|
Time-slot Interchange
{{Short description, Network switch storing data in RAM in one sequence A time-slot interchange (TSI) switch is a network switch that stores data in RAM in one sequence, and reads it out in a different sequence. It uses Random-access memory, RAM, a small routing memory and a Counter (digital), counter. Like any switch, it has input and output ports. The RAM stores the Packet (information technology), packets or other data that arrive via its input terminal. Mechanism In a pure time-slot interchange switch, there is only one physical input, and one physical output. Each physical connection is an opportunity for a switching fabric to fail. The limited number of connections of this switch is therefore valuable in a large switching fabric, because it makes this type of switching very reliable. The disadvantage of this type of switch is that it introduces a delay into the signals. When a packet (or byte, on telephone switches) comes to the input, the switch stores the data in RAM ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Network Switch
A network switch (also called switching hub, bridging hub, Ethernet switch, and, by the IEEE, MAC bridge) is networking hardware that connects devices on a computer network by using packet switching to receive and forward data to the destination device. A network switch is a multiport network bridge that uses MAC addresses to forward data at the data link layer (layer 2) of the OSI model. Some switches can also forward data at the network layer (layer 3) by additionally incorporating routing functionality. Such switches are commonly known as layer-3 switches or multilayer switches. Switches for Ethernet are the most common form of network switch. The first MAC Bridge was invented in 1983 by Mark Kempf, an engineer in the Networking Advanced Development group of Digital Equipment Corporation. The first 2 port Bridge product (LANBridge 100) was introduced by that company shortly after. The company subsequently produced multi-port switches for both Ethernet and FDDI such as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Random-access Memory
Random-access memory (RAM; ) is a form of Computer memory, electronic computer memory that can be read and changed in any order, typically used to store working Data (computing), data and machine code. A random-access memory device allows data items to be read (computer), read or written in almost the same amount of time irrespective of the physical location of data inside the memory, in contrast with other direct-access data storage media (such as hard disks and Magnetic tape data storage, magnetic tape), where the time required to read and write data items varies significantly depending on their physical locations on the recording medium, due to mechanical limitations such as media rotation speeds and arm movement. In today's technology, random-access memory takes the form of integrated circuit (IC) chips with MOSFET, MOS (metal–oxide–semiconductor) Memory cell (computing), memory cells. RAM is normally associated with Volatile memory, volatile types of memory where s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Counter (digital)
In digital electronics, a counter is a sequential logic circuit that counts and stores the number of positive or negative transitions of a clock signal. A counter typically consists of flip-flop (electronics), flip-flops, which store a value representing the current count, and in many cases, additional logic to effect particular counting sequences, qualify clocks and perform other functions. Each relevant clock transition causes the value stored in the counter to increment or decrement (increase or decrease by one). A digital counter is a finite state machine, with a ''clock'' input signal and multiple output signals that collectively represent the state. The state indicates the current count, encoded directly as a binary number, binary or binary-coded decimal (BCD) number or using encodings such as one-hot or Gray code. Most counters have a ''reset'' input which is used to initialize the count. Depending on the design, a counter may have additional inputs to control functions suc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Packet (information Technology)
In telecommunications and computer networking, a network packet is a formatted unit of Data (computing), data carried by a packet-switched network. A packet consists of control information and user data; the latter is also known as the ''Payload (computing), payload''. Control information provides data for delivering the payload (e.g., source and destination network addresses, error detection codes, or sequencing information). Typically, control information is found in packet Header (computing), headers and Trailer (computing), trailers. In packet switching, the Bandwidth (computing), bandwidth of the transmission medium is shared between multiple communication sessions, in contrast to circuit switching, in which circuits are preallocated for the duration of one session and data is typically transmitted as a continuous bit stream. Terminology In the seven-layer OSI model of computer networking, ''packet'' strictly refers to a protocol data unit at layer 3, the network layer. A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Telephone Switch
A telephone exchange, telephone switch, or central office is a central component of a telecommunications system in the public switched telephone network (PSTN) or in large enterprises. It facilitates the establishment of communication circuits, enabling telephone calls between subscribers. The term "central office" can also refer to a central location for fiber optic equipment for a fiber internet provider. In historical perspective, telecommunication terminology has evolved with time. The term ''telephone exchange'' is often used synonymously with ''central office'', a Bell System term. A central office is defined as the telephone switch controlling connections for one or more central office prefixes. However, it also often denotes the building used to house the inside plant equipment for multiple telephone exchange areas. In North America, the term ''wire center'' may be used to denote a central office location, indicating a facility that provides a telephone with a dial tone ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
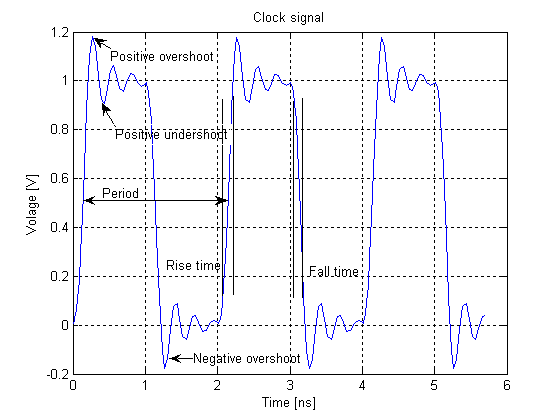
Clock Signal
In electronics and especially synchronous digital circuits, a clock signal (historically also known as ''logic beat'') is an electronic logic signal (voltage or current) which oscillates between a high and a low state at a constant frequency and is used like a metronome to synchronize actions of digital circuits. In a synchronous logic circuit, the most common type of digital circuit, the clock signal is applied to all storage devices, flip-flops and latches, and causes them all to change state simultaneously, preventing race conditions. A clock signal is produced by an electronic oscillator called a clock generator. The most common clock signal is in the form of a square wave with a 50% duty cycle. Circuits using the clock signal for synchronization may become active at either the rising edge, falling edge, or, in the case of double data rate, both in the rising and in the falling edges of the clock cycle. Digital circuits Most integrated circuits (ICs) of suffi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Algorithm
In mathematics and computer science, an algorithm () is a finite sequence of Rigour#Mathematics, mathematically rigorous instructions, typically used to solve a class of specific Computational problem, problems or to perform a computation. Algorithms are used as specifications for performing calculations and data processing. More advanced algorithms can use Conditional (computer programming), conditionals to divert the code execution through various routes (referred to as automated decision-making) and deduce valid inferences (referred to as automated reasoning). In contrast, a Heuristic (computer science), heuristic is an approach to solving problems without well-defined correct or optimal results.David A. Grossman, Ophir Frieder, ''Information Retrieval: Algorithms and Heuristics'', 2nd edition, 2004, For example, although social media recommender systems are commonly called "algorithms", they actually rely on heuristics as there is no truly "correct" recommendation. As an e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Nonblocking Minimal Spanning Switch
A nonblocking minimal spanning switch is a device that can connect N inputs to N outputs in any combination. The most familiar use of switches of this type is in a telephone exchange. The term "non-blocking" means that if it is not defective, it can always make the connection. The term "minimal" means that it has the fewest possible components, and therefore the minimal expense. Historically, in telephone switches, connections between callers were arranged with large, expensive banks of electromechanical relays, Strowger switches. The basic mathematical property of Strowger switches is that for each input to the switch, there is exactly one output. Much of the mathematical switching circuit theory attempts to use this property to reduce the total number of switches needed to connect a combination of inputs to a combination of outputs. In the 1940s and 1950s, engineers in Bell Lab began an extended series of mathematical investigations into methods for reducing the size and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Clos Network
In the field of telecommunications, a Clos network is a kind of multistage circuit-switching network which represents a theoretical idealization of practical, multistage switching systems. It was invented by Edson Erwin in 1938 and first formalized by the American engineer Charles Clos in 1952. By adding stages, a Clos network reduces the number of crosspoints required to compose a large crossbar switch. A Clos network topology (diagrammed below) is parameterized by three integers ''n'', ''m'', and ''r'': ''n'' represents the number of sources which feed into each of ''r'' ingress stage crossbar switches; each ingress stage crossbar switch has ''m'' outlets; and there are ''m'' middle stage crossbar switches. Circuit switching arranges a dedicated communications path for a connection between endpoints for the duration of the connection. This sacrifices total bandwidth available if the dedicated connections are poorly utilized, but makes the connection and bandwidth more predict ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Crossbar Switch
In electronics and telecommunications, a crossbar switch (cross-point switch, matrix switch) is a collection of switches arranged in a Matrix (mathematics), matrix configuration. A crossbar switch has multiple input and output lines that form a crossed pattern of interconnecting lines between which a connection may be established by closing a switch located at each intersection, the elements of the matrix. Originally, a crossbar switch consisted literally of crossing metal bars that provided the input and output paths. Later implementations achieved the same switching topology in solid-state electronics. The crossbar switch is one of the principal telephone exchange architectures, together with a rotary system, rotary switch, memory switch, and a crossover switch. General properties A crossbar switch is an assembly of individual switches between a set of inputs and a set of outputs. The switches are arranged in a matrix. If the crossbar switch has M inputs and N outputs, then a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Banyan Switch
In electronics, a banyan switch is a complex crossover switch used in electrical or optical switches. It is named for its resemblance to the roots of the banyan tree which cross over in complex patterns. Logical banyan switches are used in logic or signal pathways to crossover switching of signals onto new pathways. They can be mechanical microelectromechanical systems, electrical or nonlinear optics. Their complexity depends on the topology of the individual switches in a switch matrix (how wide it is by how many 'plies' or layers of switches it takes), to implement a desired crossover logic. Design Typical crossover matrices follow this formula: an N×N banyan switch uses (N/2) log2 N elements. Other formulas are used for differing number of crossover layers, and scaling is possible, but becomes very large and complex with large N×N arrays. CAD can be used to take the drudgery out of creating these designs. A banyan network is implemented by interconnecting 2×2 switching ne ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Fat Tree
The fat tree network is a universal network for provably efficient communication. It was invented by Charles E. Leiserson of the MIT in 1985. k-ary n-trees, the type of fat-trees commonly used in most high-performance networks, were initially formalized in 1997. In a tree data structure, every branch has the same thickness (bandwidth), regardless of their place in the hierarchy—they are all "skinny" (''skinny'' in this context means low-bandwidth). In a fat tree, branches nearer the top of the hierarchy are "fatter" (thicker) than branches further down the hierarchy. In a telecommunications network, the branches are data links; the varied thickness (bandwidth) of the data links allows for more efficient and technology-specific use. Mesh and hypercube topologies have communication requirements that follow a rigid algorithm, and cannot be tailored to specific packaging technologies. Applications in supercomputers Supercomputers that use a fat tree network include the two fast ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |