an area of . Mysore City Corporation is responsible for the civic administration of the city, which is also the headquarters of Mysore district and Mysore division. It served as the Capital city, capital city of the Kingdom of Mysore for nearly six centuries from 1399 until 1956. The Kingdom was ruled by the Wadiyar dynasty, with a brief period of interregnum in the late 18th century when Hyder Ali and Tipu Sultan were in power. The Wadiyars were patrons of art and culture. Tipu Sultan and Hyder Ali also contributed significantly to the cultural and economic growth of the city and the state by plan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tipu Sultan
Tipu Sultan (born Sultan Fateh Ali Sahab Tipu, 1 December 1751 – 4 May 1799), also known as the Tiger of Mysore, was the ruler of the Kingdom of Mysore based in South India. He was a pioneer of rocket artillery.Dalrymple, p. 243 He introduced a number of administrative innovations during his rule, including a new coinage system and calendar, and a new land revenue system, which initiated the growth of the Mysore silk industry. He expanded the iron-cased Mysorean rockets and commissioned the military manual '' Fathul Mujahidin''. He deployed the rockets against advances of British forces and their allies during the Anglo-Mysore Wars, including the Battle of Pollilur and Siege of Srirangapatna. Tipu Sultan and his father used their French-trained army in alliance with the French in their struggle with the British, and in Mysore's struggles with other surrounding powers: against the Marathas, Sira, and rulers of Malabar, Kodagu, Bednore, Carnatic, and Travancore. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |